| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2014 in Tonga .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 2014 in Tonga .
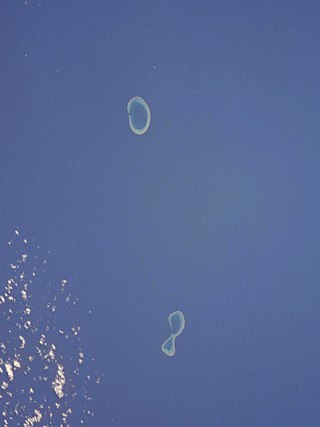
The Minerva Reefs are a group of two submerged atolls located in the Pacific Ocean between Fiji, Niue and Tonga. The islands are the subject of a territorial dispute between Fiji and Tonga, and in addition were briefly claimed by American Libertarians as the centre of a micronation, the Republic of Minerva.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Daman was the strongest cyclone of the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season. Cyclone Daman was the fourth tropical depression and the first severe tropical cyclone to form east of longitude 180° during the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season. Due to the severity of the storm, the name Daman was retired and replaced with Denia.

Tropical Cyclone Cliff was first noted as a weak tropical disturbance on April 1, 2007, within a trough of low pressure about 210 km (130 mi) to the southwest of Rotuma. Over the next couple of days the system drifted towards the southeast and Fiji, in an area of strong wind shear. During April 3, the system slightly accelerated, as it moved towards the south-southeast before the westerly wind shear around the system relaxed sufficiently to allow the depression to consolidate while it was located near Vanua Levu.
The 1996–97 South Pacific cyclone season was one of the most active and longest South Pacific tropical cyclone seasons on record, with 12 tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. The season officially ran from November 1, 1996 - April 30, 1997, however, the season ended later than normal with three systems monitored after the official end of the season. The strongest tropical cyclone of the season was Cyclone Gavin which had a minimum pressure of 925 hPa (27.32 inHg). After the season had ended 4 tropical cyclone names were retired from the naming lists, after the cyclones had caused significant impacts to South Pacific islands.
The 2010–11 South Pacific cyclone season was an average tropical cyclone season, with seven tropical cyclones and five severe tropical cyclones developing during the season. The season ran from November 1, 2010, until April 30, 2011, though if any tropical cyclones had developed between July 1, 2010, and June 30, 2011, the official tropical cyclone year, they would have been counted towards the season's total. Within the South Pacific basin tropical cyclones were officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service's Regional Specialized Meteorological Center in Nadi, Fiji, north of 25°S, and to the south the Meteorological Service of New Zealand's Tropical Cyclone Warning Center in Wellington, New Zealand. Any disturbances forming in the region were designated with a sequential number suffixed by the letter F. In addition, the United States Military's Joint Typhoon Warning Center unofficially monitored parts of the basin during the season, where any systems judged to have achieved tropical storm strength or greater received a number suffixed with the letter P. RSMC Nadi and TCWC Wellington both use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale, and measure wind speeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC measures sustained winds over a period of one minute which can be applied to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Seven named storms formed or moved into the South Pacific basin during the 2010–11 season, the strongest of which was Severe Tropical Cyclone Wilma in late January.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ami was one of the worst cyclones to affect Fiji. The system was the third cyclone and the second severe tropical cyclone of the 2002–03 South Pacific cyclone season. Cyclone Ami developed from a low-pressure area east of Tuvalu on January 12. Originally, the storm moved slowly towards the southwest early in its existence. Influenced by an upper-level trough, Ami slowed and began moving towards the south and then southeast. The cyclone attained severe tropical cyclone intensity on January 13. Ami made its first landfall at Vanua Levu, before subsequently making another landfall on Taveuni. Still intensifying, Ami reached peak intensity as a Category 3 cyclone on the Australian and Fiji cyclone scales on January 14. Accelerating to the southeast, the cyclone began to cross over cool sea surface temperatures and encountered wind shear. Ami transitioned into an extratropical cyclone the day after.