
The 24-zig is a winding mountain road in the southwest of China, which became known worldwide in the Second Sino-Japanese War as a symbol of the efforts made by the United States Army to support China.

The 24-zig is a winding mountain road in the southwest of China, which became known worldwide in the Second Sino-Japanese War as a symbol of the efforts made by the United States Army to support China.
The 24-zig from the Second Sino-Chinese War lies in Qinglong County (晴隆 县; Pinyin: Qínglóng Xiàn) in the north of the Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture , which is located in the southwest of the Chinese province of Guizhou in the border triangle of Guizhou, Yunnan and Guangxi. After the war, it was long believed that the street was in Yunnan Province. [1]
It is an extension of Ledo Road, which is also called the "Stilwell Road", named after the American general Joseph Stilwell. The street has been on the list of Monuments of the People's Republic of China (6-1050) since 2006.

Yunnan is an inland province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately 394,000 km2 (152,000 sq mi) and has a population of 48.3 million. The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi and Tibet, as well as Southeast Asian countries Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014.

Guizhou is an inland province in Southwestern China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the south, Yunnan to the west, Sichuan to the northwest, the municipality of Chongqing to the north, and Hunan to the east. The population of Guizhou stands at 38.5 million, ranking 18th among the provinces in China.

Kunming is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The city was of great significance during World War II as a Chinese military center, American air base, and transport terminus for the Burma Road. In the middle of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, Kunming is at an altitude of 1,900 metres above sea level and a latitude just north of the Tropic of Cancer. The city is the fourth most populous city in Western China, after Chongqing, Chengdu, and Xi'an, as well as the third most populous city in Southwestern China after Chongqing and Chengdu. As of 2020 census, Kunming had a total population of 8,460,088 inhabitants, of whom 5,604,310 lived in its built-up area made of all urban districts but Jinning, not conurbated yet. It is at the northern edge of Dian Lake, surrounded by temples and lake-and-limestone hill landscapes.

Guiyang is the capital of Guizhou province of the People's Republic of China. It is located in the center of the province, situated on the east of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and on the north bank of the Nanming River, a branch of the Wu River. The city has an elevation of about 1,100 meters (3,600 ft). It has an area of 8,034 square kilometers (3,102 sq mi). At the 2020 census, its population was 5,987,018, out of whom 4,506,134 lived in the six urban districts.
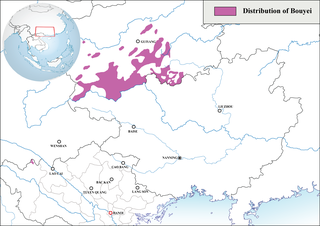
The Bouyei language is a language spoken by the Bouyei ethnic group of Southern Guizhou Province, China. Classified as a member of the Northern Tai group in the Tai language branch of the Tai–Kadai language family, the language has over 2.5 million native speakers and is also used by the Giay people in some parts of Vietnam. There are native speakers living in France or the United States as well, which emigrated from China or Vietnam. About 98% of the native speakers are in China.
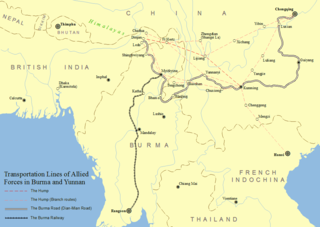
The Burma Road was a road linking Burma with southwest China. Its terminals were Lashio, Burma, in the south and Kunming, China, the capital of Yunnan province in the north. It was built in 1937–1938 while Burma was a British colony to convey supplies to China during the Second Sino-Japanese War. Preventing the flow of supplies on the road helped motivate the occupation of Burma by the Empire of Japan in 1942 during World War II. Use of the road was restored to the Allies in 1945 after the completion of the Ledo Road. Some parts of the old road are still visible today.

The Ledo Road was an overland connection between British India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan. After the Japanese cut off the Burma Road in 1942 an alternative was required, hence the construction of the Ledo Road. It was renamed the Stilwell Road, after General Joseph Stilwell of the U.S. Army, in early 1945 at the suggestion of Chiang Kai-shek. It passes through the Burmese towns of Shingbwiyang, Myitkyina and Bhamo in Kachin state. Of the 1,726 kilometres (1,072 mi) long road, 1,033 kilometres (642 mi) are in Burma and 632 kilometres (393 mi) in China with the remainder 61 km was in India. The road had the Ledo-Pangsau Pass-Tanai (Danai)-Myitkyina--Bhamo-Mansi-Namhkam-Kunming route.

This article describes the history of Yunnan, currently a province of the People's Republic of China.

Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, is an autonomous prefecture of Guizhou province, People's Republic of China, bordering Guangxi to the south and Yunnan to the west. The name, "黔西南" derives from the prefecture's southwest location in the province; "黔" is the official abbreviation for Guizhou, while "西南" means "southwest".

Southwestern China is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China.
Battle of Yunnan-Burma Road was the name of the Chinese intervention to aid their British allies in the 1942 Burma Campaign. Its forces were composed of the Fifth, Sixth and Sixty-sixth Army under the command of the Chinese Expeditionary Force in Burma, commanded by Lt. General Joseph Stilwell, Lt. General Luo Zhuoying was his executive officer.

Battle of Northern Burma and Western Yunnan was the name of the Chinese campaign with their allies in the 1943–45 Burma Campaign. The campaign ended in an Allied victory.

The Chinese Expeditionary Force was an expeditionary unit of China's National Revolutionary Army that was dispatched to Burma and India in support of the Allied efforts against the Imperial Japanese Army during the Japanese invasion and occupation of Burma in the South-East Asian theatre of the Second World War.

The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau is a highland region located in southwest China. The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou. In the southwest, the Yungui is a true plateau with relatively flatter highland areas, while in the northeast, the Yungui is a generally mountainous area of rolling hills, gorges, and karst topography.

The transport infrastructure of Yunnan is served by numerous transport modes, and forms an integral part of the structure Yunnan Province and the Southwest of China. Yunnan is served by several civilian airports and a major highway and rail network. The province is served by a network of bus routes that radiates from the capital city, Kunming.

China National Highway 320 (G320) runs southwest from Shanghai through the provinces of Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Hunan and Guizhou before ending in Ruili, Yunnan at the Sino–Burmese border. It is 3,695 kilometres (2,296 mi) in length.

Qinglong County is a county in the southwest of Guizhou province, China. It is under the administration of the Qianxinan Buyei and Miao Autonomous Prefecture. It has a population of 234,162 as of 2020, 56% belonging to ethnic minorities. Qinglong is named after the Qinglong mountain, before 1941 it was called Annang County (安南县). The county was a frontline of the 1854–1873 Miao Rebellions.

Zhijiang Dong Autonomous County, usually referred to as Zhijiang County is an autonomous county of the Dong people in Hunan Province, China. It is under the administration of Huaihua prefecture-level city.

Beipan River is a river in Guizhou and Yunnan provinces, China, and part of the great Pearl River basin.
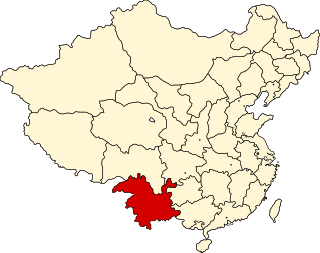
Yunnan is a de jure province in the Republic of China according to the ROC law, as the ROC government formally claims to be the legitimate government of the whole China. It was one of the 22 provinces set up during the Qing dynasty. As one of the 6 provinces in South China, the territory it administers was slightly larger than the present-day Yunnan.