
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration, is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur but these do not represent a mental illness.

Complement component 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C6 gene.

Neurotrophin-4 (NT-4), also known as neurotrophin-5 (NT-5), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTF4 gene. It is a neurotrophic factor that signals predominantly through the TrkB receptor tyrosine kinase.

Factor H is a member of the regulators of complement activation family and is a complement control protein. It is a large, soluble glycoprotein that circulates in human plasma. Its principal function is to regulate the alternative pathway of the complement system, ensuring that the complement system is directed towards pathogens or other dangerous material and does not damage host tissue. Factor H regulates complement activation on self cells and surfaces by possessing both cofactor activity for the Factor I mediated C3b cleavage, and decay accelerating activity against the alternative pathway C3-convertase, C3bBb. Factor H exerts its protective action on self cells and self surfaces but not on the surfaces of bacteria or viruses. This is thought to be the result of Factor H having the ability to adopt conformations with lower or higher activities as a cofactor for C3 cleavage or decay accelerating activity. The lower activity conformation is the predominant form in solution and is sufficient to control fluid phase amplification. The more active conformation is thought to be induced when Factor H binds to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and or sialic acids that are generally present on host cells but not, normally, on pathogen surfaces ensuring that self surfaces are protected whilst complement proceeds unabated on foreign surfaces.
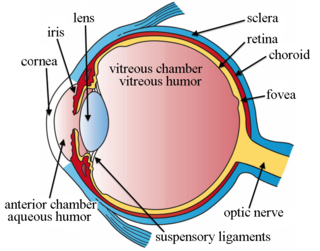
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is the creation of new blood vessels in the choroid layer of the eye. Choroidal neovascularization is a common cause of neovascular degenerative maculopathy commonly exacerbated by extreme myopia, malignant myopic degeneration, or age-related developments.

Peripherin-2 is a protein, that in humans is encoded by the PRPH2 gene. Peripherin-2 is found in the rod and cone cells of the retina of the eye. Defects in this protein result in one form of retinitis pigmentosa, an incurable blindness.

Transformer-2 protein homolog beta, also known as TRA2B previously known as splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 10 (SFRS10), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRA2B gene.

EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFEMP1 gene.
Guanylyl cyclase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCA1A gene.

Cyclic nucleotide gated channel beta 3, also known as CNGB3, is a human gene encoding an ion channel protein.

Tubby-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TULP1 gene.

Bardet–Biedl syndrome 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BBS1 gene. BBS1 is part of the BBSome complex, which required for ciliogenesis. Mutations in this gene have been observed in patients with the major form of Bardet–Biedl syndrome.

Rod outer segment membrane protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ROM1 gene.

Visual system homeobox 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VSX1 gene.

Hemicentin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMCN1 gene.

Fascin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSCN2 gene.

Norrin, also known as Norrie disease protein or X-linked exudative vitreoretinopathy 2 protein (EVR2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NDP gene. Mutations in the NDP gene are associated with the Norrie disease.

Complement factor H-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR2 gene.

Membrane frizzled-related protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MFRP gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR4 gene.

















