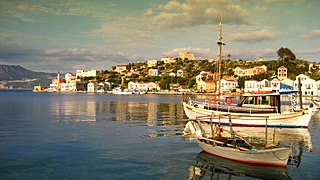Patmos is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. It is famous as the location where John of Patmos received the visions found in the Book of Revelation of the New Testament, and where the book was written.

Kos or Cos is a Greek island, which is part of the Dodecanese island chain in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Kos is the third largest island of the Dodecanese, after Rhodes and Karpathos; it has a population of 37,089, making it the second most populous of the Dodecanese after Rhodes. The island measures 42.1 by 11.5 kilometres. Administratively, Kos constitutes a municipality within the Kos regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is the town of Kos.
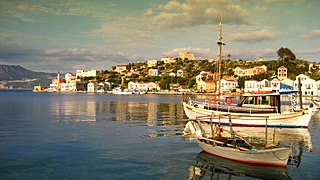
Kastellorizo or Castellorizo, officially Megisti, is a Greek island and municipality of the Dodecanese in the Eastern Mediterranean. It lies roughly 2 kilometres off the south coast of Turkey, about 570 km (354 mi) southeast of Athens and 125 km (78 mi) east of Rhodes, almost halfway between Rhodes and Antalya, and 280 km (170 mi) northwest of Cyprus. Kastellorizo is part of the Rhodes regional unit.
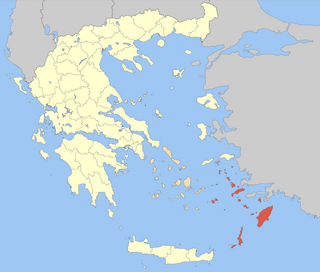
The Dodecanese are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally defines the eastern limit of the Sea of Crete. They belong to the wider Southern Sporades island group.

Lindos is an archaeological site, a fishing village and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 178.9 km2. It lies on the east coast of the island. It is about 40 km south of the city of Rhodes and its fine beaches make it a popular tourist and holiday destination. Lindos is situated in a large bay and faces the fishing village and small resort of Charaki.

Camirus or Kamiros or Cameirus or Kameiros (Κάμειρος) was a city of ancient Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Its site is on the northwest coast of the island, 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) west of the modern village of Kalavarda.

Symi, also transliterated as Syme or Simi, is a Greek island and municipality. It is mountainous and has the harbour town of Symi and its adjacent upper town Ano Symi, as well as several smaller population centres, beaches and areas of significance in history and mythology. Symi is part of the Rhodes regional unit.

Kalymnos is a Greek island and municipality in the southeastern Aegean Sea. It belongs to the Dodecanese island chain, between the islands of Kos and Leros : the latter is linked to it through a series of islets. Kalymnos lies between two and five hours away by sea from the island of Rhodes.

Leros, also called Lero, is a Greek island and municipality in the Dodecanese in the southern Aegean Sea. It lies 317 kilometres from Athens's port of Piraeus, from which it can be reached by a nine-hour ferry ride or by a 45-minute flight from Athens. It is about 32 kilometres (20 mi) from Turkey. Leros is part of the Kalymnos regional unit. It has a population of 7,992 (2021).

Tílos is a small Greek island and municipality located in the Aegean Sea. It is part of the Dodecanese group of islands, and lies midway between Kos and Rhodes. In 2021, the island had a population of 746 people. Along with the uninhabited offshore islets of Antitilos and Gaidaros, it forms the Municipality of Tilos, which has a total land area of 64.525 square kilometres (24.913 sq mi). Tilos is part of the Rhodes regional unit.

Ialysos is a town and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes, in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 16.7 km2. It is the second-largest town on the island of Rhodes. It has a population of approximately 13,000, and is located eight kilometres west of the town of Rhodes, the island's capital, on the island's northwestern coast.

Halki is a Greek island and municipality in the Dodecanese archipelago in the Aegean Sea, some 9 km (6 mi) west of Rhodes. It has an area of 28 km2 (11 sq mi). It is part of the Rhodes regional unit. It has a permanent population of 330, concentrated in the only village of Emporio. The 2021 census showed a population of 475 inhabitants. The community is divided in two parts, Chorio and Emporio.

Rhodes is the principal city and a former municipality on the island of Rhodes in the Dodecanese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it is part of the municipality Rhodes, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It has a population of approximately 56,000 inhabitants. Rhodes has been famous since antiquity as the site of Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The citadel of Rhodes, built by the Hospitalliers, is one of the best-preserved medieval towns in Europe. The Medieval city is designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Peraia, and Peraea or Peræa in Classical Antiquity referred to "a community's territory lying 'opposite', predominantly a mainland possession of an island state" according to Karl-Wilhelm Welwei. Notable examples include:

Astypalaia, is a Greek island with 1,334 residents. It belongs to the Dodecanese, an archipelago of fifteen major islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea. However, many scholars recognize Astypalaia as an extension of the Cyclades, as many cultural and ecological components of the island are more indicative of the Cyclades rather than the Dodecanese.

Ro or Rho is a small Greek island in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, more precisely in the Levantine Sea, near Kastellorizo, close to Turkey's Anatolian coast. It is part of the municipality of Megísti (Kastellorizo) in the South Aegean region.
Salakos is a village of 500 people on the west side of Rhodes Island. It is 40 km from the capital Rhodes town and 7 km from the North West coast. The village is located on the hills of Mount Prophitis Ilias. Inhabitants are mainly employed in farming, livestock rearing and tourism.

Amos was a settlement (dēmē) of ancient Caria, located near the modern town of Turunç, Turkey.

Rhodes is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is the city of Rhodes, which had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022, the island had a population of 125,113 people. It is located northeast of Crete and southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522.

The Rhodian Peraea or Peraia was the name for the southern coast of the region of Caria in western Asia Minor during the 5th–1st centuries BC, when the area was controlled and colonized by the nearby island of Rhodes.