Related Research Articles
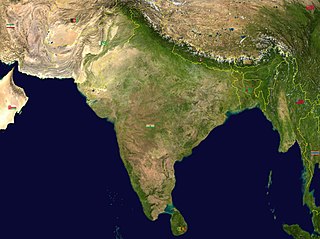
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches 1,750 km (1,090 mi) along the eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of 75,000 km2 (29,000 sq mi), it traverses the states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. The range forms a discontinuous chain of mountains along the eastern edge of the Deccan Plateau, stretching from north of the Mahanadi River in Odisha to Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu at the southern end of the Indian peninsula. The Eastern Ghats meet with the Western Ghats at Nilgiris. The average elevation is around 600 m (2,000 ft) and Arma Konda is the highest peak in the mountains at 1,680 m (5,510 ft).

Kodachadri is a mountain peak with dense forests in the Western Ghats in South India, 78 km from Shimoga. Kodachadri is the highest peak in Shivamogga district. It is declared as natural heritage site by the Karnataka Government. and it is 13th highest peak of Karnataka.

Kudremukha is the name of a mountain range and an individual mountain peak located in Chikmagalur district, in Karnataka, India. It is also the name of a small hill station and iron ore-mining town situated near the mountain, about 20 kilometres from Kalasa in Kalasa Taluk. The name Kuduremukha literally means "horse-faced" in Kannada and refers to a particular picturesque view of a side of the mountain that resembles a horse's face. It was also referred to as 'Samseparvata', historically since it was approached from Samse village. Kuduremukha is Karnataka's 2nd highest peak after Mullayanagiri and 26th highest peak in western ghats. The nearest International Airport is at Mangalore which is at a distance of 99 kilometres.

Agumbe is a village situated in the Thirthahalli taluka of Shivamogga district, Karnataka, India. It is nestled in the thickly forested Malenadu region of the Western Ghats mountain range. Owing to its high rainfall, it has received the epithet of "The Cherrapunji of South India", after Cherrapunji, one of the rainiest places in India.
Hosanagara is a panchayat town in Shimoga district in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is nested in western ghats of India. The World Cattle Conference with main emphasis on cow was held in month of April 2007 in Hosanagar. The different uses of cow were exhibited. Near Hosanagar there is a mutt named Sri Ramachandrapura Math, 6 km from the town.

Athirappilly is a first grade Grama Panchayath with 489.00 km2 area in Chalakudy Taluk, Thrissur district in Kerala, India. It is located 60 km from Thrissur city, 70 km northeast of Kochi city, 55 km northeast of Cochin International Airport, and 30 km from Chalakudy town.

Karnataka, the sixth largest state in India, was ranked as the third most popular state in the country for tourism in 2014. It is home to 507 of the 3600 centrally protected monuments in India, second only to Uttar Pradesh. The State Directorate of Archaeology and Museums protects an additional 752 monuments and another 25,000 monuments are yet to receive protection.

Honnemaradu is a tourist place situated on the back waters of River Sharavathi in India. Honnemardu derived its name from the Honne tree. However, the literal meaning of Honnemardu is Golden Lake. This is perhaps a reference to the fact that Honnemardu is located on the backwaters of the Sharavathi river.

Sri Sri Raghaveshwara Bharathi (originally, Harish Sharma), is an Indian religious guru and the present maṭhadhis (Guru) of Shri Ramachandrapura Mutt, Hosanagara in Shimoga district in the Indian state of Karnataka. He is the 36th maṭhadhis of Shri Ramachandrapura Math. He took sannyasa from Jagadguru Sri Ragavendra Bharati Mahaswamiji the previous maṭhadhis, in April 1994. He is a follower of Advaita Vedanta.

The state of Karnataka in South India has a rich diversity of flora and fauna. It has a recorded forest area of 38,720 km2 which constitutes 55% of the geographical area of the state. These forests support 25% of the elephant population and 20% of the tiger population of India. Many regions of Karnataka are still unexplored and new species of flora and fauna are still found.
Gangamoola is a hill in the Chikkamagaluru district of the state of Karnataka, India. Also known as Varaha Parvata, it is one of the hills in the Western Ghats range and is known for being the source of three rivers, Tunga, Bhadra and Netravathi.

Yana is a tourist destination located in forest of Katgal Range, which is also a part of Malenadu region of Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka state in India. Yana is one of the wettest villages in the world. It is the cleanest village in Karnataka and the second cleanest village in India. The two unique rock outcrops after the village are tourist attractions and easily approachable by two routes one from Kumta-Sirsi Highway by a small trek through 0.5 kilometres (0.31 mi) the thick forests from the nearest road head and another from Sirsi-Ankola Road.

Gavali is a small village located in the Belgaum district, Karnataka state in India, southwest of the city of Belgaum. The village is surrounded by forests, waterways and falls, which are subject to illegal mining, removal of medicinal plants and deforestation.
Sri Ananth Hegde Ashisara is an environmentalist from Uttara Kannada District, Karnataka, India and Chairman, Karnataka Biodiversity Board, Government of Karnataka.
.
Kattinahole is a small village in Hosanagara Taluk, Shimoga district of the Indian state of Karnataka. The local language of Kattinahole is Kannada.

Ramachandrapura Math (monastery) is a Hindu monastery located in Hosanagara taluk of Shimoga, Karnataka. The Matha is followed mainly by the Havyaka Brahmins in Uttara Kannada, Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Shimoga districts of Karnataka and Kasaragod district of Kerala. It was established by Adi Shankaracharya originally near Gokarna, a holy town on the west coast of India. The matha was initially known as Raghuthama Matha. The Swami of the matha is a celibate (brahmacharya) and a Havyaka by birth. He adds the title Bharati to his name. The present guru is Jagadguru Shankaracharya Shri Raghaveshwara Bharathi MahaSwamiji. He was initiated sanyasa by his guru Jagadguru Shankaracharya shri Ragavendra Bharati mahaswamiji the 35th Pontiff of Shri Ramachandrapura Mutt.

Tourism in India is economically significant and projected to continue a pattern of growth. The World Travel & Tourism Council calculated that tourism generated ₹14.02 lakh crore (US$160 billion) or 9.6% of the nation's GDP in 2016 and supported 40.343 million jobs, 9.3% of its total employment. The sector is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 6.8% to ₹28.49 lakh crore (US$330 billion) by 2027.

Farnsworth's vine snake is a species of tree snake endemic to the central Western Ghats of India.
References
- ↑ TNN (18 October 2009). "Plea to stop mining in Western Ghats". The Times of India . Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- 1 2 "Natural heritage site tag for Ambaragudda, Ammanaghatta". The Hindu . 16 February 2009. Archived from the original on 21 February 2009. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ Kaggere, Niranjan (2012). "Kodachadri now a Heritage site". Times of India- mobile e paper. Archived from the original on 27 December 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "Andolan seeks restoration of ban on mining at Ambargudda". The Hindu . Bangalore. 17 August 2005. Archived from the original on 23 April 2007. Retrieved 5 October 2012.
- ↑ Basavaraj Sampalli, P.N.Narasimhamurthy (6 July 2004). "Dynamites & JCBs greet you at this bio-diversity hotspot". Deccan Herald (Spectrum). Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 October 2012.