
Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.

Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as tuffaceous.

Peridot ( PERR-ih-dot, -doh), sometimes called chrysolite, is gem-quality olivine and a silicate mineral with the formula of (Mg, Fe)2SiO4. As peridot is a magnesium-rich variety of olivine (forsterite), the formula approaches Mg2SiO4. Its green color is dependent on the iron contents within the structure of the gem. Peridot occurs in silica-deficient rocks such as volcanic basalt and pallasitic meteorites. Peridot is one of only two gems observed to be formed not in the Earth’s crust, but in molten rock of the upper mantle. Gem-quality peridot is rare to find on Earth's surface due to its susceptibility to weathering during its movement from deep within the mantle to the surface.

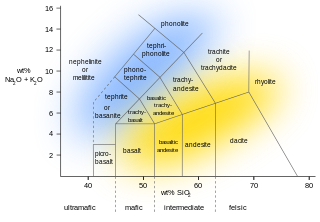
Rhyolite is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite.
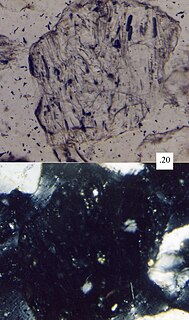
Volcanic glass is the amorphous (uncrystallized) product of rapidly cooling magma. Like all types of glass, it is a state of matter intermediate between the closely packed, highly ordered array of a crystal and the highly disordered array of liquid. Volcanic glass may refer to the interstitial material, or matrix, in an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock, or to any of several types of vitreous igneous rocks.

Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones.
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contrast, intrusive rock refers to rocks formed by magma which cools below the surface.

Volcanic rock is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic rock is artificial, and in nature volcanic rocks grade into hypabyssal and metamorphic rocks and constitute an important element of some sediments and sedimentary rocks. For these reasons, in geology, volcanics and shallow hypabyssal rocks are not always treated as distinct. In the context of Precambrian shield geology, the term "volcanic" is often applied to what are strictly metavolcanic rocks. Volcanic rocks and sediment that form from magma erupted into the air are called "volcaniclastics," and these are technically sedimentary rocks.
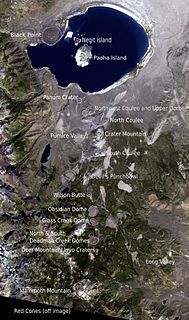
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

Amateur geology or rock collecting is the non-professional study and hobby of collecting rocks and minerals or fossil specimens from the natural environment. In Australia, New Zealand and Cornwall, the activities of amateur geologists are called fossicking. The first amateur geologists were prospectors looking for valuable minerals and gemstones for commercial purposes. Eventually, however, more people have been drawn to amateur geology for recreational purposes, mainly for the beauty that rocks and minerals provide.

Tachylite is a form of basaltic volcanic glass. This glass is formed naturally by the rapid cooling of molten basalt. It is a type of mafic igneous rock that is decomposable by acids and readily fusible. The color is a black or dark-brown, and it has a greasy-looking, resinous luster. It is very brittle and occurs in dikes, veins, and intrusive masses. The word originates from the Ancient Greek ταχύς, meaning "swift".

The Coso Volcanic Field is located in Inyo County, California, at the western edge of the Basin and Range geologic province and northern region of the Mojave Desert. The Fossil Falls are part of the Coso Field, created by the prehistoric Owens River. They are within the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake and northeast of Little Lake and U.S. Route 395.

Panum Crater is a volcanic cone that is part of the Mono–Inyo Craters, a chain of recent volcanic cones south of Mono Lake and east of the Sierra Nevada, in California, United States. Panum Crater is between 600 and 700 years old, and it exhibits all of the characteristics of the textbook rhyolitic lava dome.

Phreatomagmatic eruptions are volcanic eruptions resulting from interaction between magma and water. They differ from exclusively magmatic eruptions and phreatic eruptions. Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) clasts. It is common for a large explosive eruption to have magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.

Yucca Mountain is a mountain in Nevada, near its border with California, approximately 100 miles (160 km) northwest of Las Vegas. Located in the Great Basin, Yucca Mountain is east of the Amargosa Desert, south of the Nevada Test and Training Range and in the Nevada National Security Site. It is the site of the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository, which is currently identified by Congressional law as the nation's spent nuclear waste storage facility. However, while licensure of the site through the Nuclear Regulatory Commission is ongoing, political maneuvering led to the site being de-funded in 2010.

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 38 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek. It occupies the southeastern portion of the Tahltan Highland, an upland area of plateau and lower mountain ranges, lying east of the Boundary Ranges and south of the Inklin River, which is the east fork of the Taku River. As a volcanic complex, it consists of many types of volcanoes, including shield volcanoes, calderas, lava domes, stratovolcanoes, and cinder cones.

Red Mountain is a volcanic cinder cone located in the Coconino National Forest of northern Arizona, United States, 25 miles northwest of Flagstaff. It rises 1,000 feet (300 m) above the surroundings terrain and is shaped like the letter "U", with its opening towards the west. Geological Survey (USGS) and Northern Arizona University scientists suggest that Red Mountain was formed in eruptions nearly 740,000 years ago.

Glass Buttes are a group of volcanic mountains made up of two prominent peaks and several smaller hills. They are located in the remote northeast corner of Lake County between Bend and Burns in central Oregon, United States. Raising high above the high desert plain, the buttes are an important landmark in an area once known as the Oregon's Great Sandy Desert. The buttes are named for the numerous large deposits of obsidian found on their slopes. Today, most of the mountains and surrounding land are administered by the Bureau of Land Management. The mountains offer a number of recreational opportunities including rock collecting, hiking, camping, and hunting.
The geology of Arizona began to form in the Precambrian. Igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock may have been much older, but was overwritten during the Yavapai and Mazatzal orogenies in the Proterozoic. The Grenville orogeny to the east caused Arizona to fill with sediments, shedding into a shallow sea. Limestone formed in the sea was metamorphosed by mafic intrusions. The Great Unconformity is a famous gap in the stratigraphic record, as Arizona experienced 900 million years of terrestrial conditions, except in isolated basins. The region oscillated between terrestrial and shallow ocean conditions during the Paleozoic as multi-cellular life became common and three major orogenies to the east shed sediments before North America became part of the supercontinent Pangaea. The breakup of Pangaea was accompanied by the subduction of the Farallon Plate, which drove volcanism during the Nevadan orogeny and the Sevier orogeny in the Mesozoic, which covered much of Arizona in volcanic debris and sediments. The Mid-Tertiary ignimbrite flare-up created smaller mountain ranges with extensive ash and lava in the Cenozoic, followed by the sinking of the Farallon slab in the mantle throughout the past 14 million years, which has created the Basin and Range Province. Arizona has extensive mineralization in veins, due to hydrothermal fluids and is notable for copper-gold porphyry, lead, zinc, rare minerals formed from copper enrichment and evaporites among other resources.

Geological Museum after H. Karapetyan of Institute of Geological Sciences of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia is an academic scientific museum. It was founded in 1937 and reconstructed in 2012. The Museum has the following departments: Mineralogy, Paleontology, Petrography, Natural Resources, Mineral Waters in Armenia, Natural Monuments of Armenia.



















