
Berbers or the Berber peoples, also called by their contemporary endonym Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Arab migrations to the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis.
Moroccan music varies greatly between geographic regions and social groups. It is influenced by musical styles including Arab, Berber, Andalusi, Mediterranean, Saharan, West African, and others.

The Gnawa are an ethnic group inhabiting Morocco, that had been brought as slaves from West African Sahel, especially northern Nigeria.
Berber music refers to the musical traditions of the Berbers, a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Arab migration to the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of the mostly mutually unintelligible Berber languages. Berber music varies widely across North Africa. It is stylistically diverse, with songs being predominantly African rhythms and a stock of oral literature.

Berberism is a Berber political-cultural movement of ethnic nationalism, started mainly in Kabylia (Algeria) and in Morocco later spreading to the rest of the Berber communities in the Maghreb region of North Africa. The Berberist movement in Algeria and Morocco is in opposition to cultural Arabization, the pan-Arabist political ideology and Islamism.

The culture of Morocco is a blend of Arab, Amazighs, Andalusian cultures, with African, Hebraic and Mediterranean influences. It represents and is shaped by a convergence of influences throughout history. This sphere may include, among others, the fields of personal or collective behaviors, language, customs, knowledge, beliefs, arts, legislation, gastronomy, music, poetry, architecture, etc. While Morocco started to be stably predominantly Sunni Muslim starting from 9th–10th century AD, in the Almoravids empire period, a very significant Andalusian culture was imported and contributed to the shaping of Moroccan culture. Another major influx of Andalusian culture was brought by Andalusians with them following their expulsion from Al-andalus to North Africa after the Reconquista. In antiquity, starting from the second century A.D and up to the seventh, a rural Donatist Christianity was present, along an urban still-in-the-making Roman Catholicism. All of the cultural super strata tend to rely on a multi-millennial aboriginal Berber substratum still strongly present and dating back to prehistoric times.
This is a list of topics related to Morocco. You can also visit Moroccan portal.

Telouet Kasbah is a Kasbah along the former route of the caravans from the Sahara over the Atlas Mountains to Marrakech. The kasbah was the seat of the El Glaoui family's power, thus sometimes also called the Palace of Glaoui. Its construction started in 1860 and it was further expanded in later years. The palace can still be visited but it is steadily becoming more damaged and is slowly collapsing. In 2010, work was underway to restore the property.

Azilal is a provincial capital in central Morocco, in the Atlas Mountains. It is also the capital of the M'Goun Conservation Area.
Pashtun culture is based on Pashtunwali, as well as speaking of the Pashto language and wearing Pashtun dress.

Berber Jews are the Jewish communities of the Maghreb, in North Africa, who historically spoke Berber languages. Between 1950 and 1970 most emigrated to France, the United States, or Israel.
The indigenous population of the Maghreb region of North Africa encompass a diverse grouping of several heterogenous ethnic groups who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Arab migration to the Maghreb. They are collectively known as Berbers or Amazigh in English. The native plural form Imazighen is sometimes also used in English. While "Berber" is more widely known among English-speakers, its usage is a subject of debate, due to its historical background as an exonym and present equivalence with the Arabic word for "barbarian." When speaking English, indigenous North Africans typically refer to themselves as "Amazigh."
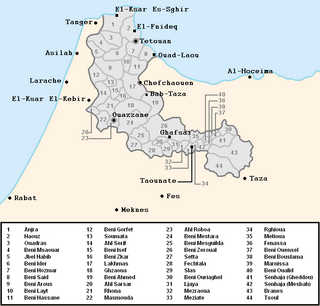
The Jebala are a tribal confederation inhabiting an area in northwest Morocco from the town of Ketema to the west. The Jbala region thus occupies the western part of the Rif mountains. The Jbala has a population of 1,284,000 and is divided into over 40 tribes, today known as "rural communes", and adjacent to them are a small group of nine tribes called the Ghmara (غمارة), who inhabit the territory between the line of mountain peaks to the north of Chefchaouen and the Mediterranean Sea. In addition to tribal heterogeneity, this region is also geographically diverse. High mountains are interspersed with hills and flatlands, and local inhabitants settle in both the high mountains and valleys. In addition to the rainy climate, which influences the way the inhabitants build their houses as well as their special agricultural practices, there are also numerous cultural characteristics that contribute to an emphasised sense of identity and make the Jbala people clearly distinguishable from their neighbours from the eastern part of the Rif Mountains where the climate is more arid, and from the former shepherds from the Atlantic coast (‘Arab). There are only a few cities in the country of the Jbala, and its population remains mostly rural. During the Middle Ages, chroniclers and historians knew the Jbala under their original name, Ghomara.

Fatima Tabaamrant is a Moroccan Berber actress and singer-songwriter. She sings and performs in her native Berber tongue.

Ahidus, also sometimes called ahidous,haidous, tahidoust or hidoussi, is a Berber style of collective performance in Morocco. It is the traditional dance in many Berber tribes and is known to be the favorite entertainment of these tribes.

Arab folk dances, also referred to as Oriental dance, Middle-Eastern dance and Eastern dance, are the traditional folk dances of the Arabs in Arab world. Arab dance has many different styles, including the three main types of folklore, classical, and contemporary. It is enjoyed and implemented throughout the Arab region, from North Africa to the Middle East.
The National List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of India is an attempt to recognize the diversity of Indian culture embedded in its intangible heritage. It aims to raise awareness about the various intangible cultural heritage elements from different states of India at national and international level and ensure their protection.

Mawsim or moussem, waada, or raqb, is the term used in the Maghreb to designate an annual regional festival in which worshippers usually combine the religious celebration of local Marabouts or Sufi Tariqas, with various festivities and commercial activities. These are very popular events, often attended by people from very distant places.

Jewelleryof the Berber cultures is a historical style of traditional jewellery that was worn by women mainly in rural areas of the Maghreb region in North Africa and inhabited by indigenous Berber people. Following long social and cultural traditions, Berber or other silversmiths in Morocco, Algeria and neighbouring countries created intricate jewellery with distinct regional variations. In many towns and cities, there were Jewish silversmiths, who produced both jewellery in specific Berber styles as well as in other styles, adapting to changing techniques and artistic innovations.

Taskiwin is a traditional dance of Morocco that is recognized by UNESCO as Intangible Cultural Heritage. It is a martial dance that is specific to the western High Atlas mountain range in central Morocco. The dance gets its name from the richly decorated horn each dancer carries, known as the Tiskt. The dance involves the art of shaking one's shoulders to the rhythm of tambourines and flutes, and stomping the feet. The practice is said to foster social cohesion and harmony and provide a sense of identity and continuity for the communities that perform it.

























