
The Christian Social Union in Bavaria is a Christian democratic and conservative political party in Germany. Having a regionalist identity, the CSU operates only in Bavaria while its larger counterpart, the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), operates in the other fifteen states of Germany. It differs from the CDU by being somewhat more conservative in social matters, following Catholic social teaching. The CSU is considered the de facto successor of the Weimar-era Catholic Bavarian People's Party.

The Free Democratic Party is a liberal political party in Germany.

Alliance 90/The Greens, often simply referred to as Greens, is a centre-left green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of the Greens and Alliance 90. The Greens had itself merged with the East German Green Party after German reunification in 1990.

Ole von Beust is a former German politician who was First Mayor of Hamburg from 31 October 2001 to 25 August 2010, serving as President of the Bundesrat from 1 November 2007 on for one year. He was succeeded as mayor by Christoph Ahlhaus.

The 2004 Hamburg state election was held on 29 February 2004 to elect the members of the 18th Hamburg Parliament. The election was triggered by the collapse of the coalition government between the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), Party for a Rule of Law Offensive (PRO), and Free Democratic Party (FDP). The election saw a collapse in support for PRO which had split after its leader Ronald Schill left in 2003. The original party and Schill's new party captured 3.5% of the vote between them, down from 19.4% in 2001. A huge amount of support flowed to the CDU, which won 63 of the 121 seats in Parliament, forming a majority government. First Mayor Ole von Beust continued in office.

The 2001 Hamburg state election was held on 23 September 2001 to elect the members of the 17th Hamburg Parliament. The incumbent coalition government of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and Green Alternative List (GAL) led by First Mayor Ortwin Runde was defeated, ending 44 years of uninterrupted SPD rule in the city-state.

Peter Harry Carstensen is a German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU). From 2005 to 2012 he was Minister President of the state of Schleswig-Holstein, serving as President of the Bundesrat in 2005/06.
The government of Hamburg is divided into executive, legislative and judicial branches. Hamburg is a city-state and municipality, and thus its governance deals with several details of both state and local community politics. It takes place in two ranks – a citywide and state administration, and a local rank for the boroughs. The head of the city-state's government is the First Mayor and President of the Senate. A ministry is called Behörde (office) and a state minister is a Senator in Hamburg. The legislature is the state parliament, called Hamburgische Bürgerschaft, and the judicial branch is composed of the state supreme court and other courts. The seat of the government is Hamburg Rathaus. The President of the Hamburg Parliament is the highest official person of the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg. This is a traditional difference to the other German states. The president is not allowed to exert any occupation of the executive.
The bases of the political system are the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany and the Constitution of the Free and Hanseatic city of Hamburg.

The Landtag of Thuringia is the parliament of the German federal state of Thuringia. It convenes in Erfurt and currently consists of 88 members from five parties. According to the free state's constitution, the primary functions of the Landtag are to pass laws, elect the Minister-President and control the government of Thuringia.
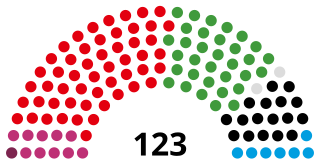
The Hamburg Parliament is the unicameral legislature of the German state of Hamburg according to the constitution of Hamburg. As of 2020 there are 123 sitting members, representing 17 electoral districts. The parliament is situated in the city hall Hamburg Rathaus and is part of the Government of Hamburg.
Grand coalition is a nickname in German politics describing a governing coalition of the parties Christian Democratic Union (CDU) along with its sister party the Christian Social Union of Bavaria (CSU) and the Social Democratic Party (SPD), since they have historically been the major parties in most state and federal elections since 1949. The meaning of the term may change due to the growth of some formerly minor parties in recent years.

The 1993 Hamburg state election was held on 19 September 1993 to elect the members of the 15th Hamburg Parliament.

The 2009 Schleswig-Holstein state election was held on 27 September 2009 to elect the members of the Landtag of Schleswig-Holstein. It was held on the same day as the 2009 federal election and the 2009 Brandenburg state election.

The 2011 Hamburg state election was held on 20 February 2011 to elect the members of the 20th Hamburg Parliament. The election was triggered by the collapse of the coalition government between the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Green Alternative List (GAL), which had governed the state since 2008. The election was a landslide defeat for the CDU, which lost half its voteshare and seats. The margin of defeat for the incumbent Ahlhaus Senate is the largest in post-war German history and has not been met since. Much of this lost support flowed to the Social Democratic Party (SPD), which won 62 of the 121 seats in Parliament, forming a majority government led by Olaf Scholz.

Rüdiger Kruse is a German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who served as a member of the German Bundestag from 2009 to 2021.

Sabine Sütterlin-Waack is a German lawyer and politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU). She currently serves as State Minister of the Interior, Municipal Affairs, Housing and Sports in the State of Schleswig-Holstein.

The 2020 Hamburg state election was held on 23 February 2020 to elect the members of the 22nd Hamburg Parliament. The outgoing government was a coalition of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and The Greens led by First Mayor Peter Tschentscher.

Tanja Gönner is a German lawyer and politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who has been serving as managing director of the Federation of German Industries (BDI), the leading lobby organization of German industry since November 2022.
A black-green or green-black coalition is a coalition between a conservative and/or Christian Democratic party and a green party.

















