
The dot-com bubble was a stock market bubble that ballooned during the late-1990s and peaked on Friday, March 10, 2000. This period of market growth coincided with the widespread adoption of the World Wide Web and the Internet, resulting in a dispensation of available venture capital and the rapid growth of valuations in new dot-com startups. Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, investments in the NASDAQ composite stock market index rose by 800%, only to fall to 78% from its peak by October 2002, giving up all its gains during the bubble.

Nvidia Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It is a software and fabless company which designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing, as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is also a dominant supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software.

The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.
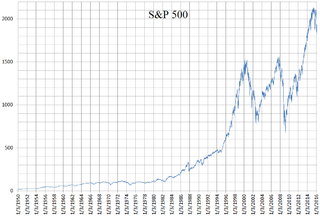
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 of the largest companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $43 trillion as of January 2024.

Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's second-most valuable semiconductor company, the world's largest dedicated independent ("pure-play") semiconductor foundry, and its country's largest company, with headquarters and main operations located in the Hsinchu Science Park in Hsinchu, Taiwan. The majority of TSMC is owned by foreign investors, and the central government of Taiwan is the largest shareholder. In 2023, the company was ranked 44th in the Forbes Global 2000.

The Korea Composite Stock Price Index or KOSPI (Korean: 한국종합주가지수) is the index of all common stocks traded on the Stock Market Division—previously, Korea Stock Exchange—of the Korea Exchange. It is the representative stock market index of South Korea, analogous to the S&P 500 in the United States.

Masayoshi Son is a Japanese billionaire technology entrepreneur, investor and philanthropist. A third-generation Zainichi Korean, he naturalized as a Japanese citizen in 1990. He is the founder, representative director, corporate officer, chairman and CEO of SoftBank Group Corp. (SBG), a strategic technology-focused investment holding company, as well as chairman of UK-based Arm Holdings.
The Russell 1000 Index is a U.S. stock market index that tracks the highest-ranking 1,000 stocks in the Russell 3000 Index, which represent about 93% of the total market capitalization of that index. As of 31 December 2023, the stocks of the Russell 1000 Index had a weighted average market capitalization of $666.0 billion and a median market capitalization of $13.9 billion. As of 8 May 2020, components ranged in market capitalization from $1.8 billion to $1.4 trillion. The index, which was launched on January 1, 1984, is maintained by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the United Kingdom-based London Stock Exchange Group.
On October 27, 1997, a global stock market crash was caused by an economic crisis in Asia, the "Asian contagion", or Tom Yum Goong crisis. The point loss that the Dow Jones Industrial Average suffered on this day currently ranks as the 18th biggest percentage loss since the Dow's creation in 1896. This crash is considered a "mini-crash" because the percentage loss was relatively small compared to some other notable crashes. After the crash, the markets still remained positive for 1997, but the "mini-crash" may be considered as the beginning of the end of the 1990s economic boom in the United States and Canada, as both consumer confidence and economic growth were mildly reduced during the winter of 1997–1998, and when both returned to pre-October levels, they began to grow at an even slower pace than before the crash.

Jen-Hsun "Jensen" Huang is an American businessman, electrical engineer, and philanthropist who is the president and chief executive officer (CEO) of Nvidia.
The CSI 300 is a capitalization-weighted stock market index designed to replicate the performance of the top 300 stocks traded on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. It has two sub-indexes: the CSI 100 Index and the CSI 200 Index. Over the years, it has been deemed the Chinese counterpart of the S&P 500 index and a better gauge of the Chinese stock market than the more traditional SSE Composite Index.
In modern finance, a flash crash is a very rapid, deep, and volatile fall in security prices occurring within a very short time period followed by a quick recovery. Flash crashes are frequently blamed by media on trades executed by black-box trading, combined with high-frequency trading, whose speed and interconnectedness can result in the loss and recovery of billions of dollars in a matter of minutes and seconds, but in reality occur because almost all participants have pulled their liquidity and temporarily paused their trading in the face of a sudden increase in risk.
The 2015–2016 stock market selloff was the period of decline in the value of stock prices globally that occurred between June 2015 to June 2016. It included the 2015–2016 Chinese stock market turbulence, in which the SSE Composite Index fell 43% in just over two months between June 2015 and August 2015, which culminated in the devaluation of the yuan. Investors sold shares globally as a result of slowing growth in the GDP of China, a fall in petroleum prices, the Greek debt default in June 2015, the effects of the end of quantitative easing in the United States in October 2014, a sharp rise in bond yields in early 2016, and finally, in June 2016, the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, in which Brexit was voted upon.
Big Tech, also known as the Tech Giants or Tech Titans, are the largest IT companies in the world. The concept of Big Tech is similar to the grouping of dominant companies in other sectors. It typically refers to the Big Five United States tech companies: Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Microsoft; or the Magnificent Seven, which includes Nvidia and Tesla. Big Tech can also include Chinese companies such as Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent, and Xiaomi (BATX).

On 20 February 2020, stock markets across the world suddenly crashed after growing instability due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It ended on 7 April 2020.

Economic turmoil associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has had wide-ranging and severe impacts upon financial markets, including stock, bond, and commodity markets. Major events included a described Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war, which after failing to reach an OPEC+ agreement resulted in a collapse of crude oil prices and a stock market crash in March 2020. The effects upon markets are part of the COVID-19 recession and are among the many economic impacts of the pandemic.
The COVID-19 recession, also known as the Great Lockdown, was a global economic recession caused by COVID-19 lockdowns. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activity, the COVID-19 lockdowns and other precautions taken in early 2020 drove the global economy into crisis. Within seven months, every advanced economy had fallen to recession.
Between 2020 and 2023, there was a worldwide chip shortage affecting more than 169 industries, which led to major price increases, long queues, and reselling among consumers and manufacturers for automobiles, graphics cards, video game consoles, computers, household appliances, and other consumer electronics that require integrated circuits.
The 2022 stock market decline was a global phenomenon. In the United States, it began on January 3, 2022, and ended on October 22, 2022; with the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the Nasdaq Composite, and the S&P 500 entered the bull market in November 2022, May 2023, and June 2023 respectively. In Japan, the Nikkei 225 reached its highest level since 1990, in May 2023. While 2022 was the worst year for Wall Street since 2008, 2024 had at least 36 days of closing at record-breaking highs.











