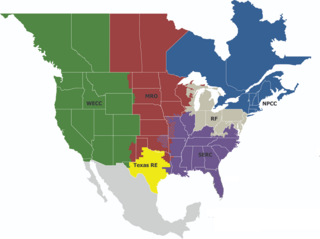
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) is a nonprofit corporation based in Atlanta, Georgia, and formed on March 28, 2006, as the successor to the North American Electric Reliability Council. The original NERC was formed on June 1, 1968, by the electric utility industry to promote the reliability and adequacy of bulk power transmission in the electric utility systems of North America. NERC's mission states that it "is to assure the effective and efficient reduction of risks to the reliability and security of the grid".
SCADA is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces for high-level supervision of machines and processes. It also covers sensors and other devices, such as programmable logic controllers, which interface with process plant or machinery.

Automatic meter reading (AMR) is the technology of automatically collecting consumption, diagnostic, and status data from water meter or energy metering devices and transferring that data to a central database for billing, troubleshooting, and analyzing. This technology mainly saves utility providers the expense of periodic trips to each physical location to read a meter. Another advantage is that billing can be based on near real-time consumption rather than on estimates based on past or predicted consumption. This timely information coupled with analysis can help both utility providers and customers better control the use and production of electric energy, gas usage, or water consumption.
The East–West Interconnector is a 500 MW high-voltage direct current submarine and subsoil power cable which connects the Irish and British electricity markets. The project was developed by the Irish national grid operator EirGrid.

The Center for Neighborhood Technology (CNT) is a non-profit organization, headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, which is committed to sustainable development and urban communities.

A smart meter is an electronic device that records information—such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor—and communicates the information to the consumer and electricity suppliers. Such an advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) differs from automatic meter reading (AMR) in that it enables two-way communication between the meter and the supplier.
Alinta Limited was an Australian energy infrastructure company. It has grown from a small, Western Australia-based gas distributor and retailer to the largest energy infrastructure company in Australia. It was bought in 2007 by a consortium including Singapore Power and various parties which include the now defunct Babcock & Brown funds.
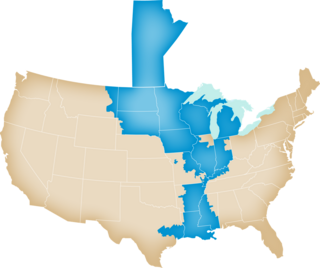
The Midcontinent Independent System Operator, Inc., formerly named Midwest Independent Transmission System Operator, Inc. (MISO) is an Independent System Operator (ISO) and Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) providing open-access transmission service and monitoring the high-voltage transmission system in the Midwest United States and Manitoba, Canada and a southern United States region which includes much of Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. MISO also operates one of the world's largest real-time energy markets. The 15 states covered by MISO are: Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, and Wisconsin.

Jon B. Wellinghoff is an American attorney who served as the chairman of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) from 2009 to 2013. The FERC is a U.S. government agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. The FERC also reviews proposals to build liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals and interstate natural gas pipelines and licenses hydropower projects.

The smart grid is an enhancement of the 20th century electrical grid, using two-way communications and distributed so-called intelligent devices. Two-way flows of electricity and information could improve the delivery network. Research is mainly focused on three systems of a smart grid – the infrastructure system, the management system, and the protection system. Electronic power conditioning and control of the production and distribution of electricity are important aspects of the smart grid.
Dynamic Infrastructure is an information technology concept related to the design of data centers, whereby the underlying hardware and software can respond dynamically and more efficiently to changing levels of demand. In other words, data center assets such as storage and processing power can be provisioned to meet surges in user's needs. The concept has also been referred to as Infrastructure 2.0 and Next Generation Data Center.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power long distances, and lastly electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids.
The Office of Electricity (OE) is a program office within the United States Department of Energy. The mission of OE is to work "closely with [...] private and public partners" and "lead the Department’s efforts to ensure that the Nation’s most critical energy infrastructure is secure and resilient." It does this through research and development of new technologies and overseeing the Federal and state electricity policies and programs for planning and market operations.

The North Seas Energy Cooperation (NSEC), officially the Political Declaration on energy cooperation between the North Seas Countries, is a collaboration between EU member-states and Norway to create an integrated offshore energy grid which links wind farms and other renewable energy sources across the northern seas of Europe. First proposed as the North Seas Countries Offshore Grid Initiative (NSCOGI), it is one of several European super grid schemes.
Smart grid policy in the United States refers to legislation and other governmental orders influencing the development of smart grids in the United States.
The National Infrastructure Advisory Council (NIAC) is a United States government advisory council, which advises the President of the United States on the security of information systems in banking, finance, transportation, energy, manufacturing, and emergency government services. The George W. Bush Administration's executive order 13231 of October 16, 2001 created the NIAC, and its functioning was last extended until September 30, 2023 by executive order 14048 of the Biden Administration.

Dr. Paul N. Stockton is the President of Paul N Stockton LLC, a strategic advisory firm in Santa Fe, NM. From 2009 to 2013, Dr. Stockton served as Assistant Secretary of Defense for Homeland Defense and Americas' Security Affairs, where he helped lead the department's response to Hurricane Sandy. He was responsible for Defense Critical Infrastructure Protection, Western Hemisphere security policy, domestic crisis management, continuity of operations planning, and a range of other responsibilities. While Assistant Secretary, Dr. Stockton also served as executive director of the Council of Governors. After serving as Assistant Secretary, Dr. Stockton was the managing director of Sonecon LLC, an advisory firm in Washington, DC, from 2013 to 2020.
The UCLA Smart Grid Energy Research Center (SMERC), located on the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) campus, is an organization focused on developing the next generation of technologies and innovation for Smart Grid. SMERC partners with government agencies, technology providers, Department of Energy (DOE) research labs, universities, utilities, policymakers, electric vehicle manufacturers, and appliance manufacturers. These partnerships provide SMERC with diverse capabilities and exceptional, mature leadership.
A cyberattack is any offensive maneuver that targets computer information systems, computer networks, infrastructures, personal computer devices, or smartphones. An attacker is a person or process that attempts to access data, functions, or other restricted areas of the system without authorization, potentially with malicious intent. Depending on the context, cyberattacks can be part of cyber warfare or cyberterrorism. A cyberattack can be employed by sovereign states, individuals, groups, societies or organizations and it may originate from an anonymous source. A product that facilitates a cyberattack is sometimes called a cyber weapon. Cyberattacks have increased over the last few years. A well-known example of a cyberattack is a distributed denial of service attack (DDoS).
Electric grid security in the US refer to the activities that utilities, regulators, and other stakeholders play in securing the national electricity grid. The American electrical grid is going through one of the largest changes in its history, which is the move to smart grid technology. The smart grid allows energy customers and energy providers to more efficiently manage and generate electricity. Similar to other new technologies, the smart grid also introduces new concerns about security.









