
Francis Walker was an English entomologist. He was born in Southgate, London, on 31 July 1809 and died at Wanstead, England on 5 October 1874. He was one of the most prolific authors in entomology, and stirred controversy during his later life as his publications resulted in a huge number of junior synonyms.
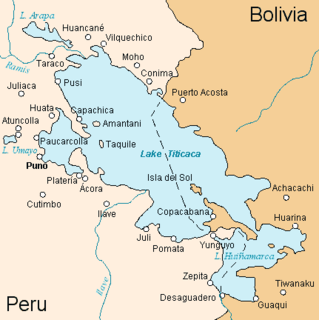
The Chiripa culture existed between the Initial Period/Early Horizon, from 1400 to 850 BCE along the southern shore of Lake Titicaca in Bolivia.

Acanthodica is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by William Schaus in 1894.

Araeopteron is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by George Hampson in 1893.

Acanthodica cabra is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Paul Dognin in 1894. It is found in Ecuador.

Acanthodica drucei is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Paul Dognin in 1889. It is found in Ecuador.

Acanthodica emittens is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found on Jamaica.

Acanthodica fosteri is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in South America, including Paraguay, French Guiana and Costa Rica.

Acanthodica hages is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Colombia.

Acanthodica lignaris is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in South America, including Peru and Brazil.
Acanthodica daunus is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Mexico south to Costa Rica.
Acanthodica fassli is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Bolivia.
Acanthodica penicillum is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Central and South America, including Costa Rica, Guatemala and Brazil.
Acanthodica frigida is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by E. Dukinfield Jones in 1921. It is found in Brazil.
Acanthodica sinuilinea is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Peru.
Acanthodica splendens is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in Panama and Ecuador.

The Erebinae are a subfamily of moths in the family Erebidae erected by William Elford Leach in 1815. Erebine moths are found on all continents except Antarctica, but reach their greatest diversity in the tropics. While the exact number of species belonging to the Erebinae is not known, the subfamily is estimated to include around 10,000 species. Some well-known Erebinae include underwing moths (Catocala) and witch moths (Thermesiini). Many of the species in the subfamily have medium to large wingspans, up to nearly 30 cm in the white witch moth, which has the widest wingspan of all Lepidoptera. Erebine caterpillars feed on a broad range of plants; many species feed on grasses and legumes, and a few are pests of castor bean, sugarcane, rice, as well as pistachios and blackberries.
Koyaga senex is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1881. It is found in Japan.
Amerila leucoptera is a species of moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by George Hampson in 1901. It is found in Benin, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Uganda and Zambia.

Mythimna prominens is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found on Malta and in Greece, France, the Iberian Peninsula and Italy. Outside of Europe, it is found in Morocco, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Réunion, Madagascar, Nigeria, South Africa and Zimbabwe.






