
Lake Champlain is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the US states of New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canadian province of Quebec.

Champlain is a town in Clinton County, New York, United States. The population was 5,754 at the 2010 census. The town is located on the western shore of Lake Champlain, near the northern end of Lake Champlain and is on the U.S./Canadian border.

Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu is a city in eastern Montérégie in the Canadian province of Quebec, about 40 kilometres (25 mi) southeast of Montreal, located roughly halfway between Montreal and the Canada–United States border with the state of Vermont. It is situated on both the west and east banks of the Richelieu River at the northernmost navigable point of Lake Champlain. As of December 2019, the population of Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu was 98,036.

The Richelieu River is a river of Quebec, Canada, and a major right-bank tributary of the St. Lawrence River. It rises at Lake Champlain, from which it flows northward through Quebec and empties into the St. Lawrence. It was formerly known by the French as the Iroquois River and the Chambly River, and was named for Cardinal Richelieu, the powerful minister under Louis XIII.

La Vallée-du-Richelieu is a regional county municipality in the Montérégie region in southwestern Quebec, Canada. Its seat is McMasterville.

The Champlain Valley is a region of the United States around Lake Champlain in Vermont and New York extending north slightly into Quebec, Canada. It is part of the St. Lawrence River drainage basin, drained northward by the Richelieu River into the St. Lawrence at Sorel-Tracy, Quebec. The Richelieu valley is not generally referred to as part of the Champlain Valley.
Montérégie is an administrative region in the southwest part of Quebec. It includes the cities of Boucherville, Brossard, Châteauguay, Longueuil, Saint-Hyacinthe, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Salaberry-de-Valleyfield and Vaudreuil-Dorion.

The Chambly Canal is a National Historic Site of Canada in the Province of Quebec, running along the Richelieu River past Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Carignan, and Chambly. Building commenced in 1831 and the canal opened in 1843. It served as a major commercial route during a time of heightened trade between the United States and Canada. Trade dwindled after World War I, and as of the 1970s, traffic has been replaced by recreational vessels.

The Missisquoi River is a transboundary river of the east shore of Lake Champlain, approximately 80 miles (130 km) long, in northern Vermont in the United States and southern Quebec in Canada.

Iberville was a city in the Montérégie region of the Canadian province of Quebec on the east side of the Richelieu River, across from Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu. It was about 30 miles (50 km) from Montreal, and about the same distance from the United States border at the head of Lake Champlain. In 2002, Iberville merged with neighbouring Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, along with several other neighbouring towns and villages.
The Rock River is a tributary of Rock River Bay, an arm of Missisquoi Bay in the northern part of Lake Champlain. The river rises in the town of Franklin, in Franklin County, Vermont, United States, flows west into the town of Highgate, Vermont, and then north into Saint-Armand, Quebec, in the Brome-Missisquoi Regional County Municipality, administrative region of Montérégie, in the southwest of the province of Quebec, Canada. The river then turns south and re-enters Highgate, flowing into Rock River Bay north of Highgate Springs.

Lacolle is a municipality in southern Quebec, Canada, located in the administrative area of the Montérégie, on the Canada–United States border. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 2,680. The Lacolle River runs eastward through the middle of the town and empties in Richelieu River. More people cross the border illegally from the United States there than at any other point. Almost nineteen thousand people were detained in 2017. The nearest town across the border is Champlain, New York.
The Lakes to Locks Passage in the United States and the corresponding Route du Richelieu in Canada form a scenic byway network located in northeastern New York and southern Quebec. This byway connects a series of water routes including the upper Hudson River, Champlain Canal, Lake George, and Lake Champlain. This network is part of a historically significant transportation route linking upstate New York with the Canadian province of Quebec.
L'Acadie is a former municipality in the Montérégie region of Quebec, Canada, on the west side of the Richelieu River, across from Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Quebec. It was about 30 miles (50 km) from Montreal, and about the same distance from the United States border at the head of Lake Champlain. In 2001 L'Acadie merged with neighbouring Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, along with several other neighbouring towns and villages.
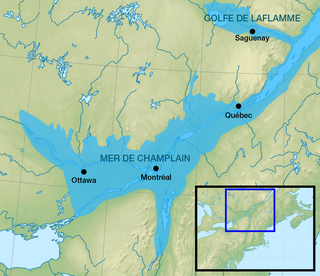
The Champlain Sea was a prehistoric inlet of the Atlantic Ocean into the North American continent, created by the retreating ice sheets during the closure of the last glacial period. The inlet once included lands in what are now the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, as well as parts of the American states of New York and Vermont. Today, the remains of the sea include the St. Lawrence Seaway, Lake Champlain, Lake of Two Mountains on the lower Ottawa River, the lower Saguenay River, as well as other lakes, islands and shores.

The Chambly Basin is a shallow, oblong body of water formed by an enlargement of the Richelieu River, extending out from the foot of the rapids on the river between Chambly and Richelieu, in the Quebec region of Montérégie. The towns of Chambly, Richelieu, Saint-Mathias-sur-Richelieu and Carignan surround the basin.

The rivière des Hurons flows for 33 kilometres (21 mi) to the east side spill in the Chambly Basin just north of the city of Chambly. Its mouth is in the municipality of Saint-Mathias-sur-Richelieu in the Rouville Regional County Municipality, in the administrative region of Montérégie, in Quebec, in Canada. Hurons River flows through the Les Maskoutains Regional County Municipality, RCM of La Vallée-du-Richelieu Regional County Municipality, then the western part of the MRC Rouville Regional County Municipality. The latter is entirely east of the Richelieu River.

Missisquoi Bay is a large extension in the northern part of Lake Champlain, at the East of the output of the latter in Richelieu River. It takes the form of a violin head, with the neck extending from the head of the lake and is about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) in diameter. The bay is divided between Quebec in Canada and Vermont in the United States. The main town on its banks is Venise-en-Québec, a major summer resort. The river of the same name flows into the bay and the Missisquoi National Wildlife Refuge is located on the American side.

The 2019 spring floods in Ontario, Quebec and New Brunswick were exceptional floods in eastern Ontario, southern Quebec and from the St.John River region to New Brunswick, Canada. In fact, flooding along the Ottawa River has been recognized as the most important weather event of the year 2019 in Canada, and the one along the Saint John River as the ninth, by Environment and Climate Change Canada. The flooding caused by the rapid spring snow melt, coupled with frozen ground, and several heavy rain events that resulted in abnormally high cumulative rainfall for April and May.
The Rouses Point Subdivision is a railway line in southwestern Quebec. It runs north–south from the northern end of Canadian Subdivision, on the border with New York, to the St-Hyacinthe Subdivision, in the vicinity of Montreal. The oldest part of the line was the original main line of the Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad, completed in 1836. Today, the Canadian National Railway owns the line. Amtrak's Adirondack operates over the full length, providing daily service between New York City and Montreal.
















