Related Research Articles
The P versus NP problem is a major unsolved problem in theoretical computer science. In informal terms, it asks whether every problem whose solution can be quickly verified can also be quickly solved.
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline.

In computational complexity theory, NP is a complexity class used to classify decision problems. NP is the set of decision problems for which the problem instances, where the answer is "yes", have proofs verifiable in polynomial time by a deterministic Turing machine, or alternatively the set of problems that can be solved in polynomial time by a nondeterministic Turing machine.

A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a2 + b2 = c2. Such a triple is commonly written (a, b, c), and a well-known example is (3, 4, 5). If (a, b, c) is a Pythagorean triple, then so is (ka, kb, kc) for any positive integer k. A primitive Pythagorean triple is one in which a, b and c are coprime (that is, they have no common divisor larger than 1). For example, (3, 4, 5) is a primitive Pythagorean triple whereas (6, 8, 10) is not. A triangle whose sides form a Pythagorean triple is called a Pythagorean triangle, and is necessarily a right triangle.
In computational complexity theory, a decision problem is PSPACE-complete if it can be solved using an amount of memory that is polynomial in the input length and if every other problem that can be solved in polynomial space can be transformed to it in polynomial time. The problems that are PSPACE-complete can be thought of as the hardest problems in PSPACE, the class of decision problems solvable in polynomial space, because a solution to any one such problem could easily be used to solve any other problem in PSPACE.
Ramsey theory, named after the British mathematician and philosopher Frank P. Ramsey, is a branch of mathematics that focuses on the appearance of order in a substructure given a structure of a known size. Problems in Ramsey theory typically ask a question of the form: "how big must some structure be to guarantee that a particular property holds?" More specifically, Ron Graham described Ramsey theory as a "branch of combinatorics".

Ronald Lewis Graham was an American mathematician credited by the American Mathematical Society as "one of the principal architects of the rapid development worldwide of discrete mathematics in recent years". He was president of both the American Mathematical Society and the Mathematical Association of America, and his honors included the Leroy P. Steele Prize for lifetime achievement and election to the National Academy of Sciences.
Proof by exhaustion, also known as proof by cases, proof by case analysis, complete induction or the brute force method, is a method of mathematical proof in which the statement to be proved is split into a finite number of cases or sets of equivalent cases, and where each type of case is checked to see if the proposition in question holds. This is a method of direct proof. A proof by exhaustion typically contains two stages:
- A proof that the set of cases is exhaustive; i.e., that each instance of the statement to be proved matches the conditions of one of the cases.
- A proof of each of the cases.
7000 is the natural number following 6999 and preceding 7001.
A computer-assisted proof is a mathematical proof that has been at least partially generated by computer.
In computer science, in particular in knowledge representation and reasoning and metalogic, the area of automated reasoning is dedicated to understanding different aspects of reasoning. The study of automated reasoning helps produce computer programs that allow computers to reason completely, or nearly completely, automatically. Although automated reasoning is considered a sub-field of artificial intelligence, it also has connections with theoretical computer science and philosophy.
In computational complexity theory, the PCP theorem states that every decision problem in the NP complexity class has probabilistically checkable proofs of constant query complexity and logarithmic randomness complexity.
In computer science and mathematical logic, satisfiability modulo theories (SMT) is the problem of determining whether a mathematical formula is satisfiable. It generalizes the Boolean satisfiability problem (SAT) to more complex formulas involving real numbers, integers, and/or various data structures such as lists, arrays, bit vectors, and strings. The name is derived from the fact that these expressions are interpreted within ("modulo") a certain formal theory in first-order logic with equality. SMT solvers are tools which aim to solve the SMT problem for a practical subset of inputs. SMT solvers such as Z3 and cvc5 have been used as a building block for a wide range of applications across computer science, including in automated theorem proving, program analysis, program verification, and software testing.
In computer science and formal methods, a SAT solver is a computer program which aims to solve the Boolean satisfiability problem. On input a formula over Boolean variables, such as "(x or y) and (x or not y)", a SAT solver outputs whether the formula is satisfiable, meaning that there are possible values of x and y which make the formula true, or unsatisfiable, meaning that there are no such values of x and y. In this case, the formula is satisfiable when x is true, so the solver should return "satisfiable". Since the introduction of algorithms for SAT in the 1960s, modern SAT solvers have grown into complex software artifacts involving a large number of heuristics and program optimizations to work efficiently.
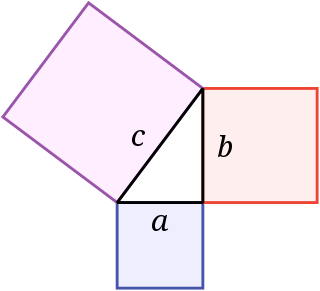
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
The Boolean Pythagorean triples problem is a problem from Ramsey theory about whether the positive integers can be colored red and blue so that no Pythagorean triples consist of all red or all blue members. The Boolean Pythagorean triples problem was solved by Marijn Heule, Oliver Kullmann and Victor W. Marek in May 2016 through a computer-assisted proof.
Pythagorean Triangles is a book on right triangles, the Pythagorean theorem, and Pythagorean triples. It was originally written in the Polish language by Wacław Sierpiński, and published in Warsaw in 1954. Indian mathematician Ambikeshwar Sharma translated it into English, with some added material from Sierpiński, and published it in the Scripta Mathematica Studies series of Yeshiva University in 1962. Dover Books republished the translation in a paperback edition in 2003. There is also a Russian translation of the 1954 edition.
Marienus Johannes Hendrikus Heule is a Dutch computer scientist at Carnegie Mellon University who studies SAT solvers. Heule has used these solvers to resolve mathematical conjectures such as the Boolean Pythagorean triples problem, Schur's theorem number 5, and Keller's conjecture in dimension seven.
References
- ↑ Lamb, Evelyn (2016-06-02). "Two-hundred-terabyte maths proof is largest ever". Nature. 534 (7605): 17–18. Bibcode:2016Natur.534...17L. doi: 10.1038/nature.2016.19990 . PMID 27251254.
- ↑ Heule, Marijn J. H.; Kullmann, Oliver; Marek, Victor W. (2016-01-01). "Solving and Verifying the Boolean Pythagorean Triples Problem via Cube-and-Conquer". Theory and Applications of Satisfiability Testing – SAT 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 9710. pp. 228–245. arXiv: 1605.00723 . doi:10.1007/978-3-319-40970-2_15. ISBN 978-3-319-40969-6. S2CID 7912943.