Related Research Articles
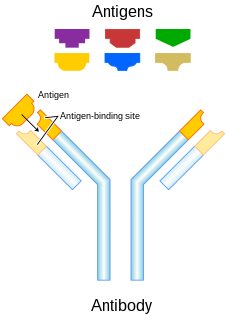
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure, such as may be present on the outside of a pathogen, that can be bound by an antigen-specific antibody or B-cell antigen receptor. The presence of antigens in the body normally triggers an immune response. The Ag abbreviation stands for an antibody generator.

The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism against disease. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.
Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders ; and the physical, chemical, and physiological characteristics of the components of the immune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo. Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of medicine, particularly in the fields of organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology.
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as activation immunotherapies, while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as suppression immunotherapies.
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens irrespective of their antigenic make-up. Other components of the immune system adapt themselves to each new disease encountered and can generate pathogen-specific immunity.
A cancer vaccine is a vaccine that either treats existing cancer or prevents development of cancer. Vaccines that treat existing cancer are known as therapeutic cancer vaccines. Some/many of the vaccines are "autologous", being prepared from samples taken from the patient, and are specific to that patient.
Cancer immunotherapy is the artificial stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspeciality of oncology.

Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), also referred to as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, is a mechanism of cell-mediated immune defense whereby an effector cell of the immune system actively lyses a target cell, whose membrane-surface antigens have been bound by specific antibodies. It is one of the mechanisms through which antibodies, as part of the humoral immune response, can act to limit and contain infection.

Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. More recently antibodies have been used to bind to molecules involved in T-cell regulation to remove inhibitory pathways that block T-cell responses. This is known as immune checkpoint therapy.
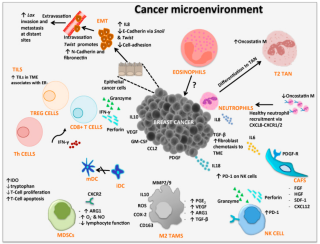
Cancer immunology is an interdisciplinary branch of biology that is concerned with understanding the role of the immune system in the progression and development of cancer; the most well known application is cancer immunotherapy, which utilises the immune system as a treatment for cancer. Cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting are based on protection against development of tumors in animal systems and (ii) identification of targets for immune recognition of human cancer.
According to the National Cancer Institute, a tumor antigen vaccine is a "vaccine made of cancer cells, parts of cancer cells, or pure tumor antigens ". A tumor antigen vaccine may stimulate the body's immune system to find and kill cancer cells. As such, tumor antigen vaccines are a type of cancer immunotherapy.
An oncoantigen is a surface or soluble tumor antigen that supports tumor growth. A major problem of cancer immunotherapy is the selection of tumor cell variants that escape immune recognition. The notion of oncoantigen was set forth in the context of cancer immunoprevention to define a class of persistent tumor antigens not prone to escape from immune recognition.
Cancer immunoprevention is the prevention of cancer onset with immunological means such as vaccines, immunostimulators or antibodies. Cancer immunoprevention is conceptually different from cancer immunotherapy, which aims at stimulating immunity in patients only after tumor onset, however the same immunological means can be used both in immunoprevention and in immunotherapy.
Vaccine therapy is a type of treatment that uses a substance or group of substances to stimulate the immune system to destroy a tumor or infectious microorganisms such as bacteria or viruses.
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralisation renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, intracellular bacteria and microbial toxin. By binding specifically to surface structures (antigen) on an infectious particle, neutralizing antibodies prevent the particle from interacting with its host cells it might infect and destroy. Immunity due to neutralizing antibodies is also known as sterilizing immunity, as the immune system eliminates the infectious particle before any infection takes place.
Professor Gustav Gaudernack is a scientist working in the development of cancer vaccines and cancer immunotherapy. He has developed various strategies in immunological treatment of cancer. He is involved in several ongoing cellular and immuno-gene therapeutic clinical trials and his research group has put major efforts into the development of various T cell-based immunotherapeutic strategies.
Racotumomab is a therapeutic cancer vaccine for the treatment of solid tumors that is currently under clinical development by Recombio, an international public-private consortium with the participation of the Center of Molecular Immunology at Havana, Cuba (CIM) and researchers from Buenos Aires University and National University of Quilmes in Argentina. It induces the patient's immune system to generate a response against a cancer-specific molecular target with the purpose of blocking tumor growth, slowing disease progression and ultimately increasing patient survival.
Cryoimmunotherapy, also referred to as cryoimmunology, is an oncological treatment for various cancers that combines cryoablation of tumor with immunotherapy treatment. In-vivo cryoablation of a tumor, alone, can induce an immunostimulatory, systemic anti-tumor response, resulting in a cancer vaccine—the abscopal effect. Thus, cryoablation of tumors is a way of achieving autologous, in-vivo tumor lysate vaccine and treat metastatic disease. However, cryoablation alone may produce an insufficient immune response, depending on various factors, such as high freeze rate. Combining cryotherapy with immunotherapy enhances the immunostimulating response and has synergistic effects for cancer treatment.
Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy is an oncological treatment that combines various tumor-ablation techniques with immunotherapy treatment. Combining ablation therapy of tumors with immunotherapy enhances the immunostimulating response and has synergistic effects for curative metastatic cancer treatment. Various ablative techniques are utilized including cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, laser ablation, photodynamic ablation, stereotactic radiation therapy, alpha-emitting radiation therapy, hyperthermia therapy, HIFU. Thus, combinatorial ablation of tumors and immunotherapy is a way of achieving an autologous, in-vivo tumor lysate vaccine and treating metastatic disease.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are powerful antigen presenting cells for the induction of antigen specific T cell response. DC vaccine has been introduced as a new therapeutic strategy in cancer patients. DC-based immunotherapy is safe and can promote antitumor immune responses and prolonged survival of cancer patients.
References
- ↑ Yang, Isaac; Han, Seungu (2009). "Heat-shock protein vaccines as active immunotherapy against human gliomas". Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy. 9 (11): 1577–82. doi:10.1586/era.09.104. PMC 3836274 . PMID 19895242.
- 1 2 Davis, Ian D (2000-06-01). "An overview of cancer immunotherapy". Immunology and Cell Biology. 78 (3): 179–195. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1711.2000.00906.x. ISSN 1440-1711. PMID 10849106.
- ↑ Brody, David L.; Holtzman, David M. (2008-06-17). "Active and Passive Immunotherapy for Neurodegenerative Disorders". Annual Review of Neuroscience. 31 (1): 175–193. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125529. ISSN 0147-006X. PMC 2561172 . PMID 18352830.
- ↑ Winblad, Bengt; Graf, Ana; Riviere, Marie-Emmanuelle; Andreasen, Niels; Ryan, J. Michael (2014-01-30). "Active immunotherapy options for Alzheimer's disease". Alzheimer's Research & Therapy. 6 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/alzrt237. ISSN 1758-9193. PMC 3979042 . PMID 24476230.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Baxter, D (2014). "Active and passive immunization for cancer". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 10 (7): 2123–9. doi:10.4161/hv.29604. PMC 4370360 . PMID 25424829.
- 1 2 "Non-specific cancer immunotherapies and adjuvants | American Cancer Society". www.cancer.org. Retrieved 2018-04-03.
- 1 2 3 Green, James; Fuge, Oliver; Allchorne, Paula; Vasdev, Nikhil (2015-05-04). "Immunotherapy for bladder cancer". Research and Reports in Urology. 7: 65–79. doi:10.2147/rru.s63447. PMC 4427258 . PMID 26000263.