Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physics, biology, and geography to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.
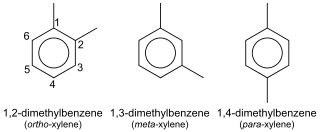
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol are any of three organic compounds with the formula (CH3)2C6H4. They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are substituted determines which of three structural isomers results. It is a colorless, flammable, slightly greasy liquid of great industrial value.

Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell (cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage.

Dry cleaning is any cleaning process for clothing and textiles using a solvent other than water.

Danvers is a town in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, located on the Danvers River near the northeastern coast of Massachusetts. The suburb is a fairly short ride from Boston and is also in close proximity to the beaches of Gloucester, Ipswich and Revere. Originally known as Salem Village, the town is most widely known for its association with the 1692 Salem witch trials. It was also the site of Danvers State Hospital, one of the state's 19th-century psychiatric hospitals. Danvers is a local center of commerce, hosting many car dealerships and the Liberty Tree Mall. As of the 2020 United States Census, the town's population was 28,087.

Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants mix with these water bodies. Contaminants can come from one of four main sources: sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. Water pollution is either surface water pollution or groundwater pollution. This form of pollution can lead to many problems, such as the degradation of aquatic ecosystems or spreading water-borne diseases when people use polluted water for drinking or irrigation. Another problem is that water pollution reduces the ecosystem services that the water resource would otherwise provide.
Green chemistry, similar to sustainable chemistry or circular chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental chemistry focuses on the effects of polluting chemicals on nature, green chemistry focuses on the environmental impact of chemistry, including lowering consumption of nonrenewable resources and technological approaches for preventing pollution.

Butan-2-ol, or sec-butanol, is an organic compound with formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3. Its structural isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and tert-butanol. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-butan-2-ol and (S)-(+)-butan-2-ol. It is normally encountered as a 1:1 mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture.

An environmental hazard are those hazards where the effects are seen in biomes or ecosystems rather than directly on living organisms. Environmental hazards can be a substance, state or event which has the potential to threaten the surrounding natural environment or adversely affect people's health. Well known examples include oil spills, water pollution, slash and burn deforestation, air pollution, and ground fissures. It can include any single or combination of toxic chemical, biological, or physical agents in the environment, resulting from human activities or natural processes. These agents may impact the health of exposed subjects, including pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, biological contaminants, toxic waste, industrial and home chemicals.

The Texas City refinery explosion occurred on March 23, 2005, when a flammable hydrocarbon vapor cloud ignited and violently exploded at the isomerization process unit of the BP oil refinery in Texas City, Texas, killing 15 workers, injuring 180 others and severely damaging the refinery. All the fatalities were contractors working out of temporary buildings located close to the unit to support turnaround activities. Property loss was $200 million. When including costs of repairs, deferred production, fines and settlements, the explosion is the world's costliest refinery accident.
Mercer Rubber Company is a manufacturer of rubber products.

The West Pharmaceutical Plant explosion was an industrial disaster that occurred on January 29, 2003 at the West Pharmaceutical Plant in Kinston, North Carolina, United States. Six people were killed and thirty-six people were injured when a large explosion ripped through the facility. Two firefighters were injured in the subsequent blaze. The disaster occurred twelve years and 170 miles (270 km) from the 1991 Hamlet chicken processing plant fire, North Carolina's second-worst industrial disaster.

The 2009 Cataño oil refinery fire, also known as the CAPECO explosion, was a fire that began with an explosion on October 23, 2009, and was extinguished on October 25 at the Caribbean Petroleum Corporation (CAPECO) oil refinery and oil depot in Bayamón, Puerto Rico. While the fire and subsequent explosion occurred close to the city of Cataño, it technically occurred within the borders of Bayamón, even though Cataño was more affected by fumes and evacuation. There were no fatalities, but 3 people were injured.

On April 17, 2013, an ammonium nitrate explosion occurred at the West Fertilizer Company storage and distribution facility in West, Texas, United States, while emergency services personnel were responding to a fire at the facility. Fifteen people were killed, more than 160 were injured, and more than 150 buildings were damaged or destroyed. Investigators confirmed that ammonium nitrate was the material that exploded. On May 11, 2016, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives stated that the fire had been deliberately set. That finding has been disputed.

The Elk River chemical spill occurred on January 9, 2014, when crude 4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (MCHM) was released from a Freedom Industries facility into the Elk River, a tributary of the Kanawha River, in Charleston in the U.S. state of West Virginia.

Groundwater pollution occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent, contaminant, or impurity in the groundwater, in which case it is more likely referred to as contamination rather than pollution. Groundwater pollution can occur from on-site sanitation systems, landfill leachate, effluent from wastewater treatment plants, leaking sewers, petrol filling stations, hydraulic fracturing (fracking) or from over application of fertilizers in agriculture. Pollution can also occur from naturally occurring contaminants, such as arsenic or fluoride. Using polluted groundwater causes hazards to public health through poisoning or the spread of disease.
Sharkey Landfill is a 90-acre property located in New Jersey along the Rockaway and Whippany rivers in Parsippany, New Jersey. Landfill operations began in 1945, and continued until September 1972, when large amounts of toluene, benzene, chloroform, dichloroethylene, and methylene chloride were found, all of which have are a hazard to human health causing cancer and organ failure. Sharkey Landfill was put on the National Priority List in 1983, and clean up operations ran until the site was deemed as not a threat in 2004.
On January 24, 2020, a building at Watson Grinding and Manufacturing in northwest Houston, Texas, United States, exploded at 4:24 a.m. Debris was scattered as far as one-half mile (0.8 km), and approximately 200 nearby houses and businesses were damaged. Officials asked local residents to search for debris and body parts to assist with an investigation into the explosion's cause. An absence of zoning ordinances separating industrial areas from residences is known to prevail in the vicinity of the explosion.
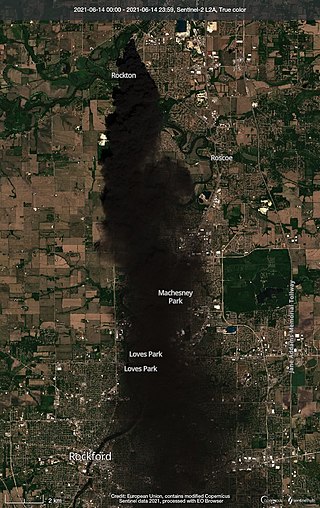
On June 14, 2021, a maintenance accident at the Chemtool Incorporated manufacturing plant in Rockton, Illinois, triggered a chemical fire that lasted four days and injured two emergency workers. Portions of the village, located north of Rockford near the Illinois-Wisconsin state line, were subject to a mandatory evacuation as a result of the fire. The fire was not contained until June 16, with the evacuations lasting until June 18.

On 21 June 1988, a large fire and explosion engulfed the BDH chemical plant in Poole, Dorset, England. 3,500 people were evacuated out of the town centre in the biggest peacetime evacuation the country had seen since World War II. Despite the intensity of the explosion, nobody was killed or seriously injured.
