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Nina was a significant tropical cyclone which impacted six island nations from December 1992 to January 1993. The system was first noted as a tropical low over the Cape York Peninsula on 21 December. Over the next few days the system moved south-westwards and moved into the Gulf of Carpentaria where it was named Nina, after it had developed into a tropical cyclone during 23 December. The system was subsequently steered south-eastwards by an upper level trough of low pressure, before it made landfall as a Category 2 tropical cyclone on the Cape York Peninsula near Cape Keerweer on 25 December. Over land the system weakened into a tropical low before it regenerated into a tropical cyclone over the Coral Sea on 28 December. The system subsequently moved north-eastwards, under the influence of Severe Tropical Cyclone Kina and an upper level ridge of high pressure. During 1 January 1993, Nina peaked with sustained wind speeds of 140 km/h (85 mph), as it affected Rennell, Bellona and Temotu provinces in the Solomon Islands. The system subsequently gradually weakened as it accelerated eastwards and affected Rotuma, Wallis and Futuna, Tonga and Niue. Nina was subsequently absorbed by Kina, while both systems were located near the Southern Cook Islands during 5 January.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Sina was the only named tropical cyclone to develop within the South Pacific basin during the 1990–91 season. The system was first noted as a shallow depression within the South Pacific Convergence Zone to the west of Wallis Island. Over the next three days the system moved towards the west-northwest, before it was named Sina during November 24, after it had developed into a tropical cyclone. Over the next couple of days the system intensified further and developed an eye feature as it erratically moved towards Fiji. Sina subsequently peaked in intensity during November 26, before the system passed through the Fijian Islands over the next two days as it started to gradually weaken. Sina subsequently passed just to the north of Tongatapu in Tonga during November 29, before it passed about 160 km (100
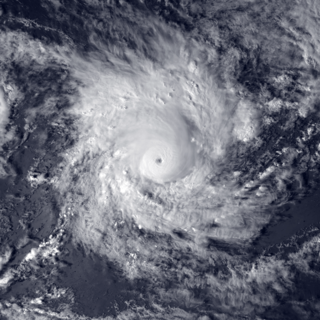
Severe Tropical Cyclone Ron was a powerful tropical cyclone that became the strongest on record to impact Tonga. The system was first noted as a tropical depression, to the northeast of Samoa on January 1, 1998. Over the next day the system gradually developed further and was named Ron as it developed into a Category 1 tropical cyclone on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale during the next day. The system subsequently continued to move south-westwards and became a Category 3 severe tropical cyclone, as it passed near Swains Island during January 3.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Eric was one of two tropical cyclones to affect the island nations of Vanuatu and Fiji within a week during January 1985. The precursor shallow depression developed within the monsoon trough during 13 January, to the west of Espiritu Santo, Vanuatu. On 16 January, the storm developed-hurricane-force winds and Eric began to undergo rapid deepening. While two different agencies differ on when and how strong Eric was at its peak, it was believed to have peaked on 17 January while passing through the Fiji island group. Shortly after its peak, Eric began to weaken steadily, and by 20 January, Severe Tropical Cyclone Eric had ceased to exist as a tropical cyclone. Combined with another storm – Cyclone Nigel – Eric caused 25 fatalities and $40 million worth of damage. A total of 299 farms were affected as well as the airport in Nadi. About 30,000 people were left homeless. Severe crop damage was also reported. Viti Levu sustained the worst effects from Cyclone Eric. During the aftermath of the storm, a number of first world countries distributed aid for victims of Eric.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Hina in March 1997 was the worst tropical cyclone to affect the South Pacific island nation of Tonga since Cyclone Isaac in 1982. The system was first noted within the monsoon trough on March 11, 1997, as a weak shallow depression within the vicinity of Rotuma. Over the next two days, the depression remained near Rotuma with no preferred movement, as it started to develop further within favorable conditions for further development. The system was subsequently named Hina on March 15, after it had started to move eastwards and had passed to the southeast of Niulakita, Tuvalu. During that day the system moved south-eastwards and impacted Wallis and Futuna, before it passed over Tonga's southern islands of Tongatapu and 'Eua during March 16. After impacting Tonga the system moved rapidly towards the south-southeast and weakened below tropical cyclone intensity, before it was last noted on March 21 about 1,500 km (930 mi) to the south of the Pitcairn Islands. During the system's post-analysis, it was determined that the warning centers had underestimated Hina's intensity as it passed over Tonga, after damage in the island nation had been greater than expected.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ian was a category 4 tropical cyclone that formed on January 2, 2014, and dissipated to an extratropical cyclone on January 15, 2014. Areas affected by the tropical cyclone include Fiji and Tonga. In Tonga, Ian caused destruction in the Ha'apai islands, with severely injured and one fatality. Damages caused by the cyclone was $120 million.
