See also
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
- Extended Boot Record (EBR)
- GUID Partition Table (GPT)
- Boot Engineering Extension Record (BEER)
- Apple Partition Map (APM)
- BSD disklabel
In computing, a rigid disk block (RDB) is the block on a hard disk where the Amiga series of computers store the disk's partition and filesystem information. The IBM's PC equivalent of the Amiga's RDB is the master boot record (MBR).
Unlike its PC equivalent, the RDB doesn't directly contain metadata for each partition. Instead it points to a linked list of partition blocks, which contain the actual partition data. The partition data includes the start, length, filesystem, boot priority, buffer memory type and "flavor", though the latter was never used. Because there is no limitation in partition block count, there is no need to distinguish primary and extended types and all partitions are equal in stature and architecture.
Additionally, it may point to additional filesystem drivers, allowing the Amiga to boot from filesystems not directly supported by the ROM, such as PFS or SFS.
The data in the rigid disk block must start with the ASCII bytes "RDSK". Furthermore, its position is not restricted to the very first block of a volume, instead it could be located anywhere within its first 16 blocks. Thus it could safely coexist with a master boot record, which is forced to be found at block 0.
Nearly all Amiga hard disk controllers support the RDB standard, enabling the user to exchange disks between controllers.

In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer. It can be initiated by hardware such as a button press, or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system.

Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.
AmigaDOS is the disk operating system of the AmigaOS, which includes file systems, file and directory manipulation, the command-line interface, and file redirection.
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.

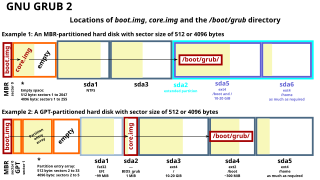
GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.

In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions, preparatory to defining file systems. fdisk features in the DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating-system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.
The Amiga Fast File System is a file system used on the Amiga personal computer. The previous Amiga filesystem was never given a specific name and known originally simply as "DOS" or AmigaDOS. Upon the release of FFS, the original filesystem became known as Amiga Old File System (OFS). OFS, which was primarily designed for use with floppy disks, had been proving slow to keep up with hard drives of the era. FFS was designed as a full replacement for the original Amiga filesystem. FFS differs from its predecessor mainly in the removal of redundant information. Data blocks contain nothing but data, allowing the filesystem to manage the transfer of large chunks of data directly from the host adapter to the final destination.
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for AmigaOS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block. It wasn't very suitable for anything except floppy disks, and it was soon replaced.

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers, which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOS systems, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.
Apple Partition Map (APM) is a partition scheme used to define the low-level organization of data on disks formatted for use with 68k and PowerPC Macintosh computers. It was introduced with the Macintosh II.
The Logical Disk Manager (LDM) is an implementation of a logical volume manager for Microsoft Windows NT, developed by Microsoft and Veritas Software. It was introduced with the Windows 2000 operating system, and is supported in Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10. The MMC-based Disk Management snap-in hosts the Logical Disk Manager. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, Microsoft deprecated LDM in favor of Storage Spaces.
An extended boot record (EBR), or extended partition boot record (EPBR), is a descriptor for a logical partition under the common DOS disk drive partitioning system. In that system, when one partition record entry in the master boot record (MBR) is designated an extended partition, then that partition can be subdivided into a number of logical partitions. The actual structure of that extended partition is described by one or more EBRs, which are located inside the extended partition. The first EBR will always be located on the very first sector of the extended partition.
A volume boot record (VBR) is a type of boot sector introduced by the IBM Personal Computer. It may be found on a partitioned data storage device, such as a hard disk, or an unpartitioned device, such as a floppy disk, and contains machine code for bootstrapping programs stored in other parts of the device. On non-partitioned storage devices, it is the first sector of the device. On partitioned devices, it is the first sector of an individual partition on the device, with the first sector of the entire device being a Master Boot Record (MBR) containing the partition table.
In BSD-derived computer operating systems and in related operating systems such as SunOS, a disklabel is a record stored on a data storage device such as a hard disk that contains information about the location of the partitions on the disk. Disklabels were introduced in the 4.3BSD-Tahoe release. Disklabels are usually edited using the disklabel utility. In later versions of FreeBSD, this was renamed as bsdlabel.
The partition type in a partition's entry in the partition table inside a master boot record (MBR) is a byte value intended to specify the file system the partition contains or to flag special access methods used to access these partitions.
The BIOS boot partition is a partition on a data storage device that GNU GRUB uses on legacy BIOS-based personal computers in order to boot an operating system, when the actual boot device contains a GUID Partition Table (GPT). Such a layout is sometimes referred to as BIOS/GPT boot.
Kickstart is the bootstrap firmware of the Amiga computers developed by Commodore International. Its purpose is to initialize the Amiga hardware and core components of AmigaOS and then attempt to boot from a bootable volume, such as a floppy disk. Most Amiga models were shipped with the Kickstart firmware stored on ROM chips.
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.