Related Research Articles

The Georgia Railroad and Banking Company also seen as "GARR", was a historic railroad and banking company that operated in the U.S. state of Georgia. In 1967 it reported 833 million revenue-ton-miles of freight and 3 million passenger-miles; at the end of the year it operated 331 miles (533 km) of road and 510 miles (820 km) of track.
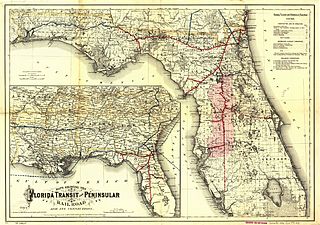
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Plant System, named after its owner, Henry B. Plant, was a system of railroads and steamboats in the U.S. South, taken over by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. The original line of the system was the Savannah, Florida and Western Railway, running across southern Georgia. The Plant Investment Company was formed in 1882 to lease and buy other railroads and expand the system. Other major lines incorporated into the system include the Savannah and Charleston Railroad and the Brunswick and Western Railroad.

The Georgia Southwestern Railroad is a Class III short line railroad company that operates over 234 miles (377 km) of track in southwestern Georgia and southeastern Alabama. Beginning in 1989 as a division of the South Carolina Central Railroad on a pair of former CSX Transportation lines, the railroad has since undergone a number of transformations through abandonments and acquisitions, before arriving at its current form. The railroad was formerly a RailAmerica property before going independent, and in 2008 it was acquired by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.
The Abbeville and Waycross Railroad was incorporated in 1889. The company started building a line between Abbeville, Georgia and Fitzgerald, Georgia in 1890 and finished in 1896. A thirteen-mile stretch of track between Abbeville and Bowens Mill was opened in 1890 and in 1891 was extended to Lulaville. In 1896, entrepreneur John Skelton Williams bought the Abbeville and Waycross Railroad and extended it nine miles from Fitzgerald, Georgia to Ocilla, Georgia. Shortly after that, the Abbeville and Waycross Railroad became part of the Georgia and Alabama Railway.
The Brunswick and Western Railroad is a historic railroad in southern Georgia that at its greatest extent ran from Brunswick near the coast to Albany. Segments of the line still exist today. The Brunswick and Florida Railroad ran from Brunswick west to Glenmore, where it would connect with the Atlantic and Gulf Railroad.
The Charleston and Savannah Railway was a 19th-century American railroad serving the coastal states of South Carolina and Georgia and running through part of the South Carolina Lowcountry. Its name varied slightly over time:
The Savannah, Americus and Montgomery Railway (SA&M) was a historic railroad located in the U.S. states of Georgia and Alabama. SA&M was built in the 1880s running between Montgomery, Alabama and Lyons, Georgia. It would be completed to Savannah, Georgia in 1896 after being renamed the Georgia and Alabama Railway. The line would notably become part of the Seaboard Air Line Railroad network in 1900.

The Wiregrass Central Railroad is a shortline railroad operating 19.5 miles (31.4 km) of track from a CSX Transportation connection at Waterford, near Newton, to Enterprise, Alabama via the south side of Fort Novosel. The company was initially a subsidiary of Gulf and Ohio Railways and began operations in 1987 following the purchase of the Enterprise Subdivision branch line of CSX Transportation.

The Heart of Georgia Railroad is a shortline railroad created in 1999 to lease and operate 177 miles (285 km) of track owned by the Georgia Department of Transportation between Mahrt, Alabama and Vidalia, Georgia, in the United States. The railroad has since expanded to include more than 233 miles (375 km) of track, reaching as far as Midville, Georgia. Initially only the portion from Rochelle to Preston, Georgia was utilized, with the Preston-Mahrt and Rochelle-Vidalia lines out of service. The Heart of Georgia also hosts the SAM passenger excursion train and is owned by parent company Atlantic Western Transportation Company.
The Abbeville Southern Railway was incorporated in Alabama in September 1892 for the purpose of building a railroad line from Grimes, Alabama northeast to Abbeville, Alabama. The route was completed in December 1893, totaling 26.9 miles (43.3 km), and was operated by the Alabama Midland Railway.
The Southwestern Alabama Railway (SWA) was incorporated in Alabama, United States, in 1897 and tasked with the construction of a branch line from a connection with the Alabama Midland Railway near Newton, Alabama towards Elba, Alabama. The route was completed to Elba in October 1898, totaled 37.2 miles (59.9 km), and was operated by the Alabama Midland Railway.
The Jesup Subdivision is a railroad line owned and operated by CSX Transportation in Georgia. The line runs from Jesup, Georgia to Folkston, Georgia for a length of 72.7 miles. It notable passes through Waycross, Georgia, a major CSX freight terminal and CSX operates numerous freight trains over the line. The Jesup Subdivision was once a major route for the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad, one of CSX's predecessors.

The Georgia, Florida and Alabama Railroad, known as the Sumatra Leaf Route, and colloquially as the Gopher, Frog & Alligator was a 180 miles (290 km)-long railroad from Richland, Georgia to Carrabelle, Florida. It was founded in 1895 as a logging railroad, the Georgia Pine Railway.
The Florida Gulf and Atlantic Railroad is a Class III railroad owned and operated by RailUSA in the Florida Panhandle. The line consists of 430 miles of track running from Baldwin, Florida west through Tallahassee to Pensacola. The line also has a short branch from Tallahassee north to Attapulgus, Georgia. The line connects to CSX lines in Baldwin, Pensacola, and Attapulgus.
The Waycross Short Line was the unofficial name of a railroad line built by Henry B. Plant that ran from Waycross, Georgia to Jacksonville, Florida on the St. Johns River. The line through Georgia was chartered by Plant as the Waycross and Florida Railroad and the Florida segment was chartered as the East Florida Railway. The line crossed the Georgia/Florida border just south of Folkston, Georgia at the St. Marys River.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Waycross—Montgomery Line was one of the company's secondary main lines running from Waycross, Georgia west to Montgomery, Alabama, a distance of over 300 miles. It was built in the late 1800s by the Atlantic Coast Line's predecessor companies. The line is still in service today and is now the Thomasville Subdivision and Dothan Subdivision of CSX Transportation, the Atlantic Coast Line's successor company through various mergers.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Albany—Thomasville Line was a historic railroad line in southern Georgia. Built in 1869 by the company's predecessors, it carried some of the Atlantic Coast Line's passenger trains on their routes from the Midwest to the Southeastern United States. The line is still in service today and is now operated by the Georgia and Florida Railway.
References
- ↑ Hilton, George W. (1990). American Narrow Gauge Railroads. Stanford University Press. p. 304. ISBN 0-8047-1731-1.
- ↑ Schaffner, Hart (1920). A History of the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad. Vol. 29. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 186–187.
- 1 2 Owen, Thomas M. (1921). History of Alabama and Dictionary of Alabama Biography. Vol. 1. S.J. Clarke Publishing Company. p. 71.
- ↑ "Savannah, Florida & Western Railway". 21 October 2008. Archived from the original on 28 November 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ↑ Solomon, Brian (2005). CSX. MBI Publishing Company. pp. 63–67. ISBN 0-7603-1796-8.