Related Research Articles
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor.

The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow.

In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities.
A photoplotter is a specialized electro-opto-mechanical machine that exposes a latent image on a medium, usually high-contrast monochromatic (black-and-white) photographic film, using a light source under computer control. Once the film has been exposed, it must be processed before it is ready for use.

In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
In electronics, an analog multiplier is a device that takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as squares, and square roots.

Audio equipment refers to devices that reproduce, record, or process sound. This includes microphones, radio receivers, AV receivers, CD players, tape recorders, amplifiers, mixing consoles, effects units, headphones, and speakers.

An opto-isolator is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/μs.

Integrated circuit layout, also known IC layout, IC mask layout, or mask design, is the representation of an integrated circuit in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal, oxide, or semiconductor layers that make up the components of the integrated circuit. Originally the overall process was called tapeout as historically early ICs used graphical black crepe tape on mylar media for photo imaging.

Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts.

A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die. Their usage has grown dramatically with the increased use of cell phones, telecommunications, portable electronics, and automobiles with electronics and digital sensors.

Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the Greek: word ανάλογος pronounced [n](analogos) meaning "proportional".
A linear circuit is an electronic circuit which obeys the superposition principle. This means that the output of the circuit F(x) when a linear combination of signals ax1(t) + bx2(t) is applied to it is equal to the linear combination of the outputs due to the signals x1(t) and x2(t) applied separately:
Robert Allen Pease was an electronics engineer known for analog integrated circuit (IC) design, and as the author of technical books and articles about electronic design. He designed several very successful "best-seller" ICs, many of them in continuous production for multiple decades.These include LM331 voltage-to-frequency converter, and the LM337 adjustable negative voltage regulator.
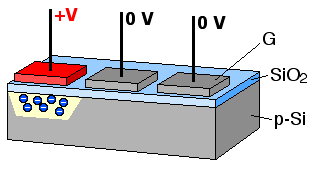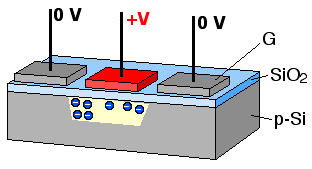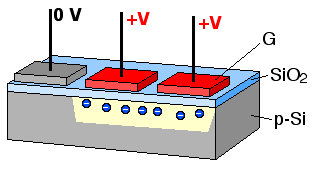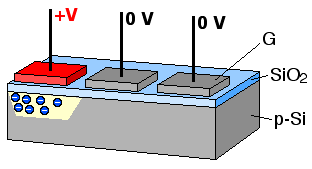
A bucket brigade or bucket-brigade device (BBD) is a discrete-time analogue delay line, developed in 1969 by F. Sangster and K. Teer of the Philips Research Labs in the Netherlands. It consists of a series of capacitance sections C0 to Cn. The stored analogue signal is moved along the line of capacitors, one step at each clock cycle. The name comes from analogy with the term bucket brigade, used for a line of people passing buckets of water.
Signal chain, or signal-processing chain is a term used in signal processing and mixed-signal system design to describe a series of signal-conditioning electronic components that receive input sequentially, with the output of one portion of the chain supplying input to the next.

Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors and capacitors.

Saraju Mohanty is an American professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and the director of the Smart Electronic Systems Laboratory, at the University of North Texas in Denton, Texas. Mohanty received a Glorious India Award – Rich and Famous NRIs of America in 2017 for his contributions to the discipline. Mohanty is a researcher in the areas of "consumer electronics for smart cities", "application-Specific things for efficient edge computing", and "methodologies for digital and mixed-signal hardware". He has made significant research contributions to security and IP protection of consumer electronic systems, hardware-assisted security and protection, high-level synthesis of digital signal processing (DSP) hardware, and mixed-signal integrated circuit computer-aided design and electronic design automation. Mohanty has been the editor-in-chief (EiC) of the IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine since 2016. He has held the Chair of the IEEE Computer Society's Technical Committee on Very Large Scale Integration since September 2014. He holds 4 US patents in the areas of his research, and has published 220 research articles and 3 books.
Suhash Chandra Dutta Roy is an Indian electrical engineer and a former professor and head of the department of electrical engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. He is known for his studies on analog and digital signal processing and is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies viz. Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy, National Academy of Sciences, India as well as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Institution of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineers, Systems Society of India and Acoustical Society of India, The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 1981.

The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, also known as the metal–oxide–silicon transistor, is a type of insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET) that is fabricated by the controlled oxidation of a semiconductor, typically silicon. The voltage of the covered gate determines the electrical conductivity of the device; this ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals.
References
- 1 2 3 "40 Years of Analog Dialogue". Norwood: BusinessWire. January 15, 2008. Retrieved November 26, 2015.
- ↑ Siegel, Bernhard. "A Note From the Editor". Analog Dialogue. Analog Devices. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- ↑ Data Conversion Handbook. Newnes. 2005. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-7506-7841-4 . Retrieved November 26, 2015.
- ↑ Analog Dialogue Volume 1, Number 1, 1967
- ↑ Analog Dialogue
- ↑ Editor's Notes Analog Dialogue Volume 33, 1999
- ↑ Analog Dialogue Archives
- ↑ "The Gold Standard of Analog Circuit Prose". Archived from the original on 2013-01-29. Retrieved 2013-02-24.
- ↑ Jung, Walter G. (2005). Op Amp Applications Handbook. Newnes. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-7506-7844-5 . Retrieved November 26, 2015.
- ↑ Surber, Jim (24 October 2016). "October 2016 Analog Dialogue Note from the Editor". EngineerZone. Analog Devices, Inc. Retrieved 30 May 2017.[ permanent dead link ]