Related Research Articles

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.

Year 342 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ahala and Rutilus. The denomination 342 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 495 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sabinus and Priscus. The denomination 495 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 230 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Barbula and Pera. The denomination 230 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 340 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Torquatus and Mus. The denomination 340 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 474 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Medullinus and Vulso. The denomination 474 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 421 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Barbatus. The denomination 421 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 428 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cossus and Cincinnatus or Cincinnatus and Atratinus. The denomination 428 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 550 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 204 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 550 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Cumae was the first ancient Greek colony on the mainland of Italy, founded by settlers from Euboea in the 8th century BC and soon becoming one of the strongest colonies. It later became a rich Roman city, the remains of which lie near the modern village of Cuma, a frazione of the comune Bacoli and Pozzuoli in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, Italy.

The Battle of Cumae was one of several battles between Cumae and the Etruscans. In 524 BC an army of Umbrians, Daunians, Etruscans, and others were defeated by the Greeks of Cumae.
Clusium was an ancient city in Italy, one of several found at the site. The current municipality of Chiusi (Tuscany) partly overlaps this Roman walled city. The Roman city remodeled an earlier Etruscan city, Clevsin, found in the territory of a prehistoric culture, possibly also Etruscan or proto-Etruscan. The site is located in northern central Italy on the west side of the Apennines.
The Battle of Mount Gaurus, 343 BC, was the first battle of the First Samnite War and also the first battle fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites. The battle is described by the Roman historian Livy as part of Book Seven of his history of Rome, Ab Urbe Condita where he narrates how the Roman consul Marcus Valerius Corvus won a hard-fought battle against the Samnites at Mount Gaurus, near Cumae, in Campania. Modern historians however believe that most, if not all, of the detail in Livy's description has been invented by him or his sources.
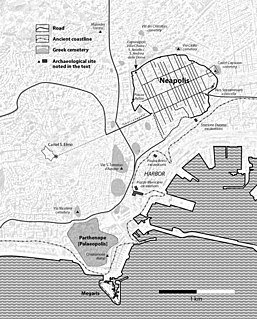
The history of Naples is long and varied, dating to Greek settlements established in the Naples area in the 2nd millennium BC. During the end of the Greek Dark Ages a larger mainland colony – initially known as Parthenope – developed around the 9-8th century BC, and was refounded as Neapolis in the 6th century BC: it held an important role in Magna Graecia. The Greek culture of Naples was important to later Roman society. When the city became part of the Roman Republic in the central province of the Empire, it was a major cultural centre.

The First Battle of Capua was fought in 212 BC between Hannibal and two Roman consular armies. The Roman force was led by two consuls, Quintus Fulvius Flaccus and Appius Claudius Pulcher. The Roman force was defeated, but managed to escape. Hannibal temporarily managed to raise the siege of Capua. A tactical Carthaginian victory, it ultimately did not help the Capuans.
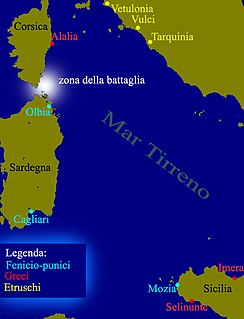
The naval Battle of Alalia took place between 540 BCE and 535 BCE off the coast of Corsica between Greeks and the allied Etruscans and Carthaginians. A Greek force of 60 Phocaean ships defeated a Punic-Etruscan fleet of 120 ships while emigrating to the western Mediterranean and the nearby colony of Alalia.
Portus Julius was the first harbour specifically constructed to be a base for the Roman western naval fleet, the classis Misenensis; the eastern fleet was based in the Port of Ravenna. The port was located at Misenum on a peninsula at the northern end of the Gulf of Naples. Portus Julius was named in honour of Octavian's great-uncle and adoptive father, Julius Caesar and the Julian clan.

The Battle of Suessula was the third and last battle between the Samnites and the Roman Republic in 343 BC, the first year of the First Samnite War. According to the Augustan historian Livy, the Samnites gathered their army at Suessula, at the eastern edge of Campania. The Roman consul Marcus Valerius Corvus took his army by forced marches to Suessula. When the Samnites had to scatter their army to forage for food, Valerius seized the opportunity to capture the Samnite camp and then rout the Samnite foragers. Modern historians believe that details of the battle were entirely invented by Livy and his annalistic sources, and the battle's historicity has also been questioned.
Aristodemus, nicknamed Malakos, was a strategos and then tyrant of Cumae. As a strategos, he twice defeated Etruscan armies. He gained popularity amongst the people of Cumae due to his opposition to the city's aristocracy and his proposals to more fairly share land and to forgive debts. He was then successful in overthrowing the aristocratic faction, yet became a tyrant himself. He was assassinated by the aristocratic faction around 490 BC.

The Roman expansion in Italy covers a series of conflicts in which Rome grew from being a small Italian city-state to be the ruler of the Italian peninsula. Roman tradition attributes to the Roman kings the first war against the Sabines and the first conquests around the Alban Hills and down to the coast of Latium. The birth of the Roman Republic after the overthrow of the Etruscan monarch of Rome in 509 BC began a series of major wars between the Romans and the Etruscans. In 390 BC, Gauls from the north of Italy sacked Rome. In the second half of the 4th century BC Rome clashed repeatedly with the Samnites, a powerful tribal coalition of the Apennine region. By the end of these wars, Rome had become the most powerful state in central Italy and began to expand to the north and to the south. The last threat to Roman hegemony came during the Pyrrhic war when Tarentum enlisted the aid of the Greek king Pyrrhus of Epirus to campaign in the South of Italy. Resistance in Etruria was finally crushed in 265-264 BC, the same year the first punic war began and brought Roman forces outside of the peninsula for the first time.
References
- ↑ "THE BATTLE OF CUMAE, ITALY (524 BC)". 4 June 2014.