
Acontias is a genus of limbless skinks, the lance skinks, in the African subfamily Acontinae. Most are small animals, but the largest member of the genus is Acontias plumbeus at approximately 40 cm (16 in) snout-vent length. All members of this genus are live-bearing sandswimmers, with fused eyelids. A recent review moved species that were formerly placed in the genera Typhlosaurus, Acontophiops, and Microacontias into this genus, as together these form a single branch in the tree of life. This new concept of Acontias is a sister lineage to Typhlosaurus, and these two genera are the only genera within the subfamily Acontinae.

Typhlosaurus is a genus of African lizards, one of a number of genera of limbless lizards in the skink family (Scincidae). This group was recently revised with most species formerly attributed to Typhlosaurus now placed in Acontias. The current definition of Typhlosaurus includes five attenuate body legless lizards from southwestern Africa. This is the sister genus to Acontias, which together form the well supported Afrotropical subfamily Acontinae.

Acontias breviceps, the shorthead lance skink or shortheaded legless skink, is a species of viviparous, legless, fossorial lizards occurring along the southern and eastern sections of the Great Escarpment in South Africa. It may grow up to 10 cm long.

Acontias percivali, also known commonly as Percival's lance skink, Percival's legless lizard, and the Tanzanian legless lizard, is a species of small, legless (snake-like) lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Africa.

The woodbush legless skink is a species of legless skink. It is found in the Wolkberg mountains of Limpopo Province, South Africa. Females of the species give birth to live young. This lizard species was formerly placed in a monotypic genus as Acontophiops lineatus. Morphologically the genus shows similarities to Acontias cregoi and a recent review placed both of these within the genus Acontias, which, as Acontias lineatus was already occupied, required a new name for this species.

Trachylepis is a skink genus in the subfamily Mabuyinae found mainly in Africa. Its members were formerly included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya, and for some time in Euprepis. As defined today, Trachylepis contains the clade of Afro-Malagasy mabuyas. The genus also contains a species from the Brazilian island of Fernando de Noronha, T. atlantica, and may occur in mainland South America with Trachylepis tschudii and Trachylepis maculata, both poorly known and enigmatic. The ancestors of T. atlantica are believed to have rafted across the Atlantic from Africa during the last 9 million years.

The Noronha skink is a species of skink from the island of Fernando de Noronha off northeastern Brazil. It is covered with dark and light spots on the upperparts and is usually about 7 to 10 cm in length. The tail is long and muscular, but breaks off easily. Very common throughout Fernando de Noronha, it is an opportunistic feeder, eating both insects and plant material, including nectar from the Erythrina velutina tree, as well as other material ranging from cookie crumbs to eggs of its own species. Introduced predators such as feral cats prey on it and several parasitic worms infect it.

Acontias gracilicauda, the slendertail lance skink or thin-tailed legless skink, is a species of skink. It is found in the Republic of South Africa and Lesotho. Acontias namaquensis was formerly included in this species as a subspecies, but is now recognized as a distinct species.

Boaedon is a genus of African lamprophiids consisting of the "brown" house snakes. The genus was originally described by Duméril but the species contained were reclassified as Lamprophis by Fitzinger in 1843, this taxonomy remained widely accepted until November 2010 when a phylogenetic study was published by C.M.R Kelly et al. who resurrected the Boaedon clade. Although commonly regarded as belonging to the Colubridae, primary literature usually lists them and related species as belonging to the family Lamprophiidae within the superfamily Elapoidea, which includes the venomous cobras and mambas.
Trachylepis bayonii, also known commonly as Bayão's skink, Bayon's mabuya, and Bayon's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Africa. There are two subspecies.
Trachylepis ozorii is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the island of Annobón in Equatorial Guinea.
Pedioplanis haackei is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is endemic to Angola.
Pedioplanis huntleyi is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is endemic to Angola.
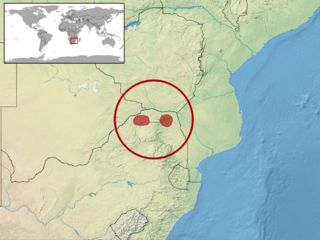
Acontias richardi, Richard's legless skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to South Africa.

Trachylepis bocagii, also known commonly as Bocage's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southern Africa.
Trachylepis raymondlaurenti, also known commonly as Laurent's long-tailed skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Africa.
Feylinia currori, also known commonly as Curror's skink, the western forest feylinia, and the western forest limbless skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is indigenous to Central Africa.
Feylinia elegans, the elegant feylinia, is an African lizard in the family Scincidae commonly known as skinks. It is found in Equatorial Guinea, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, northernmost Angola, and Central African Republic.
Sepsina copei, also known commonly as Cope's reduced-limb skink or the sepsina skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Angola.
Typhlacontias punctatissimus, also known commonly as the dotted blind dart skink, the speckled burrowing skink, and the speckled western burrowing skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southern Africa. Three subspecies are recognized.











