
Brunssum is a municipality and a town in the province of Limburg in the Netherlands. The municipality of Brunssum has 27,670 residents as of 2021.

The Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) is the military headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Allied Command Operations (ACO) that commands all NATO operations worldwide. SHAPE is situated in the village of Casteau, near Mons, Belgium.

The Royal Danish Air Force (RDAF) is the aerial warfare force of the Kingdom of Denmark and one of the four branches of the Danish Armed Forces. Initially being components of the Army and the Navy, it was made a separate service in 1950. Its main purpose is to serve as enforcer of Danish airspace and to provide air support to Danish group troops on the battlefield.
The Allied Rapid Reaction Corps (ARRC) is a rapid reaction force maintained by NATO. It is capable of deploying a High Readiness Force (Land) Headquarters at short notice for operations and crisis response.

Allied Joint Force Command Brunssum (JFCBS) is a NATO command with its headquarters at Brunssum, the Netherlands. It was established in 2004, as part of a reorganisation that reduced the number of NATO Military Command Structure headquarters.

Allied Command Transformation (ACT) is a military command of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), formed in 2003 after restructuring.

The Joint Force CommandNaples is a NATO military command based in Lago Patria, in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy. It was activated on 15 March 2004, after effectively redesigning its predecessor command, Allied Forces Southern Europe (AFSOUTH), originally formed in 1951. In NATO Military Command Structure terms, AFSOUTH was a "Major Subordinate Command". The commander of JFC Naples reports to the Supreme Allied Commander Europe at the Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe, Casteau, Belgium.

The Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic (SACLANT) was one of two supreme commanders of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), the other being the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR). The SACLANT led Allied Command Atlantic was based at Norfolk, Virginia. The entire command was routinely referred to as 'SACLANT'.
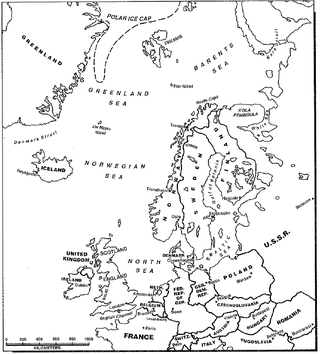
Exercise Mainbrace was the first large-scale naval exercise undertaken by the newly established Allied Command Atlantic (ACLANT), one of the two principal military commands of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It was part of a series of NATO exercises jointly commanded by Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic Admiral Lynde D. McCormick, USN, and Supreme Allied Commander Europe General Matthew B. Ridgeway, U.S. Army, during the fall of 1952.

The Allied Air Command (AIRCOM) is the central command of all NATO air and space forces and the Commander Allied Air Command is the prime air and space advisor to the Alliance. When directed by the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR), it provides the core of the headquarters responsible for the conduct of air operations. The command is based at the Ramstein Air Base in Germany.

The Multinational Corps Northeast was formed on 18 September 1999 at Szczecin, Poland, which became its headquarters. It evolved from what was for many years the only multinational corps in NATO, Allied Land Forces Schleswig-Holstein and Jutland (LANDJUT). From 1962 LANDJUT had been responsible for the defence of the Baltic Approaches from a headquarters at Rendsburg, Germany. It comprised the 6th Panzergrenadier Division and the Danish Jutland Division.

The Northern Army Group (NORTHAG) was a NATO military formation comprising four Western European Army Corps, during the Cold War as part of NATO's forward defence in western Germany.

Allied Forces Baltic Approaches (BALTAP) was a Principal Subordinate Command (PSC) of the NATO Military Command Structure, with responsibility for the Baltic Sea area. It was in existence from 1962 to 2002 and consisted of the Danish Armed Forces, units of the West German Bundeswehr and allied wartime reinforcements.
The structure of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is complex and multi-faceted. The decision-making body is the North Atlantic Council (NAC), and the member state representatives also sit on the Defence Policy and Planning Committee (DPPC) and the Nuclear Planning Group (NPG). Below that the Secretary General of NATO directs the civilian International Staff, that is divided into administrative divisions, offices and other organizations. Also responsible to the NAC, DPPC, and NPG are a host of committees that supervise the various NATO logistics and standardisation agencies.

Lieutenant General Richard Rossmanith is a German Army officer and currently Commander of the Multinational Joint Headquarters Ulm in Ulm, Germany.

The Allied Land Command (LANDCOM) formerly Allied Land Forces South-Eastern Europe (LANDSOUTHEAST) is the standing headquarters for NATO land forces which may be assigned as necessary. The Commander LANDCOM is the primary land warfare advisor to Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) and the Alliance. When directed by SACEUR, it provides the core of the headquarters responsible for the conduct of land operations. The command is based at Şirinyer (Buca), İzmir in Turkey.

Allied Command Channel (ACCHAN) was one of three major North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) commands from 1952 to 1994. Commander-in-Chief Channel was a Major NATO Commander (MNC).
The following is a hierarchical outline for the Danish armed forces at the end of the Cold War. It is intended to convey the connections and relationships between units and formations. In wartime all Danish military units would have come under the joint West German/Danish NATO command Allied Forces Baltic Approaches (BALTAP). BALTAP was a principal subordinate command under the Allied Forces Northern Europe Command (AFNORTH). The commander-in-chief of (BALTAP) was always a Danish Lieutenant General or Vice Admiral, who had the designation Commander Allied Forces Baltic Approaches (COMBALTAP). In peacetime BALTAP had only a few communication units allocated and all other units remained under national command of West Germany's Bundeswehr and Denmark's Forsvaret.
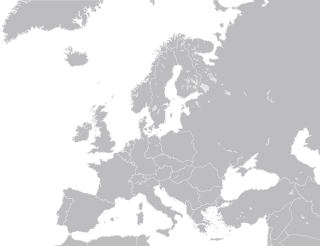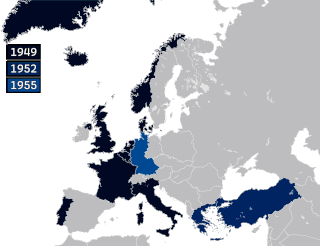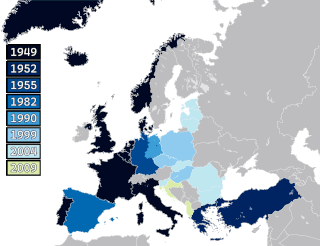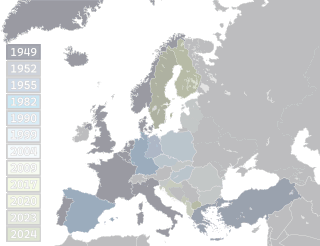
The history of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) begins in the immediate aftermath of World War II when British diplomacy set the stage to contain the Soviet Union and to stop the expansion of Soviet power in Europe. The United Kingdom and France signed, in 1947, the Treaty of Dunkirk, a defensive pact, which was expanded in 1948 with the Treaty of Brussels to add the three Benelux countries and committed them to collective defense against an armed attack for fifty years. The British worked with Washington to expand the alliance into NATO in 1949, adding the United States and Canada as well as Italy, Portugal, Norway, Denmark, and Iceland. Greece and Turkey joined in 1952, West Germany joined in 1955, Spain joined in 1982, Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland joined in 1999, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined in 2004, Albania and Croatia joined in 2009, Montenegro joined in 2017, North Macedonia joined in 2020, Finland joined in 2023, and Sweden joined in 2024.


















