| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following events occurred in Tonga in the year 2018.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following events occurred in Tonga in the year 2018.


Nukuʻalofa is the capital and largest city of Tonga. It is located on the north coast of the island of Tongatapu, in the country's southernmost island group.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Heta was a Category 5 tropical cyclone that caused moderate damage to the islands of Tonga, Niue, and American Samoa during late December 2003 and early January 2004. Heta formed on December 25, 2003; it reached a maximum intensity of 260 km/h (160 mph) and an estimated pressure of 915 hPa before dissipating on January 11, 2004. It was the first named tropical cyclone to form during the 2003–04 South Pacific cyclone season.

The Legislative Assembly of Tonga is the unicameral legislature of Tonga.
Teufaiva Sport Stadium which was previously known as Tenefaira Field Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Nukuʻalofa, Tonga. It is used mostly for rugby union, football and rugby league and the Ikale Tahi team matches. The stadium holds 10,000 people. It is the home ground of the Tonga national rugby union team. Teufaiva is where the Secondary School sports in Tonga are held.

The 2005–06 South Pacific cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It began on November 1, 2005, and ended on April 30, 2006. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the southern Pacific Ocean east of 160°E. Additionally, the regional tropical cyclone operational plan defines a tropical cyclone year separately from a tropical cyclone season, and the "tropical cyclone year" runs from July 1, 2005, to June 30, 2006.

The 2003–04 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season with only three tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2003 to April 30, 2004 with the first disturbance of the season forming on December 4 and the last disturbance dissipating on April 23. This is the period of the year when most tropical cyclones form within the South Pacific Ocean.

The 1981–82 South Pacific cyclone season was a slightly-below average South Pacific tropical cyclone season, with 6 tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific Ocean basin between 160°E and 120°W during the season. After this season, the names Gyan and Isaac were retired from the lists of names, after they caused significant impacts to South Pacific island nations.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Waka was one of the most destructive tropical cyclones ever to affect the nation of Tonga. Waka originated within the near-equatorial trough in mid-December 2001, although the system remained disorganized for more than a week. The storm gradually matured and attained tropical cyclone status on December 29, 2001. Subsequently, Waka underwent rapid intensification in which it attained its peak intensity as a Category 4 severe tropical cyclone on December 31, with winds of 185 km/h (115 mph). Shortly thereafter, it passed directly over Vavaʻu, Tonga, resulting in widespread damage. By January 1, 2002, the cyclone began to weaken as it underwent an extratropical transition. The remnants of Waka persisted for several more days and were last observed near the Southern Ocean on January 6, 2002.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Jasmine was a powerful and long-lived annular tropical cyclone that affected several countries, particularly Vanuatu and Tonga, over a 16-day span in February 2012. The system was the second cyclone and the only severe tropical cyclone of the relatively quiet 2011–12 South Pacific cyclone season. Cyclone Jasmine developed from an area of disturbed weather on 1 February in the Gulf of Carpentaria. Initially, the storm moved towards the east and across the Cape York Peninsula. As it moved across the South Pacific, earlier existing wind shear conditions lessened, and Jasmine began to strengthen at a faster rate. Steadily intensifying, Jasmine reached peak intensity on 8 February as a Category 4 equivalent on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale, while beginning to show annular characteristics.
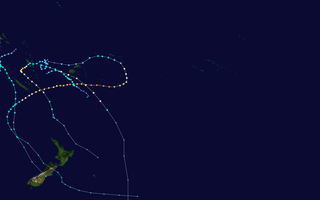
The 2017–18 South Pacific cyclone season was a slightly below-average season that produced 6 tropical cyclones, 3 of which became severe tropical cyclones. The season officially began on November 1, 2017, and ended on April 30, 2018; however, a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2017, and June 30, 2018, and would count towards the season total. During the season, tropical cyclones were officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, MetService and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, while the United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also monitored the basin and issued warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to significant tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin, while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The BoM, FMS and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate wind speeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimates sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

The 2018–19 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season that produced 5 tropical cyclones, 2 of which became severe tropical cyclones. The season officially runs from November 1, 2018, to April 30, 2019; however, a tropical cyclone could have formed at any time between July 1, 2018, and June 30, 2019, and would count towards the season total. During the season, tropical cyclones were officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, Australian Bureau of Meteorology, and New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also monitored the basin and issued warnings for American interests. RSMC Nadi attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin, while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The FMS, the BoM and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate wind speeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimates sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ian was a category 4 tropical cyclone that formed on January 2, 2014, and dissipated to an extratropical cyclone on January 15, 2014. Areas affected by the tropical cyclone include Fiji and Tonga. In Tonga, Ian caused destruction in the Ha'apai islands, with severely injured and one fatality. Damages caused by the cyclone was $120 million.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Gita was the most intense tropical cyclone to impact Tonga since reliable records began. The second named storm and first major tropical cyclone of the 2017–18 South Pacific cyclone season, Gita originated from a monsoon trough that was active in the South Pacific in early February 2018. First classified as a tropical disturbance on 3 February, the nascent system meandered near Vanuatu for several days with little development. After acquiring a steady east trajectory near Fiji, it organized into a Category 1 tropical cyclone on 9 February near Samoa. Arcing south in a clockwise turn, the system rapidly intensified, and became a severe tropical cyclone on 10 February near Niue.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean, to the east of 160°E, from 1900 to 1940.
The following is a list of all reported tropical cyclones within the South Pacific Ocean, to the east of 160°E, before 1900.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Tino was a tropical cyclone which itself and an associated convergence zone caused significant damage across ten island nations in the South Pacific Ocean during January 2020. First noted as a tropical disturbance during January 11, to the southwest of Honiara in the Solomon Islands, the system gradually developed over the next few days as it moved eastwards in between the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu prior to being named Tino as it approached Fiji during January 16. Continuing to track south-eastward, Tino continued strengthening as it passed near Fiji, bringing copious amounts of rainfall to the area. Whilst losing latitude, the system continued to strengthen and peaked as a category 3 tropical cyclone on January 17, with signs of an eye forming. Shortly after peak intensity, Tino was impacted by high wind shear and decreasing sea surface temperatures, triggering a weakening trend. Tino moved out of the tropics shortly thereafter and became an extratropical cyclone during January 19.
Brooklyn is a settlement and rural valley in the Tasman District of New Zealand's upper South Island. It is located on the outskirts of Motueka, and is dominated by orchards.
The Al-Khadeejah Mosque is a mosque in Nukuʻalofa, Tongatapu, Tonga.

The following is a list of weather events that occurred in 2018.

Parliament House in Nukuʻalofa was the base of the Legislative Assembly of Tonga until 2018 when it was destroyed by Cyclone Gita.