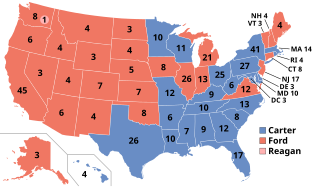
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1976. The Democratic ticket of former Georgia governor Jimmy Carter and Minnesota senator Walter Mondale narrowly defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent president Gerald Ford and Kansas senator Bob Dole. This was the first presidential election since 1932 in which the incumbent was defeated, as well as the only Democratic victory of the six presidential elections between 1968 and 1988 and the last time the Democratic ticket would win until 1992. Carter was the first non-incumbent politician representing a Southern state to be elected president since Zachary Taylor in 1848.

The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon which began in 1972 and ultimately led to Nixon's resignation in 1974. It revolved around members of a group associated with Nixon's 1972 re-election campaign breaking into and planting listening devices in the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate Office Building in Washington, D.C., on June 17, 1972, and Nixon's later attempts to hide his administration's involvement.

Harry Robbins "Bob" Haldeman was an American political aide and businessman, best known for his service as White House Chief of Staff to President Richard Nixon and his consequent involvement in the Watergate scandal.

The "Saturday Night Massacre" was a series of resignations over the dismissal of special prosecutor Archibald Cox that took place in the United States Department of Justice during the Watergate scandal in 1973. The events followed the refusal by Cox to drop a subpoena for the Nixon White House tapes at President Richard Nixon's request.

Gerald Ford's tenure as the 38th president of the United States began on August 9, 1974, upon the resignation of President Richard Nixon, and ended on January 20, 1977. Ford, a Republican from Michigan, had been appointed vice president on December 6, 1973, following the resignation of Spiro Agnew from that office. Ford was the only person to serve as president without being elected to either the presidency or the vice presidency. His presidency ended following his narrow defeat in the 1976 presidential election to Democrat Jimmy Carter, after a period of 895 days in office. His 895 day presidency remains the shortest of all U.S. presidents who did not die in office.

Alexander Porter Butterfield is a retired United States Air Force officer, public official, and businessman. He served as the deputy assistant to President Richard Nixon from 1969 to 1973. He revealed the White House taping system's existence on July 13, 1973, during the Watergate investigation but had no other involvement in the scandal. From 1973 to 1975, he served as administrator of the Federal Aviation Administration.

The Watergate scandal refers to the burglary and illegal wiretapping of the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee, in the Watergate complex by members of President Richard Nixon's re-election campaign, and the subsequent cover-up of the break-in resulting in Nixon's resignation on August 9, 1974, as well as other abuses of power by the Nixon White House that were discovered during the course of the scandal.

Jerald Franklin terHorst was an American journalist who served as the 14th White House Press Secretary during the first month of Gerald Ford's presidency. His resignation in protest of Ford's unconditional pardon of former president Richard Nixon is still regarded as a rare act of conscience by a high-ranking public official.

Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. was the 38th president of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977. A member of the Republican Party, Ford assumed the presidency after the resignation of President Richard Nixon, under whom he had served as the 40th vice president from 1973 to 1974 following Spiro Agnew's resignation. Prior to that, he served as a member of the U.S. House of Representatives from 1949 to 1973.

Shadow: Five Presidents and the Legacy of Watergate is a 1999 book by Washington Post journalist Bob Woodward, written with a narrative voice while utilizing firsthand interviews and news reports for its historical basis. For the 608-page book, Woodward used extensive notes and also interviewed President Ford, President Bush's chief of staff, James Baker, and other people of focus.

Richard Nixon's tenure as the 37th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1969, and ended when he resigned on August 9, 1974, in the face of almost certain impeachment and removal from office, the only U.S. president ever to do so. He was succeeded by Gerald Ford, whom he had appointed vice president after Spiro Agnew became embroiled in a separate corruption scandal and was forced to resign. Nixon, a prominent member of the Republican Party from California who previously served as vice president for two terms under president Dwight D. Eisenhower from 1953 to 1961, took office following his narrow victory over Democratic incumbent vice president Hubert Humphrey and American Independent Party nominee George Wallace in the 1968 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1972 presidential election, he defeated Democratic nominee George McGovern, to win re-election in a landslide. Although he had built his reputation as a very active Republican campaigner, Nixon downplayed partisanship in his 1972 landslide re-election.
The animated science fiction show Futurama presents a satirical look at politics and current affairs in a number of its episodes. Series creator Matt Groening intended from the outset that Futurama would lampoon not only the conventions of science fiction, but elements of present-day life, serving as a form of political and social satire.

