This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Greenwich Island is an island 24 km (15 mi) long and from 0.80 to 9.66 km wide, lying between Robert Island and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands. Surface area 142.7 square kilometres (55.1 sq mi). The name Greenwich Island dates back to at least 1821 and is now established in international usage.

Saddle Island is an island nearly 2 miles (3.2 km) long, consisting of twin summits which are almost separated by a narrow channel strewn with boulders, lying 5.5 miles (8.9 km) north of the west end of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands. It was discovered and charted in 1823 by British sealer James Weddell, and named by him for its peculiar shape.

Letnitsa Glacier is a 0.9 nautical miles long glacier on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica draining the southeast slopes of Imeon Range east of Organa Peak and south of Riggs Peak. It is situated southwest of Gramada Glacier and northeast of Kremena Ice Piedmont, and flows southeastward into Hisarya Cove, Osmar Strait. Bulgarian early mapping in 2009. The glacier is named after the town of Letnitsa in northern Bulgaria.

Gramada Glacier is a 1.6 nautical miles long glacier on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica draining the southeast slopes of Imeon Range east of Riggs Peak, southeast of Madan Saddle and south of Neofit Peak. It is situated southwest of Armira Glacier and northeast of Letnitsa Glacier, and flows southeastward into Brashlyan Cove on Osmar Strait. Bulgarian early mapping in 2009. The glacier is named after the town of Gramada in northwestern Bulgaria.

Armira Glacier is a 1.6 nautical miles long glacier on Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica draining the southeast slopes of Imeon Range southeast of Slaveykov Peak and east of Neofit Peak. It is situated southwest of Dragoman Glacier and northeast of Gramada Glacier, and flows southeastward into Yarebitsa Cove on Osmar Strait. Bulgarian early mapping in 2009. The glacier is named after Armira River in southeastern Bulgaria.
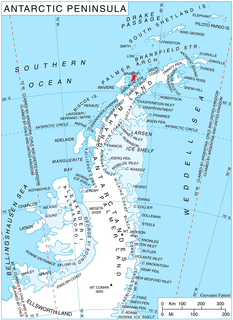
Albena Peninsula is a peninsula extending 13 km in east-west direction and 9 km wide at its base, forming the east extremity of Brabant Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It is bounded by the terminus of Lister Glacier to the north and by Hill Bay to the south, ending in Spallanzani Point to the east, and has its interior occupied by Stavertsi Ridge. The peninsula is separated from Davis Island to the north by Sumer Passage.

Rabisha Rocks is a group of rocks off the north coast of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated 1.5 km (0.93 mi) northeast of Voluyak Rocks, 1.3 km (0.81 mi) north of Kabile Island and 1.8 km (1.12 mi) west of Ongley Island.

Buchino Rocks is a group of rocks off the north coast of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated 1.5 km (0.93 mi) northwest of Stoker Island, 1.6 km (0.99 mi) southeast of Romeo Island and 1.9 km (1.2 mi) north-northwest of Tvarditsa Rocks.

Skrino Rocks is the chain of rocks off the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, extending 570 m (623 yd) in east-west direction.

Alepu Rocks is the group of rocks off the east coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, situated in an area with a diameter of 380 m (416 yd).
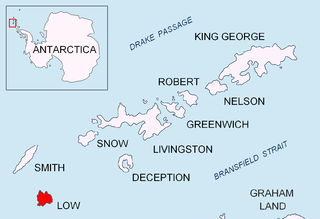
Presnakov Island is the 390 m long in southeast-northwest direction and 100 m wide rocky island lying off the west coast of Low Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Aurelia Island is the 390 m long in west–east direction and 190 m wide rocky island lying off Limets Peninsula in northern Low Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its coastline is highly indented.

Alfeus Island is the 310 m long in west-southwest to east-northeast direction and 120 m wide rocky island lying off the north coast of Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Pingvin Rocks is the group of rocks in Morton Strait off the northeast coast of Snow Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica extending 670 m in west–east direction and 300 m in south–north direction. The area was visited by early 19th-century sealers.

Bekas Rock is the 140 m long in southwest-northeast direction and 60 m wide rock lying west of Rugged Island on the west side of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Rotalia Island is the rocky island off the north coast of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica extending 310 m in southeast-northwest direction and 250 m in southwest-northeast direction.

Kondor Island is the 320 m long in west–east direction and 140 m wide rocky island lying off the north coast of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.

Fregata Island is the 480 m long in southeast-northwest direction and 230 m wide rocky island lying off the north coast of Nelson Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.