
Vorbis is a free and open-source software project headed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The project produces an audio coding format and software reference encoder/decoder (codec) for lossy audio compression. Vorbis is most commonly used in conjunction with the Ogg container format and it is therefore often referred to as Ogg Vorbis.
Free and Open source Software Developers' European Meeting (FOSDEM) is a non-commercial, volunteer-organized European event centered on free and open-source software development. It is aimed at developers and anyone interested in the free and open-source software movement. It aims to enable developers to meet and to promote the awareness and use of free and open-source software.

Kodi is a free and open-source media player and technology convergence software application developed by the XBMC Foundation, a non-profit technology consortium. Kodi is available for multiple operating systems and hardware platforms, with a software 10-foot user interface for use with televisions and remote controls. It allows users to play and view most streaming media, such as videos, music, podcasts, and videos from the Internet, as well as all common digital media files from local and network storage media, or TV gateway viewer.
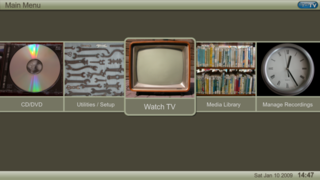
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.
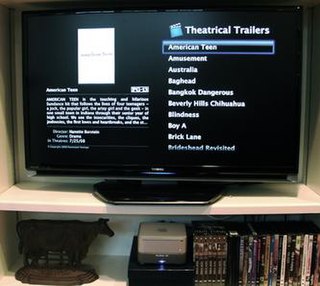
A home theater PC (HTPC) or media center computer is a convergent device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that focuses on video, photo, audio playback, and sometimes video recording functionality. Since the mid-2000s, other types of consumer electronics, including game consoles and dedicated media devices, have crossed over to manage video and music content. The term "media center" also refers to specialized application software designed to run on standard personal computers.

Altacast is a free and open-source audio encoder that can be used to create Internet streams of varying types. Many independent and commercial broadcasters use Altacast to create Internet radio stations, such as those listed on the Icecast, Loudcaster and Shoutcast station directories.

Logitech Media Server is a streaming audio server supported by Logitech, developed in particular to support their Squeezebox range of digital audio receivers.
The Hauppauge MediaMVP is a network media player. It consists of a hardware unit with remote control, along with software for a Windows PC. Out of the box, it is capable of playing video and audio, displaying pictures, and "tuning in" to Internet radio stations. Alternative software is also available to extend its capabilities. It can be used as a front-end for various PVR projects.

Apple TV is a digital media player and microconsole developed and marketed by Apple Inc. It is a small network appliance hardware that plays received media data such as video and audio to a television set or external display. Since its second generation model, it is an HDMI-compliant source device and can only be connected to an enhanced-definition or high-definition widescreen television through HDMI to function.

WLRA or sometimes called WLRA Radio, or WLRA-FM, is a college radio station broadcasting a variety format. Licensed to Lockport, Illinois, USA, the station serves the Chicago/greater Joliet region. The station is licensed to and owned by Lewis University. Lewis University is a private Roman Catholic and Lasallian university with an enrollment of around 6,800 students. The station is a member of the National Association of Broadcasters, Illinois Broadcasters Association, and Broadcast Education Association.
Sourcefabric is a non-profit organisation that develops open source software for independent news media organisations. It is based in Prague, Czech Republic, with branches in Berlin, Germany and Toronto, Canada. Sourcefabric was spun off from the Media Development Investment Fund's Campware project in April 2010. Sourcefabric is an affiliate member of the Open Source Initiative.

Newscoop is a free and open source multilingual content management system for news websites. Its localizable user interface was built with journalists, editors and publishers in mind, rather than computer experts, and it can be configured to suit different profiles of end users. Newscoop follows a newspaper publishing model, so it structures sites by default as Publications, Issues, Sections and Articles, rather than nodes or objects. Newscoop is intended for medium-to-large-size online news publications, but it can be used to manage content for smaller sites too. Newscoop allows the management of multiple journalists and publications from a single interface.

Opus is a lossy audio coding format developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force, designed to efficiently code speech and general audio in a single format, while remaining low-latency enough for real-time interactive communication and low-complexity enough for low-end embedded processors. Opus replaces both Vorbis and Speex for new applications, and several blind listening tests have ranked it higher-quality than any other standard audio format at any given bitrate until transparency is reached, including MP3, AAC, and HE-AAC.
West Africa Democracy Radio (WADR) is a trans-territorial, sub-regional broadcaster based in Dakar, Senegal. WADR is a project of the Open Society Initiative for West Africa (OSIWA) set up in 2003 to protect and defend the ideals of democratic and open societies by disseminating development information through a network of community radios in the West African sub-region.

UTA Radio is an alternative/indie rock college radio station based at The University of Texas at Arlington in Arlington, Texas. The station is an online radio operation run primarily by students with the help of faculty and staff members from the Department of Communication. Its slogan is Online All The Time.

OBS Studio is a free and open-source, cross-platform screencasting and streaming app. It is available for Windows, macOS, Linux distributions, and BSD. The OBS Project raises funds on the platforms Open Collective and Patreon.
Media Development Investment Fund (MDIF), formerly Media Development Loan Fund, is a New York-registered non-profit 501(c)(3) organization and mission-driven investment fund that provides low-cost financing to independent news and information businesses in challenging environments, mostly in countries with a history of media oppression. As one of the United States-based groups involved in direct media development, it specializes in impact investing and provides affordable debt, equity and quasi-equity financing to help journalists build sustainable businesses around professional, responsible, quality journalism.













