
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompanied or followed by regional malnutrition, starvation, epidemic, and increased mortality. Every inhabited continent in the world has experienced a period of famine throughout history. During the 19th and 20th century, Southeast and South Asia, as well as Eastern and Central Europe, suffered the greatest number of fatalities due to famine. Deaths caused by famine declined sharply beginning in the 1970s, with numbers falling further since 2000. Since 2010, Africa has been the most affected continent in the world by famine.
In 2006, an acute shortage of food affected the countries in the Horn of Africa, as well as northeastern Kenya. The United Nations's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimated on January 6, 2006, that more than 11 million people in these countries may be affected by an impending widespread famine, largely attributed to a severe drought, and exacerbated by military conflicts in the region.
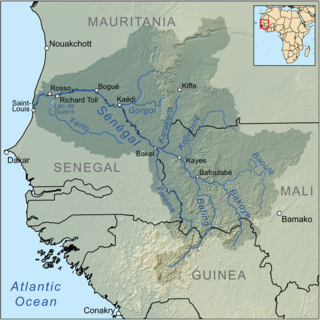
A large-scale, drought-induced famine occurred in Africa's Sahel region and many parts of the neighbouring Sénégal River Area from February to August 2010. It is one of many famines to have hit the region in recent times.

Occurring between July 2011 and mid-2012, a severe drought affected the entire East African region. Said to be "the worst in 60 years", the drought caused a severe food crisis across Somalia, Djibouti, Ethiopia and Kenya that threatened the livelihood of 9.5 million people. Many refugees from southern Somalia fled to neighboring Kenya and Ethiopia, where crowded, unsanitary conditions together with severe malnutrition led to a large number of deaths. Other countries in East Africa, including Sudan, South Sudan and parts of Uganda, were also affected by a food crisis.
Since 2016, a food insecurity crisis has been ongoing in Yemen which began during the Yemeni civil war. The UN estimates that the war has caused an estimated 130,000 deaths from indirect causes which include lack of food, health services, and infrastructure as of December 2020. In 2018, Save the Children estimated that 85,000 children have died due to starvation in the three years prior. In May 2020, UNICEF described Yemen as "the largest humanitarian crisis in the world", and estimated that 80% of the population, over 24 million people, were in need of humanitarian assistance. In September 2022, the World Food Programme estimated that 17.4 million Yemenis struggled with food insecurity, and projected that number would increase to 19 million by the end of the year, describing this level of hunger as "unprecedented." The crisis is being compounded by an outbreak of cholera, which resulted in over 3000 deaths between 2015 and mid 2017. While the country is in crisis and multiple regions have been classified as being in IPC Phase 4, an actual classification of famine conditions was averted in 2018 and again in early 2019 due to international relief efforts. In January 2021, two out of 33 regions were classified as IPC 4 while 26 were classified as IPC 3.

In the early months of 2017, parts of South Sudan experienced a famine following several years of instability in the country's food supply caused by war and drought. The famine, largely focused in the northern part of the country, affected an estimated five million people. In May 2017, the famine was officially declared to have weakened to a state of severe food insecurity.

Hassan Ali Khaire, in Ceelbuur Galguduud popularly known as Hassan Khaire, is a senior politician and is the former prime minister of Somalia. He was appointed on 23 February 2017 by Somalia President Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed "Farmaajo" and resigned on Saturday July 25, 2020 after MPs passed a disputed vote of no confidence.

