Pyrimidine is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine. One of the three diazines, it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine and pyridazine.

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases.
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule. The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate.

An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism.
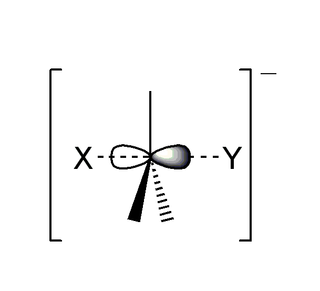
The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed in a concerted way, i.e., in one step. The name SN2 refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism: "SN" indicates that the reaction is a nucleophilic substitution, and "2" that it proceeds via a bi-molecular mechanism, which means both the reacting species are involved in the rate-determining step. The other major type of nucleophilic substitution is the SN1, but many other more specialized mechanisms describe substitution reactions.
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons.
A substitution reaction is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions are of prime importance in organic chemistry. Substitution reactions in organic chemistry are classified either as electrophilic or nucleophilic depending upon the reagent involved, whether a reactive intermediate involved in the reaction is a carbocation, a carbanion or a free radical, and whether the substrate is aliphatic or aromatic. Detailed understanding of a reaction type helps to predict the product outcome in a reaction. It also is helpful for optimizing a reaction with regard to variables such as temperature and choice of solvent.
The Hofmann rearrangement is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one less carbon atom. The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines.
An allylic rearrangement or allylic shift is an organic reaction in which the double bond in an allyl chemical compound shifts to the next carbon atom. It is encountered in nucleophilic substitution.

A nucleophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide, on an aromatic ring. Aromatic rings are usually nucleophilic, but some aromatic compounds do undergo nucleophilic substitution. Just as normally nucleophilic alkenes can be made to undergo conjugate substitution if they carry electron-withdrawing substituents, so normally nucleophilic aromatic rings also become electrophilic if they have the right substituents.
Nucleophilic acyl substitution describes a class of substitution reactions involving nucleophiles and acyl compounds. In this type of reaction, a nucleophile – such as an alcohol, amine, or enolate – displaces the leaving group of an acyl derivative – such as an acid halide, anhydride, or ester. The resulting product is a carbonyl-containing compound in which the nucleophile has taken the place of the leaving group present in the original acyl derivative. Because acyl derivatives react with a wide variety of nucleophiles, and because the product can depend on the particular type of acyl derivative and nucleophile involved, nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions can be used to synthesize a variety of different products.

Isatin, also known as tribulin, is an organic compound derived from indole with formula C8H5NO2. The compound was first obtained by Otto Linné Erdman and Auguste Laurent in 1840 as a product from the oxidation of indigo dye by nitric acid and chromic acids.

A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is a type of carbene demonstrating particular stability. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), for example diaminocarbenes with the general formula (R2N)2C:, where the four R moieties are typically alkyl and aryl groups. The groups can be linked to give heterocyclic carbenes, such as those derived from imidazole, imidazoline, thiazole or triazole.
In organic chemistry, umpolung or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule.
Pyrylium is a cation with formula C5H5O+, consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aromatic character. In particular, because of the positive charge, the oxygen atom is trivalent. Pyrilium is a mono-cyclic and heterocyclic compound, one of the oxonium ions.
The Wallach rearrangement, also named Wallach transformation, is a name reaction in the organic chemistry. It is named after Otto Wallach, who discovered this reaction in 1880. In general it is a strong acid-promoted conversion of azoxybenzenes into hydroxyazobenzenes.
The Chichibabin reaction is a method for producing 2-aminopyridine derivatives by the reaction of pyridine with sodium amide. It was reported by Aleksei Chichibabin in 1914. The following is the overall form of the general reaction:
The Stieglitz rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry which is named after the American chemist Julius Stieglitz (1867–1937) and was first investigated by him and Paul Nicholas Leech in 1913. It describes the 1,2-rearrangement of trityl amine derivatives to triaryl imines. It is comparable to a Beckmann rearrangement which also involves a substitution at a nitrogen atom through a carbon to nitrogen shift. As an example, triaryl hydroxylamines can undergo a Stieglitz rearrangement by dehydration and the shift of a phenyl group after activation with phosphorus pentachloride to yield the respective triaryl imine, a Schiff base.
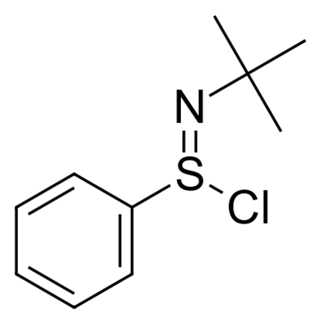
N-tert-Butylbenzenesulfinimidoyl chloride is a useful oxidant for organic synthesis reactions. It is a good electrophile, and the sulfimide S=N bond can be attacked by nucleophiles, such as alkoxides, enolates, and amide ions. The nitrogen atom in the resulting intermediate is basic, and can abstract an α-hydrogen to create a new double bond.