The inauguration of Gerald Ford as the 38th president of the United States was held on Friday, August 9, 1974, in the East Room of the White House in Washington, D.C., after President Richard Nixon resigned due to the Watergate scandal. The inauguration – the last non-scheduled, extraordinary inauguration to take place in the 20th century – marked the commencement of Gerald Ford's only term as president. Chief Justice Warren E. Burger administered the oath of office. The Bible upon which Ford recited the oath was held by his wife, Betty Ford, open to Proverbs 3:5–6. Ford was the ninth vice president to succeed to the presidency intra-term, and he remains the most recent to do so, as of 2024.
Nixon v. General Services Administration, 433 U.S 425 (1977), is a landmark court case concerning the principle of presidential privilege and whether the public is allowed to view a President's “confidential documents”. The Presidential Recordings and Materials Preservation Act, signed into law by President Gerald Ford in 1974, ordered that the Administrator of the General Services Administration obtain President Richard Nixon’s presidential papers and tape recordings. In addition, the Act further ordered that government archivists seize these materials. These archivists would preserve the material deemed historic and return to former President Nixon the materials deemed private. Furthermore, this Act stated that material that was preserved could be used in judicial hearings and proceedings. Immediately after this Act was enacted, Richard Nixon filed a lawsuit in a federal district court claiming that the Act violated the principle of separation of powers, the principle of presidential privilege, Nixon's personal privacy, his First Amendment right of association, and further asserted that it amounted to a constitutionally prohibited Bill of Attainder.

Geoffrey Carroll Shepard is an American lawyer, author and lecturer.

The impeachment process against Richard Nixon was initiated by the United States House of Representatives on October 30, 1973, during the course of the Watergate scandal, when multiple resolutions calling for the impeachment of President Richard Nixon were introduced immediately following the series of high-level resignations and firings widely called the "Saturday Night Massacre". The House Committee on the Judiciary soon began an official investigation of the president's role in Watergate, and, in May 1974, commenced formal hearings on whether sufficient grounds existed to impeach Nixon of high crimes and misdemeanors under Article II, Section 4, of the United States Constitution. This investigation was undertaken one year after the United States Senate established the Select Committee on Presidential Campaign Activities to investigate the break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate office complex during the 1972 presidential election, and the Republican Nixon administration's attempted cover-up of its involvement; during those hearings the scope of the scandal became apparent and the existence of the Nixon White House tapes was revealed.

The pardon of Richard Nixon was a presidential proclamation issued by President of the United States Gerald Ford on September 8, 1974, granting a full and unconditional pardon to Richard Nixon, his predecessor, for any crimes that he might have committed against the United States as president. In particular, the pardon covered Nixon's actions during the Watergate scandal. In a televised broadcast to the nation, Ford, who had succeeded to the presidency upon Nixon's resignation, explained that he felt the pardon was in the best interests of the country and that the Nixon family's situation was "a tragedy in which we all have played a part. It could go on and on and on, or someone must write the end to it. I have concluded that only I can do that, and if I can, I must."
Federal pardons in the United States are granted only by the U.S. president, pursuant to their authority under the U.S. Constitution to grant "reprieves and pardons for offenses against the United States". Pardons extend to all federal criminal offenses, except in cases of impeachment, and entail various forms of clemency, including commuting or postponing a sentence, remitting a fine or restitution, delaying the imposition of a punishment, and providing amnesty to an entire group or class of individuals. The pardon power extends to cases involving courts-martial against members of the United States military, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, Coast Guard, and Space Force.
Richard Nixon, the 37th President of the United States, has inspired or been portrayed in numerous cultural works.
Henry Swartley "Hank" Ruth Jr., was an American lawyer who served as the third special prosecutor during the Watergate Scandal. He was appointed after the October 1974 resignation of Leon Jaworski, and served until his own resignation in October 1975. He was succeeded by Charles F. Ruff.












