
South Atlantic tropical cyclones are unusual weather events that occur in the Southern Hemisphere. Strong wind shear, which disrupts the formation of cyclones, as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South Atlantic Ocean, make any strong tropical system extremely rare, and Hurricane Catarina in 2004 is the only recorded South Atlantic hurricane in history. Storms can develop year-round in the South Atlantic, with activity peaking during the months from November through May. Since 2011, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center has assigned names to tropical and subtropical systems in the western side of the basin, near the eastern coast of Brazil, when they have sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph), the generally accepted minimum sustained wind speed for a disturbance to be designated as a tropical storm in the North Atlantic basin. Below is a list of notable South Atlantic tropical and subtropical cyclones.
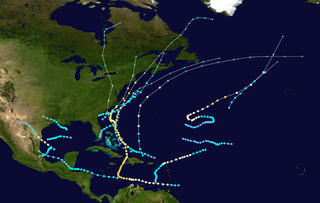
The 1954 Atlantic hurricane season was an above-average Atlantic hurricane season in terms of named storms, with 16 forming. Overall, the season resulted in $751.6 million in damage, the most of any season at the time. The season officially began on June 15, and nine days later the first named storm developed. Hurricane Alice developed in the Gulf of Mexico and moved inland along the Rio Grande, producing significant precipitation and record flooding that killed 55 people. Activity was slow until late August; only Barbara, a minimal tropical storm, developed in July. In the span of two weeks, hurricanes Carol and Edna followed similar paths before both striking New England as major hurricanes. The latter became the costliest hurricane in Maine's history.

Hurricane Charley was the second hurricane to threaten the East Coast of the United States within a year's timeframe, after Hurricane Gloria of 1985. The third tropical storm and second hurricane of the season, Charley formed as a subtropical low on August 13 along the Florida panhandle. After moving off the coast of South Carolina, the system transitioned into a tropical cyclone and intensified into a tropical storm on August 15. Charley later attained hurricane status before moving across eastern North Carolina. It gradually weakened over the north Atlantic Ocean before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on August 20. Charley's remnants remained identifiable for over a week, until after crossing Ireland and Great Britain they dissipated on August 30.

Typhoon Babs, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Loleng, was a powerful typhoon that struck the Philippines days after Typhoon Zeb hit the same area. The seventh typhoon of the inactive 1998 Pacific typhoon season, Babs formed on October 14 between the Philippines and Guam. The storm moved westward initially, failing to intensify initially due to the outflow from Typhoon Zeb to the northwest. Babs slowed and briefly turned to the south before advancing to the northwest, whereupon it rapidly intensified into a strong typhoon. On October 20, the official Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) estimated peak 10‑minute winds of 155 km/h (96 mph), while the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated peak 1‑minute winds of 250 km/h (160 mph), making Babs an unofficial super typhoon. The storm struck the Philippine island of Catanduanes at that intensity and weakened slightly before hitting Luzon. Babs turned northward once in the South China Sea, later weakening due to unfavorable conditions and transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on October 27 in the Taiwan Strait.

The climate in Brazil varies considerably from mostly tropical north to temperate zones south of the Tropic of Capricorn.

The January 2010 Rio de Janeiro floods and mudslides was an extreme weather event that affected the State of Rio de Janeiro in Brazil in the first days of January 2010. At least 85 people died, with at least 29 people in the Hotel Sankey after it was destroyed by landslides, and many more have been injured. More than 4,000 people were forced to evacuate their homes.

Severe Tropical Storm Linfa, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Chedeng, brought deadly flooding to areas of the Philippines and Japan in May and June 2003. The fourth named storm within the northwestern Pacific that year, Linfa developed as a tropical depression just off the western coast of Luzon on May 25. The disturbance quickly intensified to reach tropical storm intensity a few hours after cyclogenesis. However, intensification leveled off as Linfa executed a small clockwise loop before a subsequent landfall on Luzon on May 27. Due to land interaction the storm temporarily weakened and decoupled before reforming in the Philippine Sea. Afterwards Linfa began reintensifying and reached its peak intensity on May 29 with maximum sustained winds of 100 km/h (65 mph) and a barometric pressure of 980 mbar. Following its peak the tropical storm began to deteriorate and transitioned into an extratropical cyclone on May 30; these extratropical remnants continued to track northward through Japan before dissipating in the Sea of Okhotsk on June 4.

