
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.

UNESCO Biosphere Reserves are environment-protected scientific-research institutions of international status that are created with the intent for conservation in a natural state the most typical natural complexes of biosphere, conducting background ecological monitoring, studying of the surrounding natural environment, its changes under the activity of anthropogenic factors.

Temperate rainforests are coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rainfall.

The Dinaric calcareous silver fir forests are an endemic vegetation type of the littoral Dinaric Alps, located in southeastern Europe. Pure stands of Dinaric calcareous Silver fir —Abies alba forests appear on limestone escarpments in the montane zones of Orjen, Velebit, Biokovo and Prenj. They comprise one of the most interesting formations of Balkan vegetation types as the forests bear several rare plants and are of striking beauty. As a highly endemic and rare vegetation type of the Dinarids it needs protection.
The Corsican montane broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion, in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, are on the island of Corsica. The ecoregion includes the high-altitude regions of Corsica's mountain ranges.

California mixed evergreen forest is an ecoregion of the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome. It is found in the mountain ranges of California and into southwestern Oregon.

The Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests is an ecoregion of the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund. It consists of mesophytic plants west of the Appalachian Mountains in the Southeastern United States.

The Appalachian-Blue Ridge forests is an ecoregion in the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests Biome, in the Eastern United States. The ecoregion is located in the central and southern Appalachian Mountains, including the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians and the Blue Ridge Mountains. It covers an area of about 61,500 square miles (159,000 km2) in: northeast Alabama and Georgia, northwest South Carolina, eastern Tennessee, western North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, and central West Virginia and Pennsylvania; and small extensions into Kentucky, New Jersey, and New York.

The Euxine-Colchic deciduous forests ecoregion, in the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests Biome, is located along the southern shore of the Black Sea. The ecoregion extends along the thin coastal strip from the southeastern corner of Bulgaria in the west, to Georgia in the east, across the northern coast of Turkey, where it wraps around the eastern end of the Black Sea.
The Monti Simbruini are a mountain range in central Italy, a part of Apennines mountain system.

The Balkan mixed forests constitute a terrestrial ecoregion of Europe according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It belongs in the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests Biome and the Palearctic ecozone.

The flora of Italy was traditionally estimated to comprise about 5,500 vascular plant species. However, as of 2005, 6,759 species are recorded in the Data bank of Italian vascular flora. Geobotanically, the Italian flora is shared between the Circumboreal Region and Mediterranean Region. According to the index compiled by the Italian Ministry for the Environment in 2001, 274 vascular plant species were protected.

The climate and ecology of land immediately surrounding the Mediterranean Sea is influenced by several factors. Overall, the land has a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers. The climate induces characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation. Plant life immediately near the Mediterranean is in the Mediterranean Floristic region, while mountainous areas further from the sea supports the Sub-Mediterranean Floristic province.

The term Italian Sclerophyllous and deciduous forests ecoregion, in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub Biome, is in Italy. The region extends from the Po Basin to the Apennine Mountains of Basilicata and Calabria. Rock types are limestone, dolomite, marl, schist-marl, and sandstone.

The South Apennine mixed montane forests is an Ecoregion, in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub Biome, located in the Southern Apennine Mountains, in southern Italy and on Sicily.

The Dinaric Mountains mixed forests form a terrestrial ecoregion of the Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests Biome in Southeastern Europe, according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It also is in the Palearctic ecozone.

The Allegheny Highlands forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of North America, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund.

Central Europe contains several life zones, depending on location and elevation.
