
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi) in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems.

The Geography of Kenya is diverse, varying amongst its 47 counties. Kenya has a coastline on the Indian Ocean, which contains swamps of East African mangroves. Inland are broad plains and numerous hills. Kenya borders South Sudan to the northwest, Uganda to the west, Somalia to the east, Tanzania to the south, and Ethiopia to the north.

Transport in Kenya refers to the transportation structure in Kenya. The country has an extensive network of paved and unpaved roads.

Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a viral disease of humans and livestock that can cause mild to severe symptoms. The mild symptoms may include: fever, muscle pains, and headaches which often last for up to a week. The severe symptoms may include: loss of sight beginning three weeks after the infection, infections of the brain causing severe headaches and confusion, and bleeding together with liver problems which may occur within the first few days. Those who have bleeding have a chance of death as high as 50%.

Lake Baringo is, after Lake Turkana, the most northern of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes, with a surface area of 130 square kilometres (50 sq mi) and an elevation of 970 metres (3,180 ft). The lake is fed by several rivers: the Molo, Perkerra and Ol Arabel. It has no obvious outlet; the waters are assumed to seep through lake sediments into the faulted volcanic bedrock. It is one of the two freshwater lakes in the Rift Valley in Kenya, the other being Lake Naivasha.

Rift Valley Province of Kenya, bordering Uganda, was one of Kenya's eight provinces, before the Kenyan general election, 2013. Rift Valley Province was the largest and one of the most economically important provinces in Kenya. It was dominated by the Kenya Rift Valley which passes through it and gives the province its name. According to the 2009 Census, the former province covered an area of 182,505.1 square kilometres and would have had a population of 10,006,805, making it the largest and most populous province in the country. The bulk of the provincial population inhabited a strip between former Nairobi and Nyanza Province. The capital was the town of Nakuru.

Lake Turkana, formerly known as Lake Rudolf, is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya, with its far northern end crossing into Ethiopia. It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. By volume it is the world's fourth-largest salt lake after the Caspian Sea, Issyk-Kul, and Lake Van, and among all lakes it ranks 24th.

Eldoret is a principal town in the Rift Valley region of Kenya and serves as the capital of Uasin Gishu County. The town is known to the white settlers as Farm 64, 64 or and colloquially by locals as 'Sisibo'. As per the 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census, Eldoret is the fifth most populated urban area in the country after Nairobi, Mombasa, Nakuru and Ruiru. Lying south of the Cherangani Hills, the local elevation varies from about 2100 meters at the airport to more than 2700 meters in nearby areas (7000–9000 feet). The population was 289,380 in the 2009 Census, and it is currently the fastest growing town in Kenya with 475,716 people according to 2019 National Census. Eldoret was on course to be named Kenya's fourth city, but was edged out by Nakuru in 2021.

The East-Central Africa Division (ECD) of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which oversees the Church's work in portions of Africa, which includes the nations of Djibouti, Eritrea, Somalia, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, South Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its headquarters is in Nairobi, Kenya. The Division membership as of June 30, 2021 is 4,588,423.

Nakuru is a city in the Rift Valley region of Kenya. It is the capital of Nakuru County, and was formerly the capital of Rift Valley Province. As of 2019, Nakuru had an urban and rural population of 570,674 inhabitants, making it the largest urban center in the Rift Valley, with Eldoret in Uasin Gishu County following closely behind. The city lies along the Nairobi Nakuru Highway, a distance of 160 kilometers from Nairobi, the capital of Kenya. It is the third largest city in Kenya, behind Nairobi and Mombasa respectively. It lies about 1,850 m above sea level.
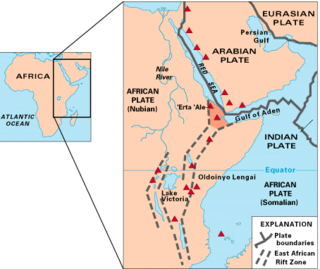
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor.

Nakuru County is a county in Kenya. It is County number 32 out of the 47 Kenyan Counties. Nakuru County is a host to Kenya's Forth City - Nakuru City. On 1st of December 2021, President Uhuru Kenyatta awarded a City Charter status to Nakuru, ranking it with Nairobi, Mombasa, and Kisumu as the cities in Kenya. With a population of 2,162,202, it is the third most populous county in Kenya after Nairobi County and Kiambu County, in that order. With an area of 7,496.5 km², it is Kenya's 19th largest county in size. Until August 21, 2010, it formed part of Rift Valley Province.

Lake Nakuru is one of the Rift Valley lakes at an elevation of 1,754 m (5,755 ft) above sea level. It lies to the south of Nakuru, in the rift valley of Kenya and is protected by Lake Nakuru National Park.

Kericho is the biggest town in Kericho County located in the highlands west of the Kenyan Rift Valley. Standing on the edge of the Mau Forest, Kericho has a warm and temperate climate making it an ideal location for agriculture and in particular, the large scale cultivation of tea.

A constitutional referendum was held in Kenya on 4 August 2010. Voters were asked whether they approved of a proposed new constitution, which had been passed by the National Assembly on 1 April 2010. The new constitution was seen as a vital step to avoid a repetition of the violent outbursts after the 2007 general elections.

The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues northward into Ethiopia. It was formed on the "Kenyan Dome" a geographical upwelling created by the interactions of three major tectonics: the Arabian, Nubian, and Somalian plates. In the past, it was seen as part of a "Great Rift Valley" that ran from Madagascar to Syria. Most of the valley falls within the former Rift Valley Province.
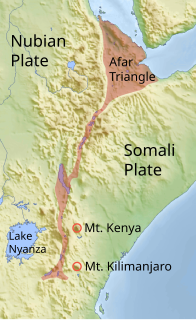
The Gregory Rift is the eastern branch of the East African Rift fracture system. The rift is being caused by the separation of the Somali plate from the Nubian plate, driven by a thermal plume. Although the term is sometimes used in the narrow sense of the Kenyan Rift, the larger definition of the Gregory Rift is the set of faults and grabens extending southward from the Gulf of Aden through Ethiopia and Kenya into Northern Tanzania, passing over the local uplifts of the Ethiopian and Kenyan domes. Ancient fossils of early hominins, the ancestors of humans, have been found in the southern part of the Gregory Rift.

The geology of Africa is varied and complex, and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent.

East Africa had a regional outbreak of Rift Valley fever in late 2006 that affected Kenya, Somalia, and Tanzania. During outbreak, 1062 people were infected with Rift Valley fever and 394 people died between December 2006 and December 2007. Rift Valley fever (RVF) is caused by a phlebovirus in the Bunyavirales order which is transmitted by mosquito bite and contact with infected animal blood; it mainly infects livestock that come into infectious contact with a viral reservoir but human beings can also be infected. The outbreak began after a heavy El Niño rain season across East Africa left greater than usual breeding ground for Aedes aegypti mosquitos, with particularly heavy rainfall over eastern Kenya, central Tanzania, and southern Somalia. While most people infected with the virus experience a relatively mild, flu-like illness without hospitalization, around 8% will develop a severe illness that can include eye disease, encephalitis, hemorrhagic fever and death. During this outbreak, of the 1,062 hospitalized, laboratory-confirmed RVF cases assays, 37% died.




















