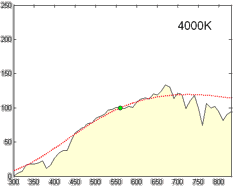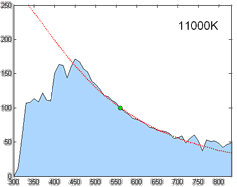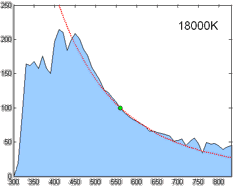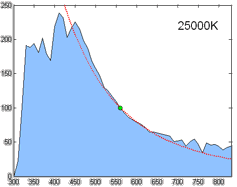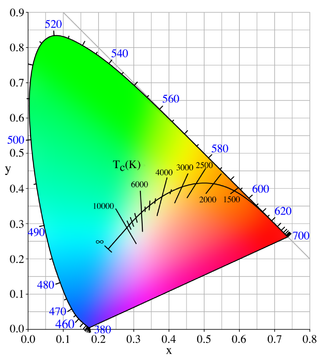
Color temperature is a parameter describing the color of a visible light source by comparing it to the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body. The temperature of the ideal emitter that matches the color most closely is defined as the color temperature of the original visible light source. The color temperature scale describes only the color of light emitted by a light source, which may actually be at a different temperature.

An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic which secures the lamp in the socket of a light fixture, which is often called a "lamp" as well. The electrical connection to the socket may be made with a screw-thread base, two metal pins, two metal caps or a bayonet mount.

Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts. Several different types of stage lighting instruments are used in this discipline. In addition to basic lighting, modern stage lighting can also include special effects, such as lasers and fog machines. People who work on stage lighting are commonly referred to as lighting technicians or lighting designers.

An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a filament that is heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either evacuated or filled with inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Electric current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections.

A halogen lamp is an incandescent lamp consisting of a tungsten filament sealed in a compact transparent envelope that is filled with a mixture of an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen, such as iodine or bromine. The combination of the halogen gas and the tungsten filament produces a halogen-cycle chemical reaction, which redeposits evaporated tungsten on the filament, increasing its life and maintaining the clarity of the envelope. This allows the filament to operate at a higher temperature than a standard incandescent lamp of similar power and operating life; this also produces light with higher luminous efficacy and color temperature. The small size of halogen lamps permits their use in compact optical systems for projectors and illumination. The small glass envelope may be enclosed in a much larger outer glass bulb, which has a lower temperature, protects the inner bulb from contamination, and makes the bulb mechanically more similar to a conventional lamp.

A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor coating in the lamp glow. Fluorescent lamps convert electrical energy into useful light much more efficiently than incandescent lamps, but are less efficient than most LED lamps. The typical luminous efficacy of fluorescent lamps is 50–100 lumens per watt, several times the efficacy of incandescent bulbs with comparable light output.

A flashlight or electric torch, usually shortened to torch, is a portable hand-held electric lamp. Formerly, the light source typically was a miniature incandescent light bulb, but these have been displaced by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) since the early 2000s. A typical flashlight consists of the light source mounted in a reflector, a transparent cover to protect the light source and reflector, a battery, and a switch, all enclosed in a case.

A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate glass bulb. The outer bulb may be clear or coated with a phosphor; in either case, the outer bulb provides thermal insulation, protection from the ultraviolet radiation the light produces, and a convenient mounting for the fused quartz arc tube.

A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL), also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent light bulb; some types fit into light fixtures designed for incandescent bulbs. The lamps use a tube that is curved or folded to fit into the space of an incandescent bulb, and a compact electronic ballast in the base of the lamp.

A metal-halide lamp is an electrical lamp that produces light by an electric arc through a gaseous mixture of vaporized mercury and metal halides. It is a type of high-intensity discharge (HID) gas discharge lamp. Developed in the 1960s, they are similar to mercury vapor lamps, but contain additional metal halide compounds in the quartz arc tube, which improve the efficiency and color rendition of the light. The most common metal halide compound used is sodium iodide. Once the arc tube reaches its running temperature, the sodium dissociates from the iodine, adding orange and reds to the lamp's spectrum from the sodium D line as the metal ionizes. As a result, metal-halide lamps have high luminous efficacy of around 75–100 lumens per watt, which is about twice that of mercury vapor lights and 3 to 5 times that of incandescent lights and produce an intense white light. Lamp life is 6,000 to 15,000 hours. As one of the most efficient sources of high CRI white light, metal halides as of 2005 were the fastest growing segment of the lighting industry. They are used for wide area overhead lighting of commercial, industrial, and public places, such as parking lots, sports arenas, factories, and retail stores, as well as residential security lighting, automotive headlamps and indoor cannabis grow operations.

Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide (HMI) is the trademark name of Osram's brand of metal-halide gas discharge medium arc-length lamp, made specifically for film and entertainment applications. Hydrargyrum comes from the Greek name for the element mercury.

Stage lighting instruments are used in stage lighting to illuminate theatrical productions, concerts, and other performances taking place in live performance venues. They are also used to light television studios and sound stages.

A multifaceted reflector light bulb is a reflector housing format for halogen as well as some LED and fluorescent lamps. MR lamps were originally designed for use in slide projectors, but see use in residential lighting and retail lighting as well. They are suited to applications that require directional lighting such as track lighting, recessed ceiling lights, desk lamps, pendant fixtures, landscape lighting, retail display lighting, and bicycle headlights. MR lamps are designated by symbols such as MR16 where the diameter is represented by numerals indicating units of eighths of an inch. Common sizes for general lighting are MR11 and MR16, with MR8 and MR20 used in specialty applications. Many run on low voltage rather than mains voltage alternating current so require a power supply.

An infrared heater or heat lamp is a heating appliance containing a high-temperature emitter that transfers energy to a cooler object through electromagnetic radiation. Depending on the temperature of the emitter, the wavelength of the peak of the infrared radiation ranges from 750 nm to 1 mm. No contact or medium between the emitter and cool object is needed for the energy transfer. Infrared heaters can be operated in vacuum or atmosphere.

An LED lamp or LED light is an electric light that produces light using light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED lamps are significantly more energy-efficient than equivalent incandescent lamps and fluorescent lamps. The most efficient commercially available LED lamps have efficiencies exceeding 200 lumens per watt (lm/W) and convert more than half the input power into light. Commercial LED lamps have a lifespan several times longer than both incandescent and fluorescent lamps.

Various governments have passed legislation to phase out manufacturing or importation of incandescent light bulbs for general lighting in favor of more energy-efficient alternatives. The regulations are generally based on efficiency, rather than use of incandescent technology.
United States Lighting Energy Policy is moving towards increased efficiency in order to lower greenhouse gas emissions and energy use. Lighting efficiency improvements in the United States can be seen through different standards and acts. The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 laid out changes in lighting legislation for the United States. This set up performance standards and the phase-out of incandescent light bulbs in order to require the use of more efficient fluorescent lighting. EISA 2007 is an effort to increase lighting efficiency by 25-30%. Opposition to EISA 2007 is demonstrated by the Better Use of Light Bulbs Act and the Light Bulb Freedom of Choice Act. The efforts to increase lighting efficiency are also demonstrated by the Energy Star program and the increase efficiency goals by 2011 and 2013. A ban on the manufacture and sale of most general purpose incandescent bulbs in the U.S. took effect on August 1, 2023.

A LED filament light bulb is a LED lamp which is designed to resemble a traditional incandescent light bulb with visible filaments for aesthetic and light distribution purposes, but with the high efficiency of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The name comes from their strings of many close-spaced series-connected diodes, which resemble the filaments of incandescent light bulbs much closer than previous bulbs with many LEDs. They are made as direct replacements for conventional incandescent bulbs, as they are made in the same shapes, they use the same bases that fit the same sockets, and they work at the same supply voltage. They may be used for their appearance, similar when lit to a clear incandescent bulb, or for their wide angle of light distribution, typically 300°. They are also more efficient than many other LED lamps.

Edison light bulbs, also known as filament light bulbs and retroactively referred to as antique light bulbs or vintage light bulbs, are either carbon- or early tungsten-filament incandescent light bulbs, or modern bulbs that reproduce their appearance. Most of the bulbs in circulation are reproductions of the wound filament bulbs made popular by Edison Electric Light Company at the turn of the 20th century. They are easily identified by the long and complicated windings of their internal filaments, and by the very warm-yellow glow of the light they produce.
Photoflood lamps are a type of incandescent light bulb designed for use as a continuous light source for photographic lighting. The filaments of such lamps are operated at much higher temperatures than is the case for standard, general lighting service lamps. The result is a brilliance of light much higher than the lamp's wattage rating would suggest. The trade-off is that the lamp has a very short service life of seldom more than ten hours.