Anamorph and its derivates may refer to:
Anamorph and its derivates may refer to:

Pan and scan is a method of adjusting widescreen film images so that they can be shown in fullscreen proportions of a standard-definition 4:3 aspect ratio television screen, often cropping off the sides of the original widescreen image to focus on the composition's most important aspects.

Standard-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to offering a similar resolution to the analog broadcast systems used when it was introduced.

Widescreen images are displayed within a set of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than 4:3 (12:9).

CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.55:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope lens.
Enhanced-definition television, or extended-definition television (EDTV) is a Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) marketing shorthand term for certain digital television (DTV) formats and devices. Specifically, this term defines an extension of the standard-definition television (SDTV) format that enables a clearer picture during high-motion scenes compared to previous iterations of SDTV, but not producing images as detailed as high-definition television (HDTV).
Anamorphic widescreen is a process by which a comparatively wide widescreen image is horizontally compressed to fit into a storage medium with a narrower aspect ratio, reducing the horizontal resolution of the image while keeping its full original vertical resolution. Compatible play-back equipment can then expand the horizontal dimension to show the original widescreen image. This is typically used to allow one to store widescreen images on a medium that was originally intended for a narrower ratio, while using as much of the frame – and therefore recording as much detail – as possible.
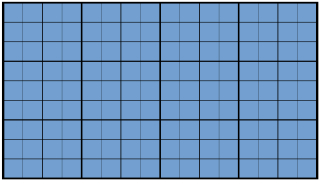
16:9 (1.78:1) is a widescreen aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9 units.
High-definition video is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for high-definition, generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines or 576 vertical lines (Europe) is considered high-definition. 480 scan lines is generally the minimum even though the majority of systems greatly exceed that. Images of standard resolution captured at rates faster than normal, by a high-speed camera may be considered high-definition in some contexts. Some television series shot on high-definition video are made to look as if they have been shot on film, a technique which is often known as filmizing.
Street Fighter II: The Animated Movie, known as Street Fighter II Movie in Japan and Australia, is a 1994 anime film adaptation of the Street Fighter II fighting game written by Kenichi Imai, directed by Gisaburō Sugii and animated by Group TAC. The film, originally released in Japan on August 6, 1994, was released theatrically in the United Kingdom, France, and Spain, and was adapted into English in dubbed and subtitled format by Animaze for Manga Entertainment. It was distributed by Toei Company in Japan, while 20th Century Fox also distributed in other countries.

Panavision is an American motion picture equipment company founded in 1953 specializing in cameras and lenses, based in Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk as a small partnership to create anamorphic projection lenses during the widescreen boom in the 1950s, Panavision expanded its product lines to meet the demands of modern filmmakers. The company introduced its first products in 1954. Originally a provider of CinemaScope accessories, the company's line of anamorphic widescreen lenses soon became the industry leader. In 1972, Panavision helped revolutionize filmmaking with the lightweight Panaflex 35 mm movie camera. The company has introduced other cameras such as the Millennium XL (1999) and the digital video Genesis (2004).

Anamorphosis is a distorted projection that requires the viewer to occupy a specific vantage point, use special devices, or both to view a recognizable image. It is used in painting, photography, sculpture and installation, toys, and film special effects. The word is derived from the Greek prefix ana-, meaning "back" or "again", and the word morphe, meaning "shape" or "form". Extreme anamorphosis has been used by artists to disguise caricatures, erotic and scatological scenes, and other furtive images from a casual spectator, while revealing an undistorted image to the knowledgeable viewer.

Ruby Gloom is a Canadian animated television series based on the Mighty Fine apparel line of the same name created by illustrator Martin Hsu. The series premiered on October 15, 2006 on YTV and ended on June 1, 2008. 40 episodes were produced by Nelvana.

Univisium is a proposed universal film format created by cinematographer Vittorio Storaro, ASC, AIC and his son, Fabrizio, to unify all future theatrical and television films into one respective aspect ratio of 2:1.

Game of Death II, also known as Tower of Death or The New Game of Death, is a 1981 Hong Kong martial arts film directed by Ng See-yuen and starring Bruce Lee, Tong Lung, Huong Cheng Li and Roy Horan. This film was marketed as a sequel to Bruce Lee's last and only partially completed film Game of Death. Bruce Lee died some years before the production of Game of Death II and most of his scenes are taken from Lee's older films, mostly Enter the Dragon. Aside from the international English dub giving the "Bruce Lee" character the name Billy Lo, this movie appears to have no connection with Robert Clouse's 1978 version of Game of Death.

Anamorph is a 2007 independent psychological thriller film directed by Henry S. Miller and starring Willem Dafoe. Dafoe plays a seasoned detective named Stan Aubray, who notices that a case he has been assigned to bears a striking similarity to a previous case of his. The film is based on the concept of anamorphosis, a painting technique that manipulates the laws of perspective to create two competing images on a single canvas.

István Orosz is a Hungarian painter, printmaker, graphic designer and animated film director. He is known for his mathematically inspired works, impossible objects, optical illusions, double-meaning images and anamorphoses. The geometric art of István Orosz, with forced perspectives and optical illusions, has been compared to works by M. C. Escher.

Windowboxing in the display of film or video occurs when the aspect ratio of the media is such that the letterbox effect and pillarbox effect occur simultaneously. Sometimes, by accident or design, a standard ratio image is presented in the central portion of a letterbox picture, resulting in a black border all around. It is generally disliked because it wastes much screen space and reduces the resolution of the original image. It can occur when a 16:9 film is set to 4:3 (letterbox), but then shown on a 16:9 TV or other output device. It can also occur in the opposite direction. Few films have been released with this aspect ratio—one example is The Crocodile Hunter: Collision Course, which had numerous scenes with Steve & Terri Irwin using widescreen pillar boxing.

Anamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen. The word anamorphic and its derivatives stem from the Greek anamorphoo, compound of morphé with the prefix aná. In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however, in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of popularity, due in large part to the higher base ISO sensitivity of digital sensors, which facilitates shooting at smaller apertures.
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as 16:9, sixteen-to-nine. For the x:y aspect ratio, the image is x units wide and y units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography.

In first person video games, the field of view or field of vision is the extent of the observable game world that is seen on the display at any given moment. It is typically measured as an angle, although whether this angle is the horizontal, vertical, or diagonal component of the field of view varies from game to game.