Related Research Articles
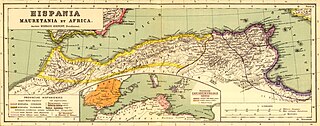
Mauretania is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean in the north to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, of Berber ancestry, were known to the Romans as the Mauri and the Masaesyli.

Garum is a fermented fish sauce that was used as a condiment in the cuisines of Phoenicia, ancient Greece, Rome, Carthage and later Byzantium. Liquamen is a similar preparation, and at times they were synonymous. Although garum enjoyed its greatest popularity in the Western Mediterranean and the Roman world, it was earlier used by the Greeks. The taste of garum is thought to be comparable to that of today's Asian fish sauces.
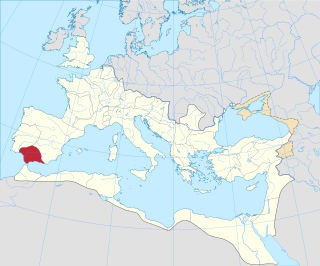
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces created in Hispania on 27 BC. Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basic divisions of Hispania under the Visigoths. Its territory approximately corresponds to modern Andalusia.
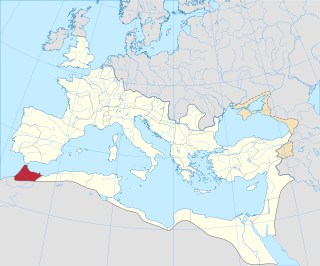
Mauretania Tingitana was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Mulucha river. Its capital city was Tingis, which is the modern Tangier. Other major cities of the province were Iulia Valentia Banasa, Septem, Rusadir, Lixus and Tamuda.

Tingis or Tingi, the ancient name of Tangier in Morocco, was an important Carthaginian, Moor, and Roman port on the Atlantic Ocean. It was eventually granted the status of a Roman colony and made the capital of the province of Mauretania Tingitana and, after Diocletian's reforms, the diocese of Hispania.

Lixus is an ancient city founded by Phoenicians before the city of Carthage. Its distinguishing feature is that it was continuously occupied from antiquity to the Islamic Era, and has ruins dating to the Phoenician, Punic, Mauretanian, Roman and Islamic periods.

The Chellah or Shalla, is a medieval fortified Muslim necropolis and ancient archeological site in Rabat, Morocco, located on the south (left) side of the Bou Regreg estuary. The earliest evidence of the site's occupation suggests that the Phoenicians established a trading emporium here in the first millennium BC. This was later the site of Sala Colonia, an ancient Roman colony in the province of Mauretania Tingitana, before it was abandoned in Late Antiquity. In the late 13th century the site began to be used as a dynastic necropolis for the Marinid dynasty. By the mid-14th century Marinid sultans had enclosed a part of the site with a new set of walls and built a religious complex inside it to accompany their mausoleums. In the 15th century the necropolis began to decline and it suffered damage over the centuries due to earthquakes and looting. Archeological excavations in the 20th century unearthed the remains of the ancient Roman town. Today the site is a tourist attraction and since 2012 it forms part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Baelo Claudia was an ancient Roman town in Hispania, located 22 kilometres (14 mi) outside of Tarifa, near the village of Bolonia, in southern Spain. On the shore of the Strait of Gibraltar, the town was originally a fishing village and trade link when it was settled approximately 2,000 years ago. Although prosperous at the time of Emperor Claudius, it went into a decline partially fueled by earthquakes and was abandoned by the 6th century.

Tamuda was an ancient Berber city and military camp in Mauretania Tingitana. It is located 6 km west of the present-day Tetouan in northern Morocco. Stone ruins from the site are found by the south bank of the Martil Valley. It was considered a city in accordance with the rules of urbanization of the time.

Rusadir was an ancient Punic and Roman town at what is now Melilla, Spain, in northwest Africa. Under the Roman Empire, it was a colony in the province of Mauretania Tingitana.

