Related Research Articles

A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture. A colloid has a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre.

An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. The term aerosol commonly refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at hydroelectric dams, irrigation mist, perfume from atomizers, smoke, dust, steam from a kettle, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an anthropogenic aerosol.
Electrical mobility is the ability of charged particles to move through a medium in response to an electric field that is pulling them. The separation of ions according to their mobility in gas phase is called ion mobility spectrometry, in liquid phase it is called electrophoresis.

A Coulter counter is an apparatus for counting and sizing particles suspended in electrolytes. The Coulter counter is the commercial term for the technique known as resistive pulse sensing or electrical zone sensing. The apparatus is based on the Coulter principle named after its inventor, Wallace H. Coulter.
Soil texture is a classification instrument used both in the field and laboratory to determine soil classes based on their physical texture. Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel, and quantitative methods such as the hydrometer method based on Stokes' law. Soil texture has agricultural applications such as determining crop suitability and to predict the response of the soil to environmental and management conditions such as drought or calcium (lime) requirements. Soil texture focuses on the particles that are less than two millimeters in diameter which include sand, silt, and clay. The USDA soil taxonomy and WRB soil classification systems use 12 textural classes whereas the UK-ADAS system uses 11. These classifications are based on the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in the soil.
A particle counter is used for monitoring and diagnosing particle contamination within specific clean media, including air, water and chemicals. Particle counters are used in a variety of applications in support of clean manufacturing practices, industries include: electronic components and assemblies, pharmaceutical drug products and medical devices, and industrial technologies such as oil and gas.
The equivalent spherical diameter of an irregularly shaped object is the diameter of a sphere of equivalent geometric, optical, electrical, aerodynamic or hydrodynamic behavior to that of the particle under investigation.

AERONET - the AERONET is a network of ground-based sun photometers which measure atmospheric aerosol properties. The measurement system is a solar-powered CIMEL Electronique 318A spectral radiometer that measures Sun and sky radiances at a number of fixed wavelengths within the visible and near-infrared spectrum. There is one sea-based reading location aboard the E/V Nautilus, the exploration vessel operated by Dr. Robert Ballard and the Sea Research Foundation. Two readings per day are taken aboard the ship while it is in operation.

In granulometry, the particle-size distribution (PSD) of a powder, or granular material, or particles dispersed in fluid, is a list of values or a mathematical function that defines the relative amount, typically by mass, of particles present according to size. Significant energy is usually required to disintegrate soil, etc. particles into the PSD that is then called a grain size distribution.

Particle size is a notion introduced for comparing dimensions of solid particles, liquid particles (droplets), or gaseous particles (bubbles). The notion of particle size applies to particles in colloids, in ecology, in granular material, and to particles that form a granular material.
Particle size analysis, particle size measurement, or simply particle sizing, is the collective name of the technical procedures, or laboratory techniques which determines the size range, and/or the average, or mean size of the particles in a powder or liquid sample.
A scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) is an analytical instrument that measures the size and number concentration of aerosol particles with diameters from 2.5 nm to 1000 nm. They employ a continuous, fast-scanning technique to provide high-resolution measurements.
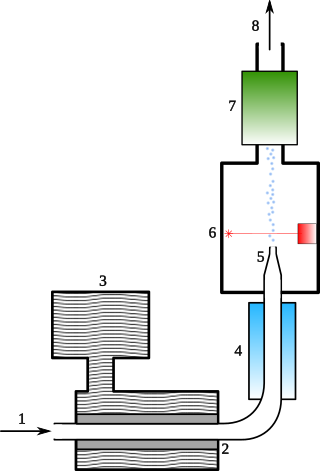
A condensation particle counter or CPC is a particle counter that detects and counts aerosol particles by first enlarging them by using the particles as nucleation centers to create droplets in a supersaturated gas.

Aerosol mass spectrometry is the application of mass spectrometry to the analysis of the composition of aerosol particles. Aerosol particles are defined as solid and liquid particles suspended in a gas (air), with size range of 3 nm to 100 μm in diameter and are produced from natural and anthropogenic sources, through a variety of different processes that include wind-blown suspension and combustion of fossil fuels and biomass. Analysis of these particles is important owing to their major impacts on global climate change, visibility, regional air pollution and human health. Aerosols are very complex in structure, can contain thousands of different chemical compounds within a single particle, and need to be analysed for both size and chemical composition, in real-time or off-line applications.
A Particle mass analyser(PMA) is an instrument for classifying aerosol particles according to their mass-to-charge ratio using opposing electrical and centrifugal forces. This allows the classifier to select particles of a specified mass-to-charge ratio independent of particle shape.
Electrical aerosol spectrometry (EAS) is a technique for measurement of the number-size distribution of aerosol using a combination of electrical charging and multiple solid state electrometer detectors. The technique combines both diffusion and field charging regimes to cover the diameter range 10 nm to 10 μm.
Atmospheric lidar is a class of instruments that uses laser light to study atmospheric properties from the ground up to the top of the atmosphere. Such instruments have been used to study, among other, atmospheric gases, aerosols, clouds, and temperature.
The Charged Aerosol Detector (CAD) is a detector used in conjunction with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) to measure the amount of chemicals in a sample by creating charged aerosol particles which are detected using an electrometer. It is commonly used for the analysis of compounds that cannot be detected using traditional UV/Vis approaches due to their lack of a chromophore. The CAD can measure all non-volatile and many semi-volatile analytes including, but not limited to, antibiotics, excipients, ions, lipids, natural products, biofuels, sugars and surfactants. The CAD, like other aerosol detectors, falls under the category of destructive general-purpose detectors.
Dustiness is the tendency of particles to become airborne in response to a mechanical or aerodynamic stimulus. Dustiness is affected by the particle shape, size, and inherent electrostatic forces. Dustiness increases the risk of inhalation exposure.

The characterization of nanoparticles is a branch of nanometrology that deals with the characterization, or measurement, of the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles measure less than 100 nanometers in at least one of their external dimensions, and are often engineered for their unique properties. Nanoparticles are unlike conventional chemicals in that their chemical composition and concentration are not sufficient metrics for a complete description, because they vary in other physical properties such as size, shape, surface properties, crystallinity, and dispersion state.
References
- ↑ Tavakoli, Farzan; Symonds, Jonathan P. R.; Olfert, Jason S. (2014). "Generation of a Monodisperse Size-Classified Aerosol Independent of Particle Charge". Aerosol Science and Technology. 48 (3): i-iv. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2013.877121 .
- ↑ Johnson, Tyler J.; Symonds, Jonathan P. R.; Olfert, Jason S.; Boies, Adam M. (2021-02-01). "Accelerated measurements of aerosol size distributions by continuously scanning the aerodynamic aerosol classifier". Aerosol Science and Technology. 55 (2): 119–141. doi:10.1080/02786826.2020.1830941. ISSN 0278-6826. S2CID 228975295.