
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about 160 km (99 mi) south of the Greek mainland, and about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of 8,450 km2 (3,260 sq mi) and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete to the north and the Libyan Sea to the south.

The Dorians were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Hellenes of Classical Greece divided themselves. They are almost always referred to as just "the Dorians", as they are called in the earliest literary mention of them in the Odyssey, where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete.

Laconia or Lakonia is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word laconic—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks.

Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon, while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.

Kythira is an island in Greece lying opposite the south-eastern tip of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is traditionally listed as one of the seven main Ionian Islands, although it is distant from the main group. Administratively, it belongs to the Islands regional unit, which is part of the Attica region, despite its distance from the Saronic Islands, around which the rest of Attica is centered. As a municipality, it includes the island of Antikythera to the south.

The Mani Peninsula, also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots, who claim descent from the ancient Spartans. The capital city of Mani is Areopoli. Mani is the central peninsula of the three which extend southwards from the Peloponnese in southern Greece. To the east is the Laconian Gulf, to the west the Messenian Gulf. The Mani peninsula forms a continuation of the Taygetos mountain range, the western spine of the Peloponnese.

Voies is a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Monemvasia, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 215.527 km2. It is on the southern tip of Cape Malea. It is a predominantly agricultural region with a few minor villages and one dominant town. Vatika is the common term for the area, but Voies is used in a more official context, particularly for postal situations. Voion, the genitive, is used for description: for example, to differentiate the village of Agios Nikolaos in Voies from other villages and towns of the same name, one would use Agios Nikolaos Voion. Neapoli is the administrative capital of the municipality, and is also the urban center to the numerous villages that surround the hinterland.

Sfakiá is a mountainous area in the southwestern part of the island of Crete, in the Chania regional unit. It is considered to be one of the few places in Greece that have never been fully occupied by foreign powers. With a 2011 census population of 1,889 inhabitants living on a land area of 467.589 km2 (180.537 sq mi), Sfakia is one of the largest and least densely populated municipalities on the island of Crete. The etymology of its name is disputed. According to the prevailing theory, it relates to its rugged terrain, deriving from the ancient Greek word σφαξ, meaning land chasm or gorge.
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 respondents recorded their ethnicity as Greek, forming almost 99% of the 667,398 Cypriot citizens and over 78% of the 840,407 total residents of the area controlled by the Republic of Cyprus. These figures do not include the 29,321 citizens of Greece residing in Cyprus, ethnic Greeks recorded as citizens of other countries, or the population of the Turkish-occupied Northern Cyprus.
Myson of Chenae, also called "of Chen", was, according to Plato, one of the Seven Sages of Greece. He is not to be confused with the Myson of 5th-century Athens who ran a pottery and inspired, and taught, many of the Mannerists including the Pan Painter.

The Maniots or Maniates are the inhabitants of Mani Peninsula, located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as Maina.

Tsakonia or the Tsakonian region refers to the small area in the eastern Peloponnese where the Tsakonian language is spoken, in the area surrounding 13 towns, villages and hamlets located around Pera Melana in Arcadia. It is not a formally defined political entity of the modern Greek state.

Afro-Turks are Turkish people of African Zanj descent, who trace their origin to the Ottoman slave trade like the Afro-Abkhazians. Afro-Turk population is estimated to be between 5,000 and 20,000 people. Afro-Turks are distinct from African immigrants in Turkey, who are around 100,000 individuals.

The Cretan Muslims or Cretan Turks were the Muslim inhabitants of the island of Crete. Their descendants settled principally in Turkey, the Dodecanese Islands under Italian administration, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Libya, and Egypt, as well as in the larger Turkish diaspora.
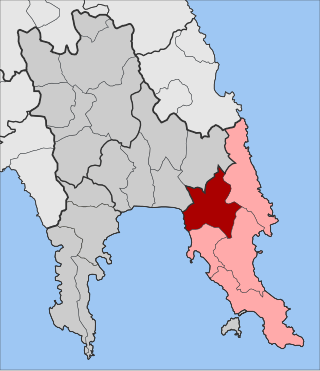
Molaoi is a town and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Monemvasia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 193.167 km2. The population in 2011 was 4,980, of which 2,534 lived in the town itself.

Pagoi is a village in the northwestern part of Corfu Island in Greece, and a community of the municipal unit Agios Georgios. The community consists of the villages Pagoi, Agios Georgios, Prinylas, and Vatonies. The community had a population of 511 as of the 2011 census.

Sparta is a city and municipality in Laconia, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population of 35,259, of whom 17,408 lived in the city.
African Greeks (also referred to as Afro-Greeks, refers to citizens or residents of Greece of African descent.

Metamorfosi is a village in Laconia, five kilometers from the center of Molaoi and about seventy-eight kilometers southeast of Sparta. The village is built at the foot of the mountain of Koulochera on the outskirts of the Parnon range. Its altitude is 120 meters. According to the 2011 census, Metamorfosi has 559 residents.

Neapoli Voion or Neapolis Voion also named Vatika is a small town in Laconia regional unit, southern Greece. It is built near the south end of Malea peninsula, close to the Cape Maleas. It is 335 km southeast of Athens and 115 km south of Sparta. Its port is the gateway for the island of south Peloponnese such as Kythera, Antikythera and Elafonisos. Neapoli is the part of Monemvasia municipality and Voies municipal unit. Its population is 3090 residents according to 2011 census.

















