| ATP:guanido phosphotransferase catalytic domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
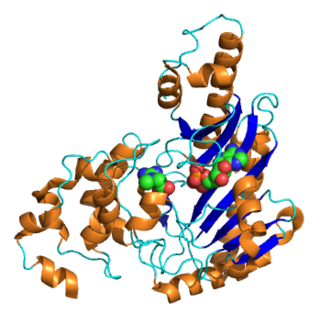
 structure of arginine kinase c271a mutant | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | ATP-gua_Ptrans | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00217 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0286 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022414 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00103 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1crk / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| ATP:guanido phosphotransferase N-terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
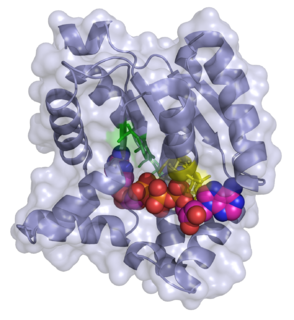
 transition state structure of an arginine kinase mutant | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | ATP-gua_PtransN | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02807 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR022413 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00103 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1crk / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase family is a family of structurally and functionally related enzymes, [1] [2] that reversibly catalyse the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphagens. The enzymes belonging to this family include:
- Glycocyamine kinase (EC 2.7.3.1), which catalyses the transfer of phosphate from ATP to guanidoacetate.
- Arginine kinase (EC 2.7.3.3), which catalyses the transfer of phosphate from ATP to arginine.
- Taurocyamine kinase (EC 2.7.3.4), an annelid-specific enzyme that catalyses the transfer of phosphate from ATP to taurocyamine.
- Lombricine kinase (EC 2.7.3.5), an annelid-specific enzyme that catalyses the transfer of phosphate from ATP to lombricine.
- Smc74, a cercaria-specific enzyme from Schistosoma mansoni. [1]
- Creatine kinase (EC 2.7.3.2) (CK), [3] [4] which catalyses the reversible transfer of high energy phosphate from ATP to creatine, generating phosphocreatine and ADP.
Creatine kinase plays an important role in energy metabolism of vertebrates. There are at least four different, but very closely related, forms of CK. Two isozymes, M (muscle) and B (brain), are cytosolic, while the other two are mitochondrial. In sea urchins there is a flagellar isozyme, which consists of the triplication of a CK-domain. A cysteine residue is implicated in the catalytic activity of these enzymes and the region around this active site residue is highly conserved.
ATP:guanido phosphotransferases contain a C-terminal catalytic domain which consists of a duplication where the common core consists of two beta-alpha-beta2-alpha repeats. [5] The substrate binding site is located in the cleft between N and C-terminal domains, but most of the catalytic residues are found in the larger C-terminal domain. [5] They also contain an N-terminal domain which has an all-alpha fold consisting of an irregular array of 6 short helices. [5]