| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2016 in Belize .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2016 in Belize .
Hurricane Earl (2016) Strikes Belize as a category 1. [1]
2016 Belize–Guatemala border standoff - Belizean soldiers shoot a 13 year old Guatemalan child. [2]

Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a water boundary with Honduras to the southeast. It has an area of 22,970 square kilometres (8,867 sq mi) and a population of 441,471 (2022). Its mainland is about 290 km (180 mi) long and 110 km (68 mi) wide. It is the least populated and least densely populated country in Central America. Its population growth rate of 1.87% per year is the second-highest in the region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. Its capital is Belmopan, and its largest city is the namesake city of Belize City. Belize is often thought of as a Caribbean country in Central America because it has a history similar to that of English-speaking Caribbean nations. Belize's institutions and official language reflect its history as a British colony.

Guatemala is mountainous, except for the south coastal area and the vast northern lowlands of Petén department. The country is located in Central America and bounded to the north and west by Mexico, to the east by Belize and by the Gulf of Honduras, to the east by Honduras, to the southeast by El Salvador, and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. Two mountain chains enter Guatemala from west to east, dividing the country into three major regions: the highlands, where the mountains are located; the Pacific coast, south of the mountains; and the limestone plateau of the Petén region, north of the mountains. These areas vary in climate, elevation, and landscape, providing dramatic contrasts between hot and humid tropical lowlands and highland peaks and valleys.

Belize is a small Central American nation, located at 17°15' north of the equator and 88°45' west of the Prime Meridian on the Yucatán Peninsula. It borders the Caribbean Sea to the east, with 386 km of coastline. It has a total of 542 km of land borders—Mexico to the north-northwest (272 km) and Guatemala to the south-southwest (266 km). Belize's total size is 22,966 km2 (8,867 sq mi), of which 22,806 km2 (8,805 sq mi) is land and 160 km2 (62 sq mi) is water.

The Republic of Guatemala is divided into 22 departments which in turn are divided into 340 municipalities. The departments are governed by a departmental governor, appointed by the President.

Hurricane Iris was a small, but powerful Category 4 hurricane that caused widespread destruction in Belize. Iris was the second-strongest storm of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season, behind Hurricane Michelle. It was the ninth named storm, fifth hurricane, and third major hurricane of the year, forming from a tropical wave on October 4 just southeast of Barbados. It moved westward through the Caribbean, intensifying into a tropical storm on October 5 south of Puerto Rico, and into a hurricane on the following day. While passing south of the Dominican Republic, Iris dropped heavy rainfall that caused landslides, killing eight people. Later, the hurricane passed south of Jamaica, where it destroyed two houses. On reaching the western Caribbean Sea, Iris rapidly intensified into a Category 4 on the Saffir–Simpson scale. A small hurricane with an eye of only 7 mi (11 km) in diameter, Iris reached peak winds of 145 mph (233 km/h) before making landfall in southern Belize near Monkey River Town on October 9. The hurricane quickly dissipated over Central America, although its remnants contributed to the formation of Tropical Storm Manuel in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The hurricane caused severe damage—destroying homes, flooding streets, and leveling trees—in coastal towns south of Belize City.
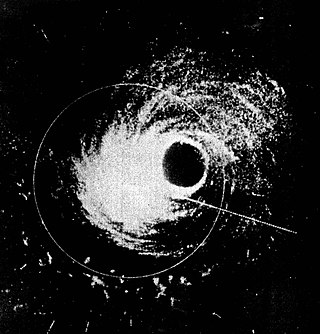
Hurricane Hattie was the strongest and deadliest tropical cyclone of the 1961 Atlantic hurricane season, reaching peak intensity as a Category 5 hurricane. The ninth tropical storm, seventh hurricane, fifth major hurricane, and second Category 5 of the season, Hattie originated from an area of low pressure that strengthened into a tropical storm over the southwestern Caribbean Sea on October 27. Moving generally northward, the storm quickly became a hurricane and later major hurricane the following day. Hattie then turned westward west of Jamaica and strengthened into a Category 5 hurricane, with maximum sustained winds of 165 mph (270 km/h). It weakened to Category 4 before making landfall south of Belize City on October 31. The storm turned southwestward and weakened rapidly over the mountainous terrain of Central America, dissipating on November 1.

Hurricane Francelia was the deadliest hurricane of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season after causing significant flooding to Central America, especially Belize and Guatemala. The sixth named storm and fourth hurricane of the season, Francelia developed from a tropical wave in the southeastern Caribbean Sea on August 29. It moved west-northwestward and strengthened into a tropical storm on the following day. On September 1, Francelia reached hurricane status, shortly before re-curving west-southwest. While approaching Central America, the storm intensified and peaked as a 100 mph (160 km/h) Category 2 hurricane on September 2. Francelia weakened slightly before making landfall near Punta Gorda, Belize late on September 3. The storm quickly weakened inland and dissipated by the following day.

Melchor de Mencos is a municipality in the Petén Department of Guatemala with population 23,813. It is situated on the eastern border with Belize, and is the only major border crossing from Guatemala to Belize. The city was established in April 1960. It is named after Sergeant Major Melchor de Mencos y Varón, who in 1754 journeyed with a tiny contingent of Spanish colonial troops from what is now Antigua, Guatemala to the coast of present-day Belize, there to combat English "pirates" who had settled that region and established a self-governing community. A large signboard-map at the border crossing between Benque Viejo del Carmen and Melchor depicts Belize as Guatemala's eastern province, consistent with Guatemala's ongoing claim.

