
Fort Capuzzo was a fort in the colony of Italian Libya, near the Libya–Egypt border, next to the Italian Frontier Wire. The Litoranea Balbo ran south from Bardia to Fort Capuzzo, 8 mi (13 km) inland, west of Sollum, then east across the Egyptian frontier to the port over the coastal escarpment. The fort was built during the Italian colonial repression of Senussi resistance in the Second Italo-Senussi War (1923–1931), as part of a barrier on the Libya–Egypt and Libya–Sudan borders.

The 7th Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army. It was formed as the Mobile Division (Egypt) on 27 September 1938, after increased tensions between Britain and the Axis powers. This was part of an effort to reinforce and maintain the British strategic presence in Egypt to defend the Suez Canal, which was seen as vital to the British Empire's interests. In February 1940, the formation was renamed as the 7th Armoured Division. During its early years, the jerboa was adopted as the mascot and divisional insignia giving rise to the nickname Desert Rats.

The 4th Infantry Division, also known as the Red Eagle Division, is an infantry division of the Indian Army. This division of the British Indian Army was formed in Egypt in 1939 during the Second World War. During the Second World War, it took part in campaigns in East Africa, Syria, North Africa and Italy. Post independence, the division is part of the I Corps and headquartered at Prayagraj.

Operation Compass was the first large British military operation of the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) during the Second World War. British metropolitan, Imperial and Commonwealth forces attacked the Italian and Libyan forces of the 10th Army in western Egypt and Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya, from December 1940 to February 1941.
The 1st South African Infantry Division was an infantry division of the army of the Union of South Africa. During World War II the division served in East Africa from 1940 to 1941 and in the Western Desert Campaign from 1941 to 1942. The division was disbanded on 1 January 1943, for conversion into what would become the 6th South African Armoured Division. The division was also briefly active after the war from 1 July 1948 to 1 November 1949.

Operation Battleaxe was a British Army offensive during the Second World War to raise the Siege of Tobruk and re-capture eastern Cyrenaica from German and Italian forces. It was the first time during the war that a significant German force fought on the defensive. The British lost over half of their tanks on the first day and only one of three attacks succeeded.

Operation Crusader was a military operation of the Western Desert campaign during World War II by the British Eighth Army against the Axis forces in North Africa commanded by Generalleutnant (Lieutenant-General) Erwin Rommel. The operation was intended to bypass Axis defences on the Egyptian–Libyan frontier, defeat the Axis armoured forces near Tobruk, raise the Siege of Tobruk and re-occupy Cyrenaica.
The 1st Army Tank Brigade was a formation of the British Army during the Second World War. A Tank Brigade was intended to support the Infantry and was mostly equipped with slow moving Infantry tanks, unlike an Armoured Brigade, which was equipped with faster cruiser tanks and later its own motorised infantry. Initially using infantry nomenclature for its smaller units, company and section and having 175 light and infantry tanks, it later adopted cavalry nomenclature of squadron and troop and later in the War grew to 240 tanks. Its designation was changed on 14 April 1940 to 1st Tank Brigade.

The Royal Tank Regiment (RTR) is the oldest tank unit in the world, being formed by the British Army in 1916 during the First World War. Today, it is the armoured regiment of the British Army's 12th Armoured Infantry Brigade. Formerly known as the Tank Corps and the Royal Tank Corps, it is part of the Royal Armoured Corps.

Operation Brevity was a limited offensive conducted in mid-May 1941, during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Conceived by the commander-in-chief of the British Middle East Command, General Archibald Wavell, Brevity was intended to be a rapid blow against weak Axis front-line forces in the Sollum–Capuzzo–Bardia area of the border between Egypt and Libya. Although the operation got off to a promising start, throwing the Axis high command into confusion, most of its early gains were lost to local counter-attacks, and with German reinforcements being rushed to the front the operation was called off after one day.

