
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver.
A signal generator is one of a class of electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.
A tetrode is a vacuum tube having four active electrodes. The four electrodes in order from the centre are: a thermionic cathode, first and second grids, and a plate. There are several varieties of tetrodes, the most common being the screen-grid tube and the beam tetrode. In screen-grid tubes and beam tetrodes, the first grid is the control grid and the second grid is the screen grid. In other tetrodes one of the grids is a control grid, while the other may have a variety of functions.

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.
This is an index of articles relating to electronics and electricity or natural electricity and things that run on electricity and things that use or conduct electricity.
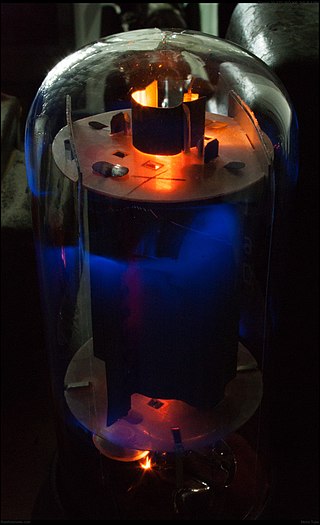
A valve amplifier or tube amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that uses vacuum tubes to increase the amplitude or power of a signal. Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers in the 1960s and 1970s. Valve amplifiers can be used for applications such as guitar amplifiers, satellite transponders such as DirecTV and GPS, high quality stereo amplifiers, military applications and very high power radio and UHF television transmitters.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.

In electrical engineering, a function generator is usually a piece of electronic test equipment or software used to generate different types of electrical waveforms over a wide range of frequencies. Some of the most common waveforms produced by the function generator are the sine wave, square wave, triangular wave and sawtooth shapes. These waveforms can be either repetitive or single-shot. Another feature included on many function generators is the ability to add a DC offset. Integrated circuits used to generate waveforms may also be described as function generator ICs.

An Alexanderson alternator is a rotating machine, developed by Ernst Alexanderson beginning in 1904, for the generation of high-frequency alternating current for use as a radio transmitter. It was one of the first devices capable of generating the continuous radio waves needed for transmission of amplitude modulated (AM) signals by radio. It was used from about 1910 in a few "superpower" longwave radiotelegraphy stations to transmit transoceanic message traffic by Morse code to similar stations all over the world.

A frequency changer or frequency converter is an electronic or electromechanical device that converts alternating current (AC) of one frequency to alternating current of another frequency. The device may also change the voltage, but if it does, that is incidental to its principal purpose, since voltage conversion of alternating current is much easier to achieve than frequency conversion.
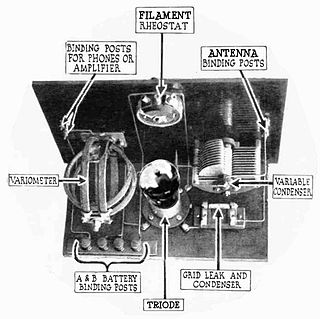
A grid leak detector is an electronic circuit that demodulates an amplitude modulated alternating current and amplifies the recovered modulating voltage. The circuit utilizes the non-linear cathode to control grid conduction characteristic and the amplification factor of a vacuum tube. Invented by Lee De Forest around 1912, it was used as the detector (demodulator) in the first vacuum tube radio receivers until the 1930s.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.
In electronics, motorboating is a type of low frequency parasitic oscillation that sometimes occurs in audio and radio equipment and often manifests itself as a sound similar to an idling motorboat engine, a "put-put-put", in audio output from speakers or earphones. It is a problem encountered particularly in radio transceivers and older vacuum tube audio systems, guitar amplifiers, PA systems and is caused by some type of unwanted feedback in the circuit. The amplifying devices in audio and radio equipment are vulnerable to a variety of feedback problems, which can cause distinctive noise in the output. The term motorboating is applied to oscillations whose frequency is below the range of hearing, from 1 to 10 hertz, so the individual oscillations are heard as pulses. Sometimes the oscillations can even be seen visually as the woofer cones in speakers slowly moving in and out.

A valve RF amplifier or tube amplifier (U.S.) is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.

In electronics, a plate detector is a vacuum tube circuit in which an amplifying tube having a control grid is operated in a non-linear region of its grid voltage versus plate current transfer characteristic, usually near plate current cutoff, to demodulate amplitude modulated carrier signal. This differs from the grid leak detector, which utilizes the non-linearity of the grid voltage versus grid current characteristic for demodulation. It also differs from the diode detector, which is a two-terminal device.
In electronics, power amplifier classes are letter symbols applied to different power amplifier types. The class gives a broad indication of an amplifier's characteristics and performance. The first three classes are related to the time period that the active amplifier device is passing current, expressed as a fraction of the period of a signal waveform applied to the input. This metric is known as conduction angle (θ). A class A amplifier is conducting through the entire period of the signal (θ=360°); Class B only for one-half the input period (θ=180°), class C for much less than half the input period (θ<180°). Class D amplifiers operate their output device in a switching manner; the fraction of the time that the device is conducting may be adjusted so a pulse-width modulation output can be obtained from the stage.