Hurricane Greta, later Hurricane Olivia, was one of fourteen named Atlantic hurricanes to cross over Central America into the eastern Pacific while remaining a tropical cyclone. The seventh named storm of the 1978 Atlantic hurricane season, Greta formed from a tropical wave just northwest of Trinidad on September 13, and despite being in a climatologically unfavorable area, gradually intensified while moving west-northwestward. On September 16, it became a hurricane south of Jamaica. Two days later, the well-defined eye approached northeastern Honduras but veered to the northwest. After reaching peak winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) that day, Greta weakened while paralleling the northern Honduras coast just offshore. On September 19, it made landfall on Belize near Dangriga and quickly weakened into a tropical depression while crossing Guatemala and southeastern Mexico. After entering the eastern Pacific, the system re-intensified into a hurricane and was renamed Olivia, the eighteenth named storm of the 1978 Pacific hurricane season which weakened before landfall and dissipated over Chiapas on September 23.

The Belizean–Guatemalan territorial dispute is an unresolved territorial dispute between the states of Belize and Guatemala, neighbours in Central America. During the late 1600s and throughout the 1700s, Britain and Spain signed several treaties regarding territories in the Americas. Both nations agreed that the territory of modern-day Belize was under Spanish sovereignty, but British settlers could use the land, in specific areas and for specific purposes. However, the area was never fully under British or Spanish rule at this time and the British settlers continually expanded far past the boundaries set by the treaties. When the Spanish Empire fell, Guatemala said that it inherited Spain's sovereign rights over the territory. Since independence, Guatemala has claimed, in whole or in part, the territory of Belize.

Hurricane Richard was a damaging tropical cyclone that affected areas of Central America in October 2010. It developed on October 20 from an area of low pressure that had stalled in the Caribbean Sea. The system moved to the southeast before turning to the west. The storm slowly organized, and the system intensified into a tropical storm. Initially, Richard only intensified slowly in an area of weak steering currents. However, by October 23, wind shear diminished, and the storm intensified faster as it headed toward Belize. The next day, Richard intensified into hurricane status, and further into its peak intensity as a Category 2 hurricane, reaching maximum winds of 100 mph (160 km/h). The hurricane made its only landfall on Belize at peak intensity. Over land, Richard quickly weakened, and later degenerated into a remnant low on October 25.

Hurricane Ernesto was a Category 2 hurricane and a damaging tropical cyclone that affected several Caribbean Islands and areas of Central America during August 2012. The fifth named storm and second hurricane of the 2012 Atlantic hurricane season, Ernesto originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the west coast of Africa in late July. Moving westward, the system developed into a tropical depression in the central Atlantic, and further into a tropical storm prior to entering the Caribbean Sea. The system encountered high wind shear south of Jamaica but subsequently reached its peak intensity as a Category 2 hurricane as it made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula. Ernesto briefly emerged in the Bay of Campeche as a strong tropical storm before dissipating over the mountainous terrain of Mexico. The remnant circulation emerged in the eastern Pacific basin, contributing to the formation of Tropical Storm Hector.
The following lists events that happened during 2016 in Guatemala.

The 2016 Belize–Guatemala border standoff began when Belizean soldiers fatally shot a 13-year-old Guatemalan in the Cebada area of the Chiquibul National Park in western Belize with Guatemala.

Hurricane Earl was the deadliest Atlantic hurricane to impact Mexico since Hurricane Stan in 2005. The fifth named storm and second hurricane of the 2016 Atlantic hurricane season, Earl formed from a tropical wave south of Jamaica on August 2. The precursor to Earl brought torrential rainfall and flooding to the Lesser Antilles. Upon classification, the storm moved westward through the Caribbean Sea, brushing the north coast of Honduras. Earl strengthened into an 85 mph (140 km/h) hurricane before making landfall on Belize on August 4. It weakened while moving across the Yucatán Peninsula, but reintensified in the Bay of Campeche and followed the coastline. On August 6, Earl dissipated after moving ashore Veracruz.
Julio René AlvaradoRuano was a fourteen-year-old Guatemalan male who was killed in the Belize–Guatemala adjacency zone during an armed confrontation between the Belize Defence Force, Belizean park rangers, and Guatemalan farmers. The incident raised tensions between Belize and Guatemala, who have an ongoing border dispute since 1821. Belizean officials maintain that the Belize Defence Force acted in self-defence. However, the Guatemalan government claims the incident was a deliberate attack carried out by Belize's military. After the incident, the Organisation of American States agreed to investigate the death of Julio Alvarado at the request of both countries.

Hurricane Nana was a small, short-lived tropical cyclone that caused relatively minor damage in Belize and Mexico in early September 2020. The sixteenth tropical cyclone, fourteenth named storm, and fifth hurricane of the record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Nana originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of West Africa on August 23. The system progressed westward with little development for the next week before crossing into the Caribbean Sea. The wave gradually developed organized convection and a defined surface low on September 1, signifying the formation of Tropical Storm Nana as it approached Jamaica. Persistent wind shear stifled development of the storm, though following repeated bursts of deep convection, it intensified into a minimal hurricane on September 3. Nana attained peak winds of 75 mph (121 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 994 mbar shortly before striking Belize. Once onshore, the hurricane rapidly degraded and its surface low dissipated over Guatemala on September 4. The mid-level remnants of Nana later reorganized over the Gulf of Tehuantepec and became Tropical Storm Julio.

Belize, formerly known as British Honduras, is a Caribbean country located on the northeastern coast of Central America. Belize is bordered on the northwest by Mexico, on the east by the Caribbean Sea, and on the south and west by Guatemala. It has an area of 22,970 square kilometres (8,867 sq mi) and a population of 408,487 (2019). Its mainland is about 290 km (180 mi) long and 110 km (68 mi) wide. It has the lowest population and population density in Central America.

Central America is a region containing seven countries that connects the two continents of North America and South America.