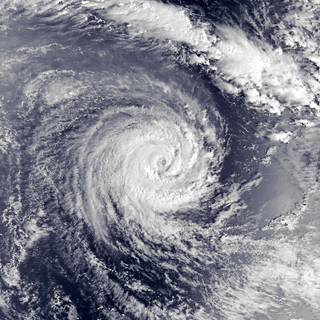
Severe Tropical Cyclone Raja was a tropical cyclone that holds the 24-hour rainfall record of 674.9 mm (26.57 in) for the French Overseas Territory of Wallis and Futuna. The system was first noted by the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS) as a weak tropical disturbance northeast of Tokelau in mid-December 1986. The system developed further as it moved southwest over the next few days, and it was classified as Tropical Cyclone Raja on 23 December. The newly named system slowed and unexpectedly recurved southeast towards the French territory of Wallis and Futuna on 24 December. Over the next two days, Raja interacted with what would become Severe Cyclone Sally and executed a tight loop, passing within 55 km (35 mi) of Futuna. The system peaked as a Category 3 severe tropical cyclone on 28 December, with estimated 10-minute sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h). The storm turned southwest the next day and threatened Fiji, where it passed within 20 km (10 mi) of Vanua Levu and near several smaller islands in the Lau group during the following day. Raja gradually weakened over the next few days as it moved south of Fiji; it was last noted on 5 January 1987 after it filled up over the north Tasman Sea.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ula was a powerful and long-lived tropical cyclone during late December 2015 and mid-January 2016. It originated from a tropical disturbance on December 26, 2015, east of the Solomon Islands. Moving generally east, development was initially slow and the system finally reached cyclone strength—having gale-force winds—on December 30. The newly christened Tropical Cyclone Ula turned sharply south and rapidly intensified, attaining hurricane strength the following day. A shift to the southwest brought the system close to the northern islands of Tonga on January 2, 2016. It subsequently brushed several islands in the Lau Group of Fiji before weakening. Nearly degrading to a tropical depression, Ula turned to the northwest and regained strength. After turning back to the southwest, it achieved its peak intensity as a Category 4 on the Australian scale with winds of 185 km/h (115 mph) on January 10. Thereafter, the storm bypassed Vanuatu to the southeast and New Caledonia to the east as it accelerated southward.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Gita was the most intense tropical cyclone to impact Tonga since reliable records began. The second named storm and first major tropical cyclone of the 2017–18 South Pacific cyclone season, Gita originated from a monsoon trough that was active in the South Pacific in early February 2018. First classified as a tropical disturbance on 3 February, the nascent system meandered near Vanuatu for several days with little development. After acquiring a steady east trajectory near Fiji, it organized into a Category 1 tropical cyclone on 9 February near Samoa. Arcing south in a clockwise turn, the system rapidly intensified, and became a severe tropical cyclone on 10 February near Niue.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean, to the east of 160°E, from 1900 to 1940.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E after the start of World War II in September 1939 and before the start of the 1950s decade.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean, to the east of 160°E, before 1900.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Tino was a tropical cyclone which itself and an associated convergence zone caused significant damage across ten island nations in the South Pacific Ocean during January 2020. First noted as a tropical disturbance during January 11, to the southwest of Honiara in the Solomon Islands, the system gradually developed over the next few days as it moved eastwards in between the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu prior to being named Tino as it approached Fiji during January 16. Continuing to track south-eastward, Tino continued strengthening as it passed near Fiji, bringing copious amounts of rainfall to the area. Whilst losing latitude, the system continued to strengthen and peaked as a category 3 tropical cyclone on January 17, with signs of an eye forming. Shortly after peak intensity, Tino was impacted by high wind shear and decreasing sea surface temperatures, triggering a weakening trend. Tino moved out of the tropics shortly thereafter and became an extratropical cyclone during January 19.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E during the 1960s.