The Loukkos River is a major river in northern Morocco. Although it is relatively short, the river is the third largest in Morocco with an average flow of 50 m³/s. The Loukkos river's source is located in the Rif Mountains and flows into the Atlantic Ocean in the city of Larache; the city's port is on the river. The Loukkos river basin is 3,730 km2 and contains one of the most fertile and productive agricultural lands in the country. One of the river's tributaries, Oued Makhazine, bears great historical importance since it witnessed one of the most decisive battles in the history of Morocco: the Battle of Alcácer Quibir. In the battle on 4 August 1578, the joint army of deposed Moroccan monarch Abu Abdallah Mohammed II Saadi and his ally, King Sebastian of Portugal, was defeated by the army of the new Moroccan sultan from the same Saadi dynasty.

Thamusida was a Punic river port that was in the present-day towns of Kénitra and Mehdya in Morocco. Under the Roman Empire, it formed a part of the province of Mauretania Tingitana.
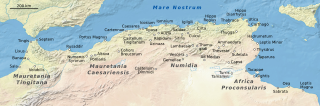
Altava was an ancient Romano-Berber city in present-day Algeria. It served as the capital of the ancient Berber Kingdom of Altava. During the French presence, the town was called Lamoriciere. It was situated in the modern Ouled Mimoun near Tlemcen.

Mogador Island is the main island of the Iles Purpuraires near Essaouira in Morocco. It is about 3 kilometres long and 1.5 kilometres wide, and lies about 1.5 kilometres from Essaouira.

Iulia Campestris Babba is a Mauretanian city created as Roman colony around 30 BC by emperor Augustus. Its actual location is currently unknown, though its existence is confirmed by the literature.

Rapidum was a Roman settlement and fort located in Mauretania Caesariensis, nearly 100 km south of Icosium (Algiers).
The Limes Mauretaniae was a portion of a 4,000-kilometre (2,500 mi) Roman fortified border (limes) in Africa approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) south of the modern day Algiers.

Kouass is a settlement in northern Morocco near the town of Asilah. It was occupied in both the Punic and Roman periods and later in the Medieval period, and served as an important port and industrial centre.: A number of structures have been identified at the site, including a Roman aqueduct and ovens for the production of pottery.
Miquel Tarradell was an archaeologist and prehistorian, specialist in the Punic, Iberian and Roman world.

Exilissa was an ancient city in northern Mauretania, facing the strait of Gibraltar and next to the Roman Septem.
References
- ↑ Macdonald, Allanah (2017). Murex-Purple Dye: The Archaeology behind the Production and an Overview of Sites in the Northwest Maghreb Region (Thesis). University of Southern Denmark.
- 1 2 Mark Ellingham and Shaun McVeigh. The Real Guide, Morocco. p. 64.
- 1 2 Tonnes Bekker-Nielsen. - Ancient Fishing and Fish Processing in the Black Sea Region (Black Sea Studies)-Aarhus University Press (2004). pp. 66–68.
- ↑ Abdelmalik Ennaciri, ed. (2013). المدن المراسي في تاريخ المغرب: أشغال الأيام الوطنية الثامنة عشر للجمعية المغربية للبحث التاريخي[Port cities in the history of Morocco: Proceedings of the 18th national days of the Moroccan Association for Historical Research, Casablanca, 27-29 October 2010] (in Arabic). Rabat: Moroccan Association for Historical Research. pp. 64–65. ISBN 9789954328002.
- ↑ El Ouazghari, Abderrahman. El mundo indígena y roma en el Marruecos antiguo (PDF) (in Spanish). Universidad de Granada.
- ↑ "Perseus, Natural History, CHAP. 1.—THE TWO MAURITANIAS, Note 5" . Retrieved 2024-11-16.
- 1 2 3 Cheddad, Abdelmouhcin (2018). دليل المدن والمواقع الأثرية القديمة بشبه الجزيرة الطنجية[Guide to ancient cities and sites in Tingitana] (1 ed.). Tetouan, Morocco. ISBN 9789920367752.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)