Related Research Articles
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator, was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was censor in 230 BC. His agnomen, Cunctator, usually translated as "the delayer", refers to the strategy that he employed against Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War. Facing an outstanding commander with superior numbers, he pursued a then-novel strategy of targeting the enemy's supply lines, and accepting only smaller engagements on favourable ground, rather than risking his entire army on direct confrontation with Hannibal himself. As a result, he is regarded as the originator of many tactics used in guerrilla warfare.

Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest military commanders in history.

The Battle of Cannae was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman and Italian army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history.
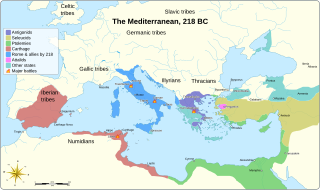
The First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
The gens Baebia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Gnaeus Baebius Tamphilus, in 182 BC. During the later Republic, the Baebii were frequently connected with the patrician family of the Aemilii.

Titus Quinctius Flamininus was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece.
The Fabian strategy is a military strategy where pitched battles and frontal assaults are avoided in favor of wearing down an opponent through a war of attrition and indirection. While avoiding decisive battles, the side employing this strategy harasses its enemy through skirmishes to cause attrition, disrupt supply and affect morale. Employment of this strategy implies that the side adopting this strategy believes time is on its side, usually because the side employing the strategy is fighting in, or close to, their homeland and the enemy is far from home and by necessity has long and costly supply lines. It may also be adopted when no feasible alternative strategy can be devised.
Maharbal was a Numidian army commander in charge of the cavalry under Hannibal and his second-in-command during the Second Punic War. Maharbal was a very close friend to Hannibal and admired him greatly. He was often critical to the battlefield success of Carthage over Rome. Throughout his Italian campaign Hannibal maintained numerical superiority in cavalry, and thus relied upon them and Maharbal to give his army an advantage.

Gaius Claudius Nero was a Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as legate in 214 BC, he was propraetor in 211 BC during the siege of Capua, before being sent to Spain that same year. He became consul in 207 BC.
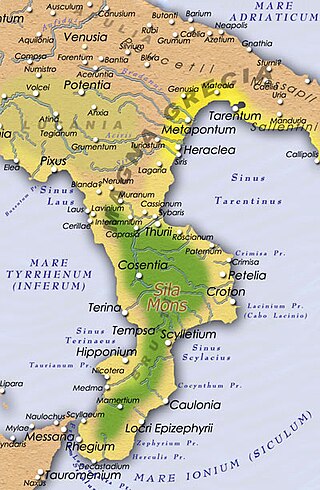
The battle or, more precisely, the battles of Croton in 204 and 203 BC were, as well as the raid in Cisalpine Gaul, the last larger scale engagements between the Romans and the Carthaginians in Italy during the Second Punic War. After Hannibal’s retreat to Bruttium due to the Metaurus debacle, the Romans continuously tried to block his forces from gaining access to the Ionian Sea and cut his eventual escape to Carthage by capturing Croton. The Carthaginian commander struggled to retain his hold on the last efficient port which had remained in his hands after years of fighting and was ultimately successful.

The first Battle of Herdonia was fought in 212 BC during the Second Punic War between Hannibal's Carthaginian army and Roman forces led by Praetor Gnaeus Fulvius Flaccus, brother of the consul. The Roman army was destroyed, leaving Apulia free of Romans for the year.

The second battle of Herdonia took place in 210 BC during the Second Punic War. Hannibal, leader of the Carthaginians, who had invaded Italy eight years earlier, encircled and destroyed a Roman army which was operating against his allies in Apulia. The heavy defeat increased the war's burden on Rome and, piled on previous military disasters, aggravated the relations with her exhausted Italian allies. For Hannibal the battle was a tactical success, but did not halt for long the Roman advance. Within the next three years the Romans reconquered most of the territories and cities lost at the beginning of the war and pushed the Carthaginian general to the southwestern end of the Apennine peninsula. The battle was the last Carthaginian victory of the war; all battles which followed were either inconclusive or Roman victories.

The siege of Capua was fought in 211 BC, when the Romans besieged Capua. It is described by Polybius at 9.4-7, by Livy at 26.4-6, and by Appian at 37-44 of his Hannibalic War.

The Battle of Insubria in 203 BC was the culmination of a major war, carried out by the Carthaginian commander Mago, brother of Hannibal Barca, at the end of the Second Punic war between Rome and Carthage in what is now northwestern Italy. Mago had landed at Genoa, Liguria, two years before, in an effort to keep the Romans busy to the North and thus hamper indirectly their plans to invade Carthage's hinterland in Africa. He was quite successful in reigniting the unrest among various peoples against the Roman dominance. Rome was forced to concentrate large forces against him which finally resulted in a battle fought in the land of the Insubres (Lombardy). Mago suffered defeat and had to retreat. The strategy to divert the enemy's forces failed as the Roman general Publius Cornelius Scipio laid waste to Africa and wiped out the Carthaginian armies that were sent to destroy the invader. To counter Scipio, the Carthaginian government recalled Mago from Italy. However, the remnants of the Carthaginian forces in Cisalpine Gaul continued to harass the Romans for several years after the end of the war.
Publius Sempronius C.f. Tuditanus was a Roman Republican consul and censor, best known for leading about 600 men to safety at Cannae in August, 216 BC and for the Treaty of Phoenice which ended the First Macedonian War, in 205 BC.
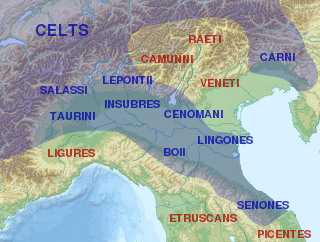
The Cenomani, was an ancient tribe of the Cisalpine Gauls, who occupied the tract north of the Padus, between the Insubres on the west and the Veneti on the east. Their territory appears to have extended from the river Addua to the Athesis.

The Battle of Canusium also known as the Battle of Asculum was a three-day engagement between the forces of Rome and Carthage. It took place in Apulia during the spring of 209 BC, the tenth year of the Second Punic War. A larger Roman offensive, of which it was a part, aimed to subjugate and to punish cities and tribes that had abandoned the alliance with Rome after the Battle of Cannae, and to narrow the base of the Carthaginian leader, Hannibal, in southern Italy.
The gens Calavia was a distinguished Campanian family of Roman times. Several members of this gens were involved in the events of the Samnite Wars and during the Second Punic War. The most famous of its members was undoubtedly Pacuvius Calavius, the chief magistrate of Capua during Hannibal's invasion of Italy, and son-in-law of Publius Claudius Pulcher.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the epithet Africanus, literally meaning "the African," but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa.
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio was a Roman statesman who served as Roman consul in 203 BC.
References
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita xxi. 12, &c.
- ↑ Kern, Paul Bentley (1999). Ancient Siege Warfare. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. p. 326. ISBN 0-253-33546-9.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Alorcus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 133.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Alorcus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 133.