Tropical Storm Andrea brought flooding to Cuba, the Yucatan Peninsula, and portions of the East Coast of the United States in June 2013. The first tropical cyclone and named storm of the annual hurricane season, Andrea originated from an area of low pressure in the eastern Gulf of Mexico on June 5. Despite strong wind shear and an abundance of dry air, the storm strengthened while initially heading north-northeastward. Later on June 5, it re-curved northeastward and approached the Big Bend region of Florida. Andrea intensified and peaked as a strong tropical storm with winds at 65 mph (105 km/h) on June 6. A few hours later, the storm weakened slightly and made landfall near Steinhatchee, Florida later that day. It began losing tropical characteristics while tracking across Florida and Georgia. Andrea transitioned into an extratropical cyclone over South Carolina on June 7, though the remnants continued to move along the East Coast of the United States, until being absorbed by another extratropical system offshore Maine on June 10.

Tropical Storm Rolf, also known as Tropical Storm 01M, was an unusual Mediterranean tropical storm that brought flooding to Italy, France, Spain, and Switzerland in November 2011. Rolf originated from an extratropical system near western France on 4 November. Despite the generally unfavorable conditions in the Mediterranean Sea, Rolf transitioned into a subtropical depression on 7 November, before becoming a tropical storm later that day. On 8 November, Rolf reached its peak intensity, with 1-minute sustained winds peaking at 85 km/h (53 mph) and a minimum central pressure of 991 mb (29.3 inHg). During the next day, the storm made landfall on the island of Île du Levant, in France, and soon afterward, near Hyères in southeastern France. Following its second landfall, Rolf quickly weakened and dissipated on 10 November. Rolf was the first tropical cyclone ever to be officially monitored by the NOAA in the Mediterranean Sea.

The 2022 Atlantic hurricane season was a destructive Atlantic hurricane season, which had an average number of named storms, a slightly above-average number of hurricanes, a slightly below-average number of major hurricanes, and a near-average accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index. Despite this, it became the third-costliest Atlantic hurricane season on record, behind only 2017 and 2005, mostly due to Hurricane Ian. The season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most subtropical or tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic Ocean. This year's first Atlantic named storm, Tropical Storm Alex, developed five days after the start of the season, making this the first season since 2014 not to have a pre-season named storm.
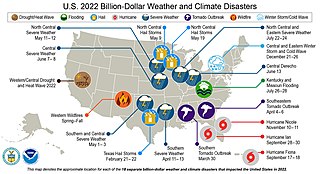
The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2022. The year began with a La Niña. There were several natural disasters around the world from various types of weather, including blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones. The deadliest weather event of the year were the European heat waves, which killed over 26,000 people, 11,000 of which were in France. The costliest weather event of the year was Hurricane Ian, which caused at least $112.9 billion in damages in Florida and Cuba. Another significant weather event was the Pakistan floods, which killed 1,739 people and a total of $14.9 billion in damages.

The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2015. There were several natural disasters around the world from various types of weather, including blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones.

Subtropical Storm Yakecan was a subtropical cyclone that during its path, passed through the southern region of Brazil, specifically in Rio Grande do Sul and Uruguay. The cyclone came from the sea towards the Rio Grande territory and arrived with less strength in the state of Santa Catarina, where it returned to the sea. It was the sixteenth named storm to hit Brazil since Cyclone Catarina in 2004.

Floods and mudslides occurred in the Northeast region of Brazil in 2022. Its cause was the rains that hit mainly the state of Pernambuco, but also Sergipe, Alagoas, Paraíba and Rio Grande do Norte. Precipitation volumes surpassed the historical monthly average in several cities in just three days.

The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2023. The year saw a transition from La Niña to El Niño, with record high global average surface temperatures. The most common weather events to have a significant impact are blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones.

During the 2023 Brazilian Carnival holiday weekend, record-breaking rainfall—reaching 682 mm (26.9 in) in 24 hours—caused deadly floods and landslides across the state of São Paulo. At least 64 people were killed, of which 63 were in São Sebastião.















