
Al-Qaeda is a pan-Islamist militant organization led by Sunni Jihadists who self-identify as a vanguard spearheading a global Islamist revolution to unite the Muslim world under a supra-national Islamic caliphate. Its membership is mostly composed of Arabs, but also includes people from other ethnic groups. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian, economic and military targets of the US and its allies; such as the 1998 US embassy bombings, the USS Cole bombing and the September 11 attacks. The organization is designated as a terrorist group by NATO, the UN Security Council, the European Union, and various countries around the world.

Khalid Muhammad Abdallah al-Mihdhar was a Saudi terrorist hijacker. He was one of the five hijackers of American Airlines Flight 77, which was flown into the Pentagon as part of the 11 September attacks.

Nawaf Muhammed Salin al-Hazmi was a Saudi terrorist hijacker who was one of five hijackers of American Airlines Flight 77, which they crashed into the Pentagon as part of the September 11 attacks.

The USS Cole bombing was a suicide attack by al-Qaeda against USS Cole, a guided missile destroyer of the United States Navy, on 12 October 2000, while she was being refueled in Yemen's Aden harbor.
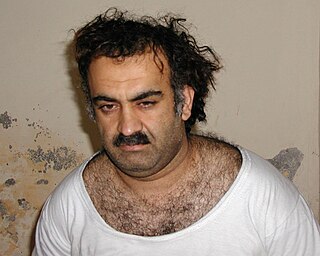
Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, often known by his initials KSM, is a Pakistani terrorist, mechanical engineer and the former Head of Propaganda for al-Qaeda. He is currently held by the United States at the Guantanamo Bay detention camp under terrorism-related charges. He was named as "the principal architect of the 9/11 attacks" in the 2004 9/11 Commission Report.

A series of Islamist terrorist attacks linked to al-Qaeda were planned to occur on or near January 1, 2000, in the context of millennium celebrations, including bombing plots against four tourist sites in Jordan, the Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), USS The Sullivans, and the hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight 814.

Walid Muhammad Salih bin Mubarak bin Attash is a Yemeni prisoner held at the United States' Guantanamo Bay detention camp under terrorism-related charges and is suspected of playing a key role in the early stages of the 9/11 attacks. The Office of the Director of National Intelligence has described him as a "scion of a terrorist family". American prosecutors at the Guantanamo military commissions allege that he helped in the preparation of the 1998 East Africa Embassy bombings and the USS Cole bombing and acted as a bodyguard to Osama bin Laden, gaining himself the reputation of an "errand boy". He is formally charged with selecting and helping to train several of the hijackers of the September 11 attacks. On 31 July 2024, Attash agreed to plead guilty to avoid the death penalty. His plea deal was revoked by Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin two days later.

Abdullah Ahmed Abdullah was a high-ranking Egyptian member of al-Qaeda. He has been described as al-Qaeda's most experienced operational planner and was said to be the second-in-command in the organization at the time of his death.
The 20th hijacker is a possible additional terrorist in the September 11 attacks of 2001 who, for unknown reasons, was unable to participate. The 20th hijacker, though not present during the actual attacks, is said to have been deeply involved in the preparations. There were many variations of the 9/11 plot, with the number of terrorists fluctuating with available resources and changing circumstances. In the end, there were 19 hijackers: three of the planes were taken over by five members each and the fourth was hijacked by four people. The latter plane, United Airlines Flight 93, crashed into a field near Shanksville, Pennsylvania, due to the resistance from passengers before it could reach its target in Washington, D.C.
On September 11, 2001, 19 al-Qaeda terrorists took control of four commercial aircraft and used them as suicide weapons in a series of four coordinated acts of terrorism to strike the World Trade Center in New York City, The Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, and an additional target in Washington, D.C. Two aircraft hit the World Trade Center while the third hit the Pentagon. A fourth plane did not arrive at its target, but crashed into a field in Pennsylvania after a passenger revolt. The intended target is believed to have been the United States Capitol. As a result, 2,977 victims were killed, making it the deadliest foreign attack on U.S. soil, exceeding Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941, which killed 2,335 members of the United States Armed Forces and 68 civilians. The effort was carefully planned by al-Qaeda, which sent 19 terrorists to take over Boeing 757 and Boeing 767 aircraft, operated by American Airlines and United Airlines.
Fahd Mohammed Ahmed al-Quso, also known as Abu Huthaifah, Abu Huthaifah Al-Yemeni, Abu Al-Bara', Abu Hathayfah Al-Adani, Abu Huthaifah Al-Adani, Fahd Mohammed Ahmed Al-Awlaqi, Huthaifah Al-Yemeni, or Abu Huthaifah Al-Abu Al-Bara, was alleged to be a terrorist by American and Yemeni officials, and on the FBI Most Wanted Terrorists list. He was wanted by the FBI, Interpol, and the United States Department of State, which had offered 5 million dollars to anyone with information about him. He was killed by a US drone strike in Yemen on 6 May 2012.
The following is a list of attacks which have been carried out by Al-Qaeda.
American officials have reported that the late al Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden had numerous bodyguards. They reported that the detainees held in the Guantanamo Bay detention camp included at least 30 of Bin Laden's bodyguards.

Hamza bin Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden, better known as Hamza bin Laden, was a Saudi Arabian-born member of al-Qaeda. He was a son of al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden, and, following his father's death in 2011, he was described as an emerging leader of the al-Qaeda organization.

The international activities of Al-Qaeda includes involvements in Europe, where members of the group have been involved in militant and terrorist activities in several countries. Al-Qaeda has been responsible for or involved in attacks in Western Europe and Russia, including the 2004 Madrid train bombings, 2010 Moscow Metro bombings, 2011 Domodedovo International Airport bombing, and the January 2015 Île-de-France attacks.
Pakistan's role in the War on Terror is a widely discussed topic among policy-makers of various countries, political analysts and international delegates around the world. Pakistan has simultaneously received allegations of harbouring and aiding terrorists and commendation for its anti-terror efforts. Since 2001, the country has also hosted millions of Afghan refugees who fled the war in Afghanistan.
At around 9:30 pm on September 11, 2001, George Tenet, director of the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), told President George W. Bush and U.S. senior officials that the CIA's Counterterrorism Center had determined that Osama bin Laden and al-Qaeda were responsible for the September 11 attacks. Two weeks after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001, the Federal Bureau of Investigation connected the hijackers to al-Qaeda, a militant Salafist Islamist multi-national organization. In a number of video, audio, interview and printed statements, senior members of al-Qaeda have also asserted responsibility for organizing the September 11 attacks.

Mohammed Atef was an Egyptian militant and prominent military chief of al-Qaeda, and a deputy of Osama bin Laden, although Atef's role in the organization was not well known by intelligence agencies for years. He was killed in a US airstrike in November 2001.

The Looming Tower is an American drama television miniseries, based on Lawrence Wright's 2006 book of the same name, which premiered on Hulu on February 28, 2018. The 10-episode drama series was created and executive produced by Dan Futterman, Alex Gibney, and Wright. Futterman also acted as the series's showrunner and Gibney directed the first episode. The series stars an ensemble cast featuring Jeff Daniels, Tahar Rahim, Wrenn Schmidt, Bill Camp, Louis Cancelmi, Virginia Kull, Ella Rae Peck, Sullivan Jones, Michael Stuhlbarg, and Peter Sarsgaard.
al-Qaeda has five distinct phases in its development: its beginnings in the late 1980s, a "wilderness" period in 1990–1996, its "heyday" in 1996–2001, a network period from 2001 to 2005, and a period of fragmentation from 2005 to 2009.










