
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Historically, these terms have been applied to any astronomical object orbiting the Sun that did not resolve into a disc in a telescope and was not observed to have characteristics of an active comet such as a tail. As minor planets in the outer Solar System were discovered that were found to have volatile-rich surfaces similar to comets, these came to be distinguished from the objects found in the main asteroid belt. The term "asteroid" refers to the minor planets of the inner Solar System, including those co-orbital with Jupiter. Larger asteroids are often called planetoids.

Pallas is the second asteroid to have been discovered, after 1 Ceres. Like Ceres, it is believed to have a mineral composition similar to carbonaceous chondrite meteorites, though significantly less hydrated than Ceres. It is the third-largest asteroid in the Solar System by both volume and mass, and is a likely remnant protoplanet. It is 79% the mass of 4 Vesta and 22% the mass of Ceres, constituting an estimated 7% of the mass of the asteroid belt. Its estimated volume is equivalent to a sphere 505 to 520 kilometers in diameter, 90–96% the volume of Vesta.

An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.

The term Spaceguard loosely refers to a number of efforts to discover, catalogue, and study near-Earth objects (NEO), especially those that may impact Earth.

A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. As of June 2021, there are 429 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass and density of the primary, allowing insights of their physical properties that is generally not otherwise possible.

Radar astronomy is a technique of observing nearby astronomical objects by reflecting microwaves off target objects and analyzing the reflections. This research has been conducted for six decades. Radar astronomy differs from radio astronomy in that the latter is a passive observation and the former an active one. Radar systems have been used for a wide range of solar system studies. The radar transmission may either be pulsed or continuous.

The Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) project is a collaboration of the United States Air Force, NASA, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory for the systematic detection and tracking of near-Earth objects. LINEAR was responsible for the majority of asteroid discoveries from 1998 until it was overtaken by the Catalina Sky Survey in 2005. As of 15 September 2011, LINEAR had detected 231,082 new small Solar System bodies, of which at least 2,423 were near-Earth asteroids and 279 were comets. The instruments used by the LINEAR program are located at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site (ETS) on the White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) near Socorro, New Mexico.
Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) was a program run by NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, surveying the sky for near-Earth objects. NEAT was conducted from December 1995 until April 2007, at GEODSS on Hawaii, as well as at Palomar Observatory in California. With the discovery of more than 40 thousand minor planets, NEAT has been one of the most successful programs in this field, comparable to the Catalina Sky Survey, LONEOS and Mount Lemmon Survey.
Damocloids are a class of minor planets such as 5335 Damocles and 1996 PW that have Halley-type or long-period highly eccentric orbits typical of periodic comets such as Halley's Comet, but without showing a cometary coma or tail. David Jewitt defines a damocloid as an object with a Jupiter Tisserand invariant (TJ) of 2 or less, while Akimasa Nakamura defines this group with the following orbital elements:

25143 Itokawa (provisional designation 1998 SF36) is a sub-kilometer near-Earth object of the Apollo group and a potentially hazardous asteroid. It was discovered by the LINEAR program in 1998 and later named after Japanese rocket engineer Hideo Itokawa. The peanut-shaped S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 12.1 hours and measures approximately 330 meters (1,100 feet) in diameter. Due to its low density and high porosity, Itokawa is considered to be a rubble pile, consisting of numerous boulders of different sizes rather than of a single solid body.
Catalina Sky Survey is an astronomical survey to discover comets and asteroids. It is conducted at the Steward Observatory's Catalina Station, located near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States.
The OCA–DLR Asteroid Survey (ODAS) was an astronomical survey to search for small Solar System bodies focusing on near-Earth objects in the late 1990s. This European scientific project was a collaboration between the French Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur (OCA) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). The survey is credited for the discovery of one comet and more than 1000 minor planets during 1996–1999.
The Uppsala–DLR Asteroid Survey is an astronomical survey, dedicated for the search and follow–up characterization of asteroids and comets. UDAS puts a special emphasis on near-Earth objects (NEOs) in co-operation and support of global efforts in NEO-research, initiated by the Working Group on Near-Earth Objects of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), and the Spaceguard Foundation. UDAS began regular observations in September 1999, with some test runs during 1998. Discoveries of NEOs are reported to the Minor Planet Center (MPC).
99942 Apophis is a near-Earth asteroid and potentially hazardous asteroid with a diameter of 370 metres that caused a short period of concern in December 2004 when initial observations briefly indicated a probability up to 2.7% that it would hit Earth on April 13, 2029. Additional observations provided improved predictions that eliminated the possibility of an impact on Earth in 2029. Until 2006, a small probability however remained that Apophis would pass during its 2029 close encounter with Earth through a gravitational keyhole of no more than about 800 metres in diameter, which would have set up a future impact exactly seven years later on April 13, 2036. This possibility kept it at Level 1 on the Torino impact hazard scale until August 2006, when the probability that Apophis would pass through the keyhole was determined to be very small and Apophis's rating on the Torino scale was lowered to zero. By 2008, the keyhole had been determined to be less than 1 km wide. During the short time when it had been of greatest concern, Apophis set the record for highest rating ever on the Torino scale, reaching level 4 on December 27, 2004.

The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical cameras, telescopes and a computing facility that is surveying the sky for moving or variable objects on a continual basis, and also producing accurate astrometry and photometry of already-detected objects. In January 2019 the second Pan-STARRS data release was announced. At 1.6 petabytes, it is the largest volume of astronomical data ever released.
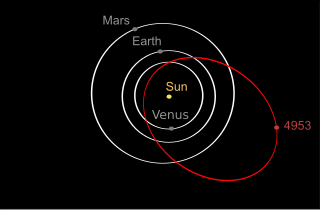
(4953) 1990 MU is a large Earth-crossing asteroid (ECA) belonging to the Apollo group of near-Earth objects which also cross the orbits of Mars and Venus. At approximately 3 km in diameter, it is one of the largest known ECAs. It has been assigned a permanent number from the Minor Planet Center (4953) indicating that its orbit has been very well determined. With an observation arc of 45 years, the asteroid's trajectory and uncertainty regions are well known through to the year 2186.
(8201) 1994 AH2 is a highly eccentric, rare-type asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group of asteroids, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 January 1994, by Australian amateur astronomer Gordon Garradd during the AANEAS survey at the Siding Spring Observatory, Australia. It has an Earth minimum orbit intersection distance of 0.1 AU (15 million km) and is associated with the Beta Taurids daytime meteor shower.

469219 Kamoʻoalewa, provisional designation 2016 HO3, is a very small asteroid, fast rotator and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 41 meters (135 feet) in diameter. It is currently the smallest, closest, and most stable (known) quasi-satellite of Earth. The asteroid was discovered by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on 27 April 2016. It was named Kamoʻoalewa, a Hawaiian word that refers to an oscillating celestial object.










