
Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi)1 in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided between two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

The Falkland Sound is a sea strait in the Falkland Islands. Running southwest-northeast, it separates West and East Falkland.
Hope Bay is a bay 3 nautical miles long and 2 nautical miles wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound.
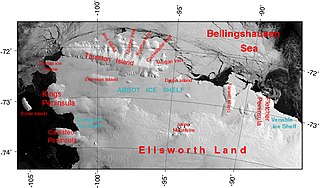
The Abbot Ice Shelf is an ice shelf 250 nautical miles long and 40 nautical miles wide, bordering Eights Coast from Cape Waite to Pfrogner Point in Antarctica. Thurston Island lies along the northern edge of the western half of this ice shelf; other sizable islands lie partly or wholly within this shelf.

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 40 nautical miles in a north–south direction.

Ferrar Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica. It is about 35 nautical miles long, flowing from the plateau of Victoria Land west of the Royal Society Range to New Harbour in McMurdo Sound. The glacier makes a right (east) turn northeast of Knobhead, where it where it is apposed, i.e., joined in Siamese-twin fashion, to Taylor Glacier. From there, it continues east along the south side of Kukri Hills to New Harbor.
Martin Peninsula is a peninsula about 60 nautical miles long and 20 nautical miles wide that is ice-covered except for a few rock outcrops along its margins, located between Getz Ice Shelf and Dotson Ice Shelf on the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. The farthest point of the peninsula is Jacobsen Head.
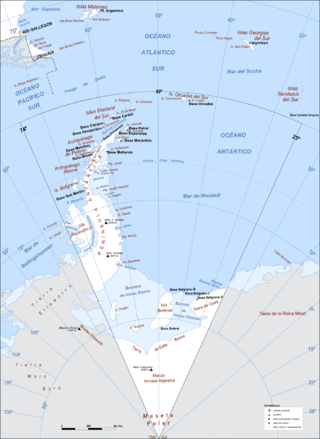
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.
The Aviator Glacier is a major valley glacier in Antarctica that is over 60 nautical miles long and 5 nautical miles wide, descending generally southward from the plateau of Victoria Land along the west side of Mountaineer Range, and entering Lady Newnes Bay between Cape Sibbald and Hayes Head where it forms a floating tongue.

Port Albemarle is a settlement on West Falkland, in the Falkland Islands. It is in the far south of the island, on the east side, at the southern end of Falkland Sound.
Grantham Sound is a bay on East Falkland, Falkland Islands, which opens out into the Falkland Sound. At its landward end, it narrows and becomes Brenton Loch. Mount Usborne overlooks it.

The Bay of Harbours is a bay/fjord on the south east coast of East Falkland. It is in Lafonia between Eagle Passage and the Adventure Sound, and forms the lower segment of the "E" of the peninsula. North Arm is at its landward end.
The Iroquois Plateau is a large, mainly ice-covered plateau situated east of the southern part of the Washington Escarpment in the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.

Antarctic was a Swedish steamship built in Drammen, Norway, in 1871. She was used on several research expeditions to the Arctic region and to Antarctica from 1893 to 1903. In 1895 the first confirmed landing on the mainland of Antarctica was made from this ship.
The Addo Elephant National Park Marine Protected Area is a marine conservation area in Algoa Bay, adjacent to the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality, near Gqeberha, previously Port Elizabeth.
Bone Bay is a rectangular bay along the northwest coast of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. It is nearly 10 nautical miles wide at the entrance between Notter Point and Cape Roquemaurel.










