
Atlantis is a fictional island mentioned in Plato's works Timaeus and Critias as part of an allegory on the hubris of nations. In the story, Atlantis is described as a naval empire that ruled all Western parts of the known world, making it the literary counter-image of the Achaemenid Empire. After an ill-fated attempt to conquer "Ancient Athens," Atlantis falls out of favor with the deities and submerges into the Atlantic Ocean. Since Plato describes Athens as resembling his ideal state in the Republic, the Atlantis story is meant to bear witness to the superiority of his concept of a state.

The Hollow Earth is a concept proposing that the planet Earth is entirely hollow or contains a substantial interior space. Notably suggested by Edmond Halley in the late 17th century, the notion was disproven, first tentatively by Pierre Bouguer in 1740, then definitively by Charles Hutton in his Schiehallion experiment around 1774.

Richard Sharpe Shaver was an American writer and artist who achieved notoriety in the years following World War II as the author of controversial stories that were printed in science fiction magazines. In Shaver's story, he claimed that he had had personal experience of a sinister ancient civilization that harbored fantastic technology in caverns under the earth. The controversy stemmed from the claim by Shaver, and his editor and publisher Ray Palmer, that Shaver's writings, while presented in the guise of fiction, were fundamentally true. Shaver's stories were promoted by Ray Palmer as "The Shaver Mystery".
Lemuria, or Limuria, was a continent proposed in 1864 by zoologist Philip Sclater, theorized to have sunk beneath the Indian Ocean, later appropriated by occultists in supposed accounts of human origins. The theory was discredited with the discovery of plate tectonics and continental drift in the 20th century.

Franz Bardon was a Czech occultist and student and teacher of Hermetics.

Vril: The Power of the Coming Race, originally published as The Coming Race, is a novel by Edward Bulwer-Lytton, published anonymously in 1871.

The Secret Doctrine, the Synthesis of Science, Religion and Philosophy, is a pseudoscientific esoteric book as two volumes in 1888 written by Helena Blavatsky. The first volume is named Cosmogenesis, the second Anthropogenesis. It was an influential example of the revival of interest in esoteric and occult ideas in the modern age, in particular because of its claim to reconcile ancient eastern wisdom with modern science. Proponents widely claim the literature contains clues as to how the nature of prayer was 'covered' and expunged from common wisdom, except for those with a keen eye.

Root races are concepts in the esoteric cosmology of Theosophy. As described in Helena Petrovna Blavatsky's book The Secret Doctrine (1888), these races correspond to stages of human evolution, and existed mainly on now-lost continents. Blavatsky's model was developed by later theosophists, most notably William Scott-Elliot in The Story of Atlantis (1896) and The Lost Lemuria (1904). Annie Besant further developed the model in Man: Whence, How and Whither (1913). Both Besant and Scott-Elliot relied on information from Charles Webster Leadbeater obtained by "astral clairvoyance". Further elaboration was provided by Rudolf Steiner in Atlantis and Lemuria (1904). Rudolf Steiner, and subsequent theosophist authors, have called the time periods associated with these races Epochs.

Namora is a character appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by artists Ken Bald and Syd Shores, the character first appeared in Marvel Mystery Comics #82. Namora is from Atlantis and is the daughter of an Atlantean father and a human mother. She is the cousin of the antihero Namor the Sub-Mariner.

The legendary island of Atlantis has often been depicted in literature, television shows, films and works of popular culture.

Mera is a superheroine appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. Created by Jack Miller and Nick Cardy, the character first appeared in Aquaman #11.
Aquaman has made several appearances in numerous adaptations since his comic book debut in 1941. The character has also been referenced beyond the scope of traditional comics entertainment.

The Ragged Edge of Science is a science book by L. Sprague de Camp, illustrated by Don Simpson. It was first published by Owlswick Press in 1980.
Master Jesus is the theosophical concept of Jesus in theosophy and the Ascended Master Teachings.

Esoteric Nazism, also known as Esoteric Fascism or Esoteric Hitlerism, refers to a range of mystical interpretations and adaptations of Nazism. After the Second World War, esoteric interpretations of the Third Reich were adapted into new religious movements of white nationalism and neo-Nazism. They included beliefs in finding a mythical Hyperborea.

California's Mount Shasta has been the subject of a large number of myths and legends. In particular, it is often said there is a secret city beneath its peaks. In some stories, the city is no longer inhabited, while in others, it is inhabited by a technologically advanced society of human beings or mythical creatures.
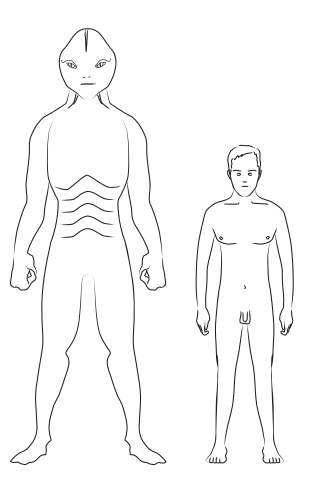
Reptilians are supposed reptilian humanoids, which play a prominent role in fantasy, science fiction, ufology, and conspiracy theories. The idea of reptilians was popularised by David Icke, an anti-semitic conspiracy theorist who claims shapeshifting reptilian aliens control Earth by taking on human form and gaining political power to manipulate human societies. Icke has stated on multiple occasions that many world leaders are, or are possessed by, so-called reptilians.

Man: Whence, How and Whither, A Record of Clairvoyant Investigation, published in 1913, is a theosophical book compiled by the second president of the Theosophical Society (TS) - Adyar, Annie Besant, and by a TS member, Charles W. Leadbeater. The book is a study on early times on planetary chains, beginnings of early root races, early civilizations and empires, and past lives of men.

Theosophy is a religious and philosophical system established in the United States in the late 19th century. Founded primarily by Russian mystic and spiritualist Helena Blavatsky, and based largely on her writings, it draws heavily from both older European philosophies such as Gnosticism and Neoplatonism and Indian religions such as Hinduism and Buddhism. Although many adherents maintain that Theosophy is not a religion, it is variably categorized by religious scholars as both a new religious movement and a form occultism from within Western esotericism.

Esoteric Buddhism is a book originally published in 1883 in London; it was compiled by a member of the Theosophical Society, A. P. Sinnett. It was one of the first books written for the purpose of explaining theosophy to the general public, and was "made up of the author's correspondence with an Indian mystic." This is the most significant theosophical work of the author. According to Goodrick-Clarke, it "disseminated the basic teachings of Theosophy in its new Asian cast."

















