Related Research Articles
AirTrain is the name of several passenger railway operations connecting airports to existing rapid transport systems and city centres:

Roma Street railway station is located in the Brisbane central business district, Queensland, Australia. It is the junction station for the North Coast, Main, Gold Coast and NSW North Coast lines. The station is one of four inner city stations that form a core corridor through the centre of Brisbane.
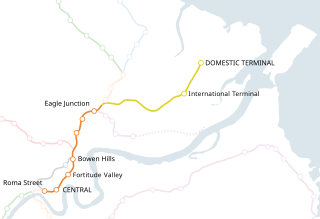
Airtrain is the privately owned commuter railway line that extends 13.0 km (8.1 mi) northeast from Brisbane, the state capital of Queensland, to Brisbane Airport (BNE) at both its separate International and Domestic terminals. It was opened in 2001.

Domestic Terminal railway station is the terminus station of the Airport line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Domestic Terminal at Brisbane Airport, opening on 5 May 2001 at the same time as the line.

International Terminal railway station is located on the Airport line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the International Terminal at Brisbane Airport, opening on 5 May 2001 at the same time as the line.

The Gold Coast railway line is an interurban railway line operated by Queensland Rail in Queensland, Australia, connecting Brisbane with the Gold Coast. The line currently includes stops at 17 stations. In 2021, a journey from Central station to the terminus of this line is scheduled to take 1 hour 23 minutes. Several new stations along the existing line and an extension south are planned.

The Airport Link is Sydney's inner-southern railway line connecting Sydney Airport to the Central Business District and the south-western suburbs of Sydney. With the exception of Wolli Creek, the Airport Line stations are operated by a private company, the Airport Link Company, as part of a public private partnership. The contract allows the company to charge a surcharge on top of the normal fare. The line is served by Sydney Trains T8 Airport & South line services.

The rail network in Queensland, Australia, was the first in the world to adopt 1,067 mm narrow gauge for a main line, and now the second largest narrow gauge network in the world, consists of:

The Airport Link Company is the operator of the Green Square, Mascot, Domestic Airport and International Airport railway stations on the Airport Link tunnel in Sydney, Australia. The line is serviced by T8 Airport & South Line services of the Sydney Trains network.

The Gold Coast is the largest regional city and fastest growing city in Australia. As a result, the Gold Coast has a wide range of public and private transport options from cars and bikes to buses, heavy rail and light rail. The car is the dominant mode of transport in the city with an extensive arterial road network that connects the standard residential streets with major suburbs and motorways.

Brisbane Airport is a coastal suburb in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Brisbane Airport had a population of 0 people.

The Interurban multiple units (IMU) are a class of electric multiple units manufactured by Walkers Limited/Downer EDI Rail, Maryborough for Queensland Rail's Citytrain division between 1996 and 2011. The IMU is divided into in three subclasses, units 101-110 as the 100 series, units 121-124 as the 120 series, and units 161-188, as the 160 series.

High-speed rail in Australia has been under investigation since the early 1980s. Every Federal Government since this time has investigated the feasibility of constructing high-speed rail with speeds above 200 km/h, but to date nothing has ever gone beyond the detailed planning stage. The most commonly suggested route is between Australia's two largest cities, Sydney and Melbourne, which, as of 2023, is the world's fifth busiest air corridor. Various corridors have been proposed for a potential high-speed line. The distance between them is around 800 km (500 miles), which requires very high speeds to make trains competitive with air travel.

Brisbane, the capital city of the Australian state of Queensland, has a network of suburban railways that carry commuters, long-distance passengers, and freight. Suburban and interurban passenger services in Brisbane and South East Queensland are operated by the Queensland Rail City network, a branch of Queensland Rail, which operates long-distance trains across the state. Aurizon and Pacific National operate freight services.

One Rail Australia was an Australian rail freight operator company. Founded by a United States short line railroad holding company, Genesee & Wyoming Inc, in 1997 as Australian Southern Railroad, and successively renamed Australian Railroad Group and Genesee & Wyoming Australia, it was renamed One Rail Australia in February 2020 after the American company sold its remaining shareholding. In July 2022, assets from the South Australian, Northern Territory and interstate operations of the company were sold to rail operator company Aurizon Holdings Limited. The remaining assets, relating to coal haulage in New South Wales and Queensland, were sold in February 2023 to Magnetic Rail Group.

The John Holland Group is an infrastructure, building, rail and transport business operating in Australia and New Zealand. Headquartered in Melbourne, it is a subsidiary of China Communications Construction.

The Redcliffe Peninsula line is a 12 km (7.5 mi) stretch of heavy gauge dual-track railway between Petrie and Kippa-Ring on the Redcliffe peninsula. The new line is part of Queensland Rail's City suburban network, branching from the North Coast line. It starts 200 metres (656 ft) north of Petrie railway station, extending from.
Thiess Pty Ltd is an international mining services company based in Brisbane, Australia. Established in the 1930s as Horn & Thiess, the company later became Thiess Bros and Thiess Contractors before being bought by Leighton Holdings in 1983 to become part of the CIMIC Group. Thiess' headquarters are located in the Thiess Centre in South Bank in the Brisbane CBD near the TAFE Brisbane City campus.

Transfield Holdings is a privately owned Australian investment company with experience in industrial services, infrastructure, and renewable energy.

The New Generation Rollingstock (NGR) is a class of individually-propelled carriages manufactured by Bombardier Transportation in Savli, India for the Queensland Rail City network that entered service between December 2017 and December 2019. They are Queensland Rail's largest fleet of electric trains.
References
- ↑ "Airport link" Railway Gazette International February 1996 page 62
- ↑ Brisbane Airport Rail Link Deadline Extended Archived 20 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine Minister for Transport 2 September 1997
- ↑ Btisbane Airport Rail Link Deed Signed Archived 20 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine Government of Queensland 21 April 1998
- ↑ "Brisbane Airport rail link go-ahead" Railway Digest June 1998 pages 26, 27
- ↑ Brisbane airport BOT Archived 14 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine Railway Gazette International 1 April 1999
- ↑ "Airport Line Tracklaying Commences in Brisbane" Railway Digest October 2000 page 11
- ↑ Brisbane Airtrain Transfield
- ↑ "Brisbane Airport rail link to go ahead". Ministerial Media Statements. 11 February 1999. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012.
- ↑ Airtrain set for sale to British pension fund for $109 m The Courier-Mail 22 December 2012
- ↑ UK pension scheme buys Brisbane railway Archived 20 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine Money Management 27 March 2013