XForms is an XML format used for collecting inputs from web forms. XForms was designed to be the next generation of HTML / XHTML forms, but is generic enough that it can also be used in a standalone manner or with presentation languages other than XHTML to describe a user interface and a set of common data manipulation tasks.
James Clark is a software engineer and creator of various open-source software including groff, expat and several XML specifications.
An XML editor is a markup language editor with added functionality to facilitate the editing of XML. This can be done using a plain text editor, with all the code visible, but XML editors have added facilities like tag completion and menus and buttons for tasks that are common in XML editing, based on data supplied with document type definition (DTD) or the XML tree.

XBRL is a freely available and global framework for exchanging business information. XBRL allows the expression of semantics commonly required in business reporting. The standard was originally based on XML, but now additionally supports reports in JSON and CSV formats, as well as the original XML-based syntax. XBRL is also increasingly used in its Inline XBRL variant, which embeds XBRL tags into an HTML document. One common use of XBRL is the exchange of financial information, such as in a company's annual financial report. The XBRL standard is developed and published by XBRL International, Inc. (XII).
Microsoft BizTalk Server is an inter-organizational middleware system (IOMS) that automates business processes through the use of adapters which are tailored to communicate with different software systems used in an enterprise. Created by Microsoft, it provides enterprise application integration, business process automation, business-to-business communication, message broker and business activity monitoring.
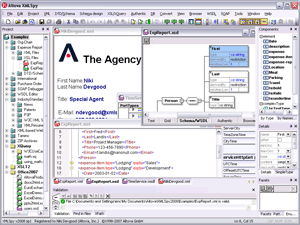
XMLSpy is a proprietary XML editor and integrated development environment (IDE) developed by Altova. XMLSpy allows developers to create XML-based and Web services applications using technologies such as XML, JSON, XBRL, XML Schema, XSLT, XPath, XQuery, WSDL and SOAP.

The Oxygen XML Editor is a multi-platform XML editor, XSLT/XQuery debugger and profiler with Unicode support. It is a Java application so it can run in Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. It also has a version that can run as an Eclipse plugin.
TigerLogic Corporation was an American internet and software development company that designed, developed, sold and supported software infrastructure products. This software was categorized into the following product lines: Yolink search enhancement technology, XML Data Management Server (XDMS), Multidimensional Data Management System (MDMS) and Rapid Application Development (RAD) software tools. TigerLogic was dissolved in 2016, with its MultiValue database products sold to Rocket Software, and its Omnis products sold to UK-based OLS Holdings Ltd.
Parasoft SOAtest is a testing and analysis tool suite for testing and validating APIs and API-driven applications. Basic testing functionality include functional unit testing, integration testing, regression testing, system testing, security testing, simulation and mocking, runtime error detection, web UI testing, interoperability testing, WS-* compliance testing, and load testing.
Content Assembly Mechanism (CAM) is an XML-based standard for creating and managing information exchanges that are interoperable and deterministic descriptions of machine-processable information content flows into and out of XML structures. CAM is a product of the OASIS Content Assembly Technical Committee.

UModel is a UML software modeling tool from Altova, the creator of XMLSpy. UModel supports all 14 UML 2 diagram types and adds a unique diagram for modeling XML Schemas in UML. UModel also supports SysML for embedded system developers, and business process modeling for enterprise analysts. UModel includes code engineering functionality including code generation in Java, C#, and Visual Basic, reverse engineering of existing applications, and round-trip engineering.

DatabaseSpy is a multi-database query, design, and database comparison tool from Altova, the creator of XMLSpy. DatabaseSpy connects to many major relational databases, facilitating SQL querying, database structure design, database content editing, and database comparison and conversion.
Liquid XML Studio IDE is a Windows based XML editor and XML data binding toolkit. It includes graphical editors for authoring XML, XML Schema, WSDL, XSLT and HTML. It also includes user interface extension to Microsoft Visual Studio through the Visual Studio Industry Partner (VSIP) program.
Stylus Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) for the Extensible Markup Language (XML). It consists of a variety of tools and visual designers to edit and transform XML documents and legacy data such as electronic data interchange (EDI), comma-separated values (CSV) and relational data.

Basic4Android is a rapid application development tool for native Android applications, developed and marketed by Anywhere Software Ltd.

Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains. It is used by businesses and organizations to not only model the architecture of their systems, but to process the implementation of these models across the full application development life-cycle.






