Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2022 in Chad .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2022 in Chad .
Ongoing — COVID-19 pandemic in Chad

The politics of Chad take place in a framework of a presidential republic, whereby the President of Chad is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. Chad is one of the most corrupt countries in the world.
The Chad National Army consists of the five Defence and Security Forces listed in Article 185 of the Chadian Constitution that came into effect on 4 May 2018. These are the National Army, the National Police, the National and Nomadic Guard (GNNT) and the Judicial Police.

Idriss Déby Itno was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the 6th president of Chad from 1991 until his death in 2021 during the Northern Chad offensive. His term of office of more than 30 years makes him Chad's longest-serving president.

Chad holds elections on national level for a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The National Assembly has 155 members, elected for a four-year term in 25 single-member constituencies and 34 multi-member constituencies. Chad is a one party dominant state with the Patriotic Salvation Movement in power, although according to the African Union, elections in Chad are generally free and fair. Human Rights Watch, however, has criticized the election process in Chad, arguing that they have problems such as electoral fraud, multiple voting, underage voting, and low voter turnout.
Mohammed Nour Abdelkerim is a former Chadian rebel leader. After signing a peace agreement with the government, he served as Minister of Defense for nine months in 2007.
The United Front for Democratic Change was a Chadian rebel alliance, made up of eight individual rebel groups, all with the goals of overthrowing the government of Chadian president Idriss Déby. It is now part of the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development. UFDC was founded between 26–28 December 2005 in Modeina in eastern Chad. FUC's "president" is Mahamat Nour Abdelkerim, the former leader of the Rally for Democracy and Liberty rebel group, "first vice president" Hassan Salleh Algadam, "second vice president" Abakar Tollimi, and "secretary-general" Abdelwahit About. On 18 December the RDL and another allied rebel group, Platform for Change, Unity and Democracy, attacked the city of Adré. The attack was repulsed by the Chadian military, and the Chadian government accused the Sudanese government of supporting the rebels, which Sudanese President Omar al-Bashir denies. Chad declared a "state of belligerance" with Sudan on 23 December 2005, resulting in the Chad-Sudan Conflict. The result was the Tripoli Agreement.
Abdelwahid Aboud Mackaye is a Chadian insurgent leader involved in the war to topple the Chadian President Idriss Déby. Originally a fighter in the Democratic Revolutionary Council (CDR) militia during the first Chadian Civil War, under Déby he became a civil servant before defecting to the rebels in 2003. After having been for a time first in the FUC and later in the UFDD, he has founded in 2007 the UFDD-Fundamental, which has participated in February 2008 to the unsuccessful attack on N'Djamena.
Lol Mahamat Choua was a Chadian politician who served as his country's head of state for four months in 1979. He was the President of the Rally for Democracy and Progress (RDP) political party.
The Union of Forces for Democracy and Development is the largest group of Chadian rebel forces opposed to former President Idriss Déby. It was formed in October 2006 under the leadership of Mahamat Nouri.
Events from the year 2007 in Chad.
General Mahamat Nouri is a Chadian insurgent leader who currently commands the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development (UFDD). A Muslim from northern Chad, he began his career as a FROLINAT rebel, and when the group's Second Army split in 1976 he sided with his kinsman Hissène Habré. As Habré's associate he obtained in 1978 the first of the many ministerial positions in his career, becoming Interior Minister in a coalition government. When Habré reached the presidency in 1982, Nouri was by his side and played an important role in the regime.
The Battle of N'Djamena began on February 2, 2008, when Chadian rebel forces opposed to Chadian President Idriss Déby entered N'Djamena, the capital of Chad, after a three-day advance through the country. The rebels were initially successful, taking a large part of the city and attacking the heavily defended presidential palace. They did not capture the palace, and after two days of fighting they withdrew to outside the city. Around two days later they retreated east.
The populations of eastern Chad and western Sudan established social and religious ties long before either nation's independence, and these remained strong despite disputes between governments. In recent times, relations have been strained due to the conflict in Darfur and a civil war in Chad, which both governments accuse the other of supporting.

Mahamat Idriss Déby Itno is a Chadian politician and military officer who has been the leader of Chad since 2021, first as President of the Transitional Military Council from 2021 to 2022, then as Transitional President from 2022 to 2024, and then as the 7th President since 2024 following his victory in the presidential elections. He is widely known in Chad by his nickname Kaka. He is also the General Secretary of the Patriotic Salvation Movement since 2022. He gained power on 20 April 2021, succeeding his father and predecessor, Idriss Déby, who died in action while commanding troops in the Northern Chad offensive. He previously served as the second in-command of the military for the Chadian Intervention in Northern Mali (FATIM).

The Front for Change and Concord in Chad, or FACT, is a political and military organisation created by SG Mahamat Mahdi Ali in March 2016 in Tanua, in the north of Chad, with the goal of overthrowing the government of Chad. It is a splinter group of the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development (UFDD). Ali declared his preparation for military operations against President Idriss Déby. The group was responsible for the death of Déby in April 2021, when he was killed while commanding troops on the frontline fighting the militants.

The Military Command Council for the Salvation of the Republic is a Chadian militant rebel group that seeks to overthrow the government of Chad. Founded in 2016, it currently operates in the border regions of northern Chad, southern Libya, eastern Niger, and western Sudan. The CCMSR has become involved in the Second Libyan Civil War, and took control of the Kouri Bougoudi area in northern Chad in 2018.
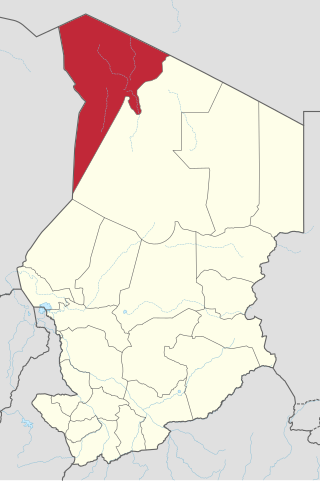
The Northern Chad offensive was a military offensive in Northern Chad, initiated by the Chadian rebel group Front for Change and Concord in Chad (FACT), took place from 11 April to 9 May 2021. It began in the Tibesti Region in the north of the country following the 2021 Chadian presidential election.

The Transitional Military Council was a military junta that ruled Chad from 2021 to 2022. It announced the death of former President Idriss Déby on 20 April 2021, and declared that it would take charge of the government of Chad and continue hostilities against FACT rebels in the north of the country. It was chaired by Mahamat Idriss Déby, the son of the late President, making him the de facto President of Chad. It was dissolved on 10 October 2022, following a "national dialogue" that named Déby Transitional President and replaced the CMT with a transitional administration appointed by him.

In 2016, the Front for Change and Concord in Chad (FACT) and the Military Command Council for the Salvation of the Republic (CCMSR) began a rebellion against the Chadian government. From their rear bases in southern Libya, FACT and CCMSR have launched offensives and raids into Northern Chad seeking to overthrow the government of former president Idriss Déby, who had been in power since a December 1990 coup. Other rebel groups are also involved in the insurgency, though to a lesser extent.
Events in the year 2022 in Qatar.