The blockade of Yemen refers to a sea, land and air blockade on Yemen which started with the positioning of Saudi Arabian warships in Yemeni waters in 2015 with the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen. In November 2017, after a Houthi missile heading towards King Khalid International Airport was intercepted, the Saudi-led military coalition stated it would close all sea land and air ports to Yemen, but shortly began reopening them after criticism from the United Nations and over 20 aid groups and some humanitarian supplies were allowed into the country. In March 2021, Saudi Arabia denied the blockade continued, however, UN authorized ships continued to be delayed by Saudi warships.
Poverty in Niger is widespread and enduring in one of the world's most impoverished countries. In 2015, the United Nations (UN) Human Development Index ranked Niger as the second least-developed of 188 countries. Additionally, in 2015 the Global Finance Magazine ranked Niger 7th among the twenty-three poorest countries in the world. Two out of three residents live below the poverty line and more than 40 percent of the population earn less than $1 a day. Civil war, terror, illness, disease, poverty and hunger plague Niger. Hunger is one of the most significant problems the population faces daily. With a national population of 19,899,120, 45.7% of this population live below the poverty line.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, food insecurity intensified in many places. In the second quarter of 2020, there were multiple warnings of famine later in the year. In an early report, the Nongovernmental Organization (NGO) Oxfam-International talks about "economic devastation" while the lead-author of the UNU-WIDER report compared COVID-19 to a "poverty tsunami". Others talk about "complete destitution", "unprecedented crisis", "natural disaster", "threat of catastrophic global famine". The decision of the WHO on 11 March 2020, to qualify COVID as a pandemic, that is "an epidemic occurring worldwide, or over a very wide area, crossing international boundaries and usually affecting a large number of people" also contributed to building this global-scale disaster narrative.
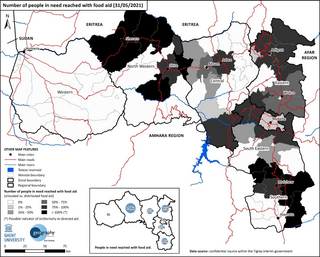
Beginning with the onset of the Tigray War in November 2020, acute food shortages leading to death and starvation became widespread in northern Ethiopia, and the Tigray, Afar and Amhara Regions in particular. As of August 2022, there are 13 million people facing acute food insecurity, and an estimated 150,000–200,000 had died of starvation by March 2022. In the Tigray Region alone, 89% of people are in need of food aid, with those facing severe hunger reaching up to 47%. In a report published in June 2021, over 350,000 people were already experiencing catastrophic famine conditions. It is the worst famine to happen in East Africa since 2011–2012.
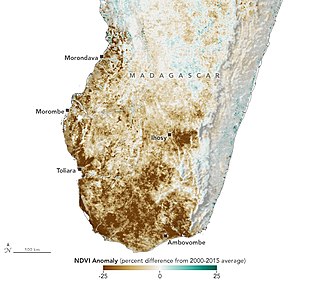
In mid-2021, a severe drought in southern Madagascar caused hundreds of thousands of people, with some estimating more than 1 million people including nearly 460,000 children, to suffer from food insecurity or Kere (famine). Some organizations have attributed the situation to the impact of climate change and the handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the country.
During 2021-2023, Somalia confronted its most severe drought in forty years, affecting more than 7.8 million people —about half of Somalia’s population. As of 2024, drought-related impacts still continue to affect 4.4 million individuals across Somalia, who face including acute food insecurity. This includes an estimated 724,000 people at IPC Phase 4 (Emergency).
Events in the year 2022 in Somalia.
During 2022 and 2023 there were food crises in several regions as indicated by rising food prices. In 2022, the world experienced significant food price inflation along with major food shortages in several regions. Sub-Saharan Africa, Iran, Sri Lanka, Sudan and Iraq were most affected. Prices of wheat, maize, oil seeds, bread, pasta, flour, cooking oil, sugar, egg, chickpea and meat increased. Many factors have contributed to the ongoing world food crisis. These include supply chain disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2021–2023 global energy crisis, the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and floods and heatwaves during 2021. Droughts were also a factor; in early 2022, some areas of Spain and Portugal lost 60–80% of their crops due to widespread drought.
The war in Afghanistan ended with the Taliban victorious when the United States withdrew its troops from Afghanistan. The aftermath has been characterized by marked change in the social and political order of Afghanistan as Taliban took over the country once again after the fall of Kabul in 2021.
Grain From Ukraine is a humanitarian food program that was launched on November 26, 2022, on the 90th anniversary of the beginning of the Holodomor of 1932–1933, by the President of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelenskyy, to supply grain to the poorest countries in Africa.

The 2020–present Horn of Africa drought is an ongoing drought that hit the countries of Somalia, Ethiopia, and Kenya. The rainy season of 2022 was recorded to be the driest in over 40 years, with an estimated 43,000 in Somalia dying in 2022. As of 2023, the region is now in its 5th failed rainy season and a 6th failed season is predicted.
The humanitarian crisis following the 2023 Sudan conflict was further exacerbated by the violence occurring during a period of high temperatures, drought and the conflict starting during the latter part of the fasting month of Ramadan. Most residents were unable to venture outside of their homes to obtain food and supplies for fear of getting caught in the crossfire. A doctors' group said that hospitals remained understaffed and were running low on supplies as wounded people streamed in. The World Health Organization recorded around 26 attacks on healthcare facilities, some of which resulted in casualties among medical workers and civilians. The Sudanese Doctors' Union said more than two-thirds of hospitals in conflict areas were out of service with 32 forcibly evacuated by soldiers or caught in the crossfire. The United Nations reported that shortages of basic goods, such as food, water, medicines and fuel have become "extremely acute". The delivery of badly-needed remittances from overseas migrant workers was also halted after Western Union announced it was closing all operations in Sudan until further notice.
Throughout 2024, the population of Sudan suffered from severe malnutrition and famine conditions as a result of the Sudanese civil war beginning in 2023, primarily in Darfur, Kordofan, and neighboring refugee-taking nations such as Chad. On 1 August, the Global Famine Review Committee released a report officially declaring that it was possible that IPC Phase 5 famine conditions were ongoing in North Darfur near Al-Fashir and there was a high risk of similar conditions throughout internally displaced persons (IDP) camps. Human rights groups say famine conditions were caused in part by deliberate attempts by the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) to siege and loot cities with civilians trapped in them and by both sides blocking off supply routes making it difficult to allow food and humanitarian aid to flow through. More than 1,050 deaths have been caused by the famine and over 9 million people have been displaced as a result of the famine and war.










