
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases.

In chemistry, an acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their application in solving related problems; these are called the acid–base theories, for example, Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.
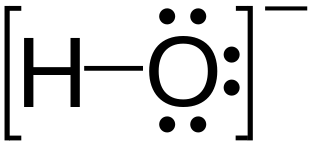
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.

Potassium chloride is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste. Potassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. KCl is used as a fertilizer, in medicine, in scientific applications, domestic water softeners, and in food processing, where it may be known as E number additive E508.

A lye is an alkali metal hydroxide. Traditionally it was obtained by using rainwater to leach wood ashes, which are strongly alkaline and highly soluble in water, of their potassium hydroxide (KOH), producing lye water, a caustic basic solution. Then the lye water would either be used as such, as for curing olives before brining them, or evaporated of water to leave crystalline lye behind. "Lye" most accurately refers to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), but historically has been conflated to include other alkali materials, most notably potassium hydroxide.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Soda lime, a mixture of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and calcium oxide (CaO), is used in granular form within recirculating breathing environments like general anesthesia and its breathing circuit, submarines, rebreathers, and hyperbaric chambers and underwater habitats. Its purpose is to eliminate carbon dioxide from breathing gases, preventing carbon dioxide retention and, eventually, carbon dioxide poisoning. The creation of soda lime involves treating slaked lime with a concentrated sodium hydroxide solution.

In chemistry, neutralization or neutralisation is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react with an equivalent quantity of each other. In a reaction in water, neutralization results in there being no excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions present in the solution. The pH of the neutralized solution depends on the acid strength of the reactants.
The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which are commodity chemicals required by industry. Thirty five million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry.
In chemistry, a strong electrolyte is a solute that completely, or almost completely, ionizes or dissociates in a solution. These ions are good conductors of electric current in the solution.

Copper(II) hydroxide is the hydroxide of copper with the chemical formula of Cu(OH)2. It is a pale greenish blue or bluish green solid. Some forms of copper(II) hydroxide are sold as "stabilized" copper(II) hydroxide, although they likely consist of a mixture of copper(II) carbonate and hydroxide. Cupric hydroxide is a strong base, although its low solubility in water makes this hard to observe directly.

Strontium hydroxide, Sr(OH)2, is a caustic alkali composed of one strontium ion and two hydroxide ions. It is synthesized by combining a strontium salt with a strong base. Sr(OH)2 exists in anhydrous, monohydrate, or octahydrate form.

Sodium formate, HCOONa, is the sodium salt of formic acid, HCOOH. It usually appears as a white deliquescent powder.
Zinc hydroxide Zn(OH)2 is an inorganic chemical compound. It also occurs naturally as 3 rare minerals: wülfingite (orthorhombic), ashoverite and sweetite (both tetragonal).

The alkali–silica reaction (ASR), also commonly known as concrete cancer, is a deleterious internal swelling reaction that occurs over time in concrete between the highly alkaline cement paste and the reactive amorphous silica found in many common aggregates, given sufficient moisture.

Concrete degradation may have many different causes. Concrete is mostly damaged by the corrosion of reinforcement bars due to the carbonatation of hardened cement paste or chloride attack under wet conditions. Chemical damage is caused by the formation of expansive products produced by chemical reactions, by aggressive chemical species present in groundwater and seawater, or by microorganisms Other damaging processes can also involve calcium leaching by water infiltration, physical phenomena initiating cracks formation and propagation, fire or radiant heat, aggregate expansion, sea water effects, leaching, and erosion by fast-flowing water.















