
The Church of Sweden is an Evangelical Lutheran national church in Sweden. A former state church, headquartered in Uppsala, with around 5.4 million members at year end 2023, it is the largest Christian denomination in Sweden, the largest Lutheran denomination in Europe and the third-largest in the world, after the Ethiopian Evangelical Church Mekane Yesus and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Tanzania.

Östersund Municipality is a municipality in Jämtland County in northern Sweden. Its seat is located in Östersund, which is also the county seat of Jämtland County.
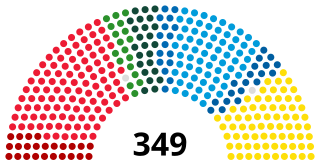
The Riksdag is the parliament and the supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members, elected proportionally and serving, since 1994, fixed four-year terms. The 2022 Swedish general election is the most recent general election.

Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.
The Swedish People's Party of Finland is a Finnish political party founded in 1906. Its primary aim is to represent the interests of the minority Swedish-speaking population of Finland. The party is currently a participant in the Government of Petteri Orpo, holding the posts of Minister of Education, Minister for European Affairs, and Minister of Youth, Sport and Physical Activity.
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in the legislature. It is sworn into office, with or without the formal support of other parties, enabling a government to be formed. Under such a government, legislation can only be passed with the support or consent of enough other members of the legislature to provide a majority, encouraging multi-partisanship. In bicameral legislatures, the term relates to the situation in the chamber whose confidence is considered most crucial to the continuance in office of the government.
A political party platform, party program, or party manifesto is a formal set of principal goals which are supported by a political party or individual candidate, to appeal to the general public, for the ultimate purpose of garnering the general public's support and votes about complicated topics or issues. A component of a political platform is often called a plank – the opinions and viewpoints about an individual topic, as held by a party, person, or organization. The word "plank" depicts a component of an overall political platform, as a metaphorical reference to a basic stage made of boards or planks of wood. The metaphor can return to its literal origin when public speaking or debates are actually held upon a physical platform.
Nonpartisan democracy is a system of representative government or organization such that universal and periodic elections take place without reference to political parties. Sometimes electioneering and even speaking about candidates may be discouraged, so as not to prejudice others' decisions or create a contentious atmosphere.

The 2004 European Parliament election was held between 10 and 13 June 2004 in the 25 member states of the European Union, using varying election days according to local custom. The European Parliamental parties could not be voted for, but elected national parties aggregated in European Parliamental parties after the elections.
The June List was a Swedish left Eurosceptic political party. Founded in 2004, it received 14% in the European Parliament election of the same year - gaining three seats. In the elections of 2009, however, it saw a drop of 11 percentage points in support and lost all of its seats. Due to its subsequent decline the party has been inactive since the 2014 European Parliament election.
Elections in Spain encompass four different types: general elections, regional elections, local elections, and elections to the European Parliament. General elections and regional elections are typically conducted at the conclusion of the national or regional legislative mandate, which usually spans four years since the previous election. However, early elections can be called in certain circumstances. On the other hand, local council elections and elections to the European Parliament follow fixed dates, although some local government bodies, such as provincial councils, are not directly elected. In most elections, a party-list proportional representation (PR) system is employed, while the Senate utilizes the plurality system.
Nominating groups are political parties and other organisations that take part in the elections to the various governing bodies of the Church of Sweden.

Apportionment is the process by which seats in a legislative body are distributed among administrative divisions, such as states or parties, entitled to representation. This page presents the general principles and issues related to apportionment. The page apportionment by country describes the specific practices used around the world. The page Mathematics of apportionment describes mathematical formulations and properties of apportionment rules.

The National Assembly of the State of Eritrea has 150 members, 75 members appointed and 75 members representing the members of the Central Committee of the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ), the sole legal political party of Eritrea. According to the IPU, the National Assembly has 150 indirectly elected members. The National Assembly was composed in 1994, and its meeting place is located in Asmara.

General elections were held in Sweden on 19 September 2010 to elect the 349 members of the Riksdag. The main contenders of the election were the governing centre-right coalition the Alliance, consisting of the Moderate Party, the Centre Party, the Liberal People's Party and the Christian Democrats; and the opposition centre-left coalition the Red-Greens, consisting of the Social Democrats, the Left Party and the Green Party.
The 1996 European Parliament election in Finland was the first election of the Finnish delegation to the European Parliament.

The 1979 Spanish local elections were held on Tuesday, 3 April 1979, to elect all 67,505 councillors in the 7,870 municipalities of Spain and all 1,152 seats in 43 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with local elections in the four foral deputations of the Basque Country and Navarre and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.

The 1983 Spanish local elections were held on Sunday, 8 May 1983, to elect all 67,505 councillors in the 7,781 municipalities of Spain and all 1,024 seats in 38 provincial deputations. The elections were held simultaneously with regional elections in thirteen autonomous communities, as well as local elections in the three foral deputations of the Basque Country and the ten island councils in the Balearic and Canary Islands.
The Swedish Church Assembly elections were held on 15 September 2013. All 249 seats in the General Synod of the Church of Sweden were up for election, as well as local governing bodies.
The Swedish Church Assembly elections were held on 19 September 2021. All 251 seats in the General Synod of the Church of Sweden were up for election, as well as local governing bodies.