The Battle of Gazala, also the Gazala Offensive was fought near the village of Gazala during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, west of the port of Tobruk in Libya, from 26 May to 21 June 1942. Axis troops of the Panzerarmee Afrika consisting of German and Italian units fought the British Eighth Army composed mainly of British Commonwealth, Indian and Free French troops.
The 150th Infantry Brigade was an infantry formation of the British Army that saw active service in the Second World War. A 1st Line Territorial Army brigade, it was part of the 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division. It served in the Battle of France and was evacuated from Dunkirk. Later it served in the Middle East and was overrun and forced to surrender during the Battle of Gazala in the North African Campaign. For almost 72 hours during the battle the 150th Brigade and the 44th Royal Tank Regiment held out against Erwin Rommel's concentrated attacks, without any support. On 1 June the German Army finally forced their surrender. The brigade was not reformed.

The 23rd Armoured Brigade, originally formed as the 23rd Army Tank Brigade, was an armoured brigade of the British Army that saw service during the Second World War. The brigade was a 2nd Line Territorial Army (TA) formation. It was reorganised and renamed the 23rd Armoured Brigade, when it was assigned to the 8th Armoured Division, although it never operated under command of the division.

The 22nd Armoured Brigade was an armoured brigade of the British Army that saw service during and after the Second World War. The brigade was formed on the outbreak of war on 3 September 1939 from Territorial Army (TA) armoured regiments. It saw a considerable amount of action during the war, beginning with the Western Desert Campaign where it was engaged in Operation Crusader and at the Battles of Gazala, Mersa Matruh, First Alamein and Alam el Halfa. It then joined the 7th Armoured Division for the Second Battle of El Alamein. It remained part of 7th Armoured for the rest of the war, including the campaigns in Tunisia, Italy and North West Europe. It continued in the postwar TA until 1956. The brigade's identity was re-established in the Regular Army between 1981 and 1993.
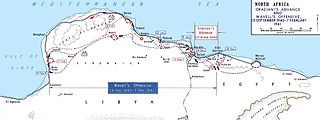
The Battle of Beda Fomm took place following the rapid British advance during Operation Compass. The Italian 10th Army was forced to evacuate Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya. In late January, the British learned that the Italians were retreating along the Litoranea Balbo from Benghazi. The 7th Armoured Division was dispatched to intercept the remnants of the 10th Army by moving through the desert, south of the Jebel Akhdar via Msus and Antelat as the 6th Australian Division pursued the Italians along the coast road, north of the jebel. The terrain was hard going for the British tanks and Combeforce, a flying column of wheeled vehicles, was sent ahead across the chord of the jebel.

The Frontier Wire was a 271 km (168 mi) obstacle in Italian Libya, along the length of the border of British-held Egypt, running from El Ramleh, in the Gulf of Sollum south to Jaghbub parallel to the 25th meridian east, the Libya–Egypt and Libya–Sudan borders. The frontier wire and its line of covering forts was built by the Italians during the Second Italo-Senussi War (1923–1931), as a defensive system to contain the Senussi population, who crossed from Egypt during their resistance against Italian colonisers.

The Italian invasion of Egypt was an offensive in the Second World War from Italian Libya, against British, Commonwealth and Free French in the neutral Kingdom of Egypt. The invasion by the Italian 10th Army ended border skirmishing on the frontier and began the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) proper. The Italian strategy was to advance from Libya along the Egyptian coast to seize the Suez Canal. After numerous delays, the scope of the offensive was reduced to an advance as far as Sidi Barrani and the defeat of any British forces in the area.

Combeforce or Combe Force was an ad hoc flying column of the British Army during the Second World War, commanded by Lieutenant-Colonel John Combe. It comprised parts of the 7th Armoured Division of the Western Desert Force. The rapid British advance during Operation Compass forced the Italian 10th Army to evacuate Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya. In late January, the British learned that the Italians were retreating from Benghazi, along the coast road. The 7th Armoured Division was dispatched to intercept the remnants of the 10th Army by moving through the desert, south of the Jebel Akhdar via Msus and Antelat, as the 6th Australian Division pursued the Italians along the coast road, north of the jebel.

The Battle of Sidi Barrani(10–11 December 1940) was the opening battle of Operation Compass, the first big British attack of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Sidi Barrani, on the Mediterranean coast in Egypt, had been occupied by the Italian 10th Army, during the Italian invasion of Egypt (9–16 September 1940) and was attacked by British, Commonwealth and imperial troops, who re-captured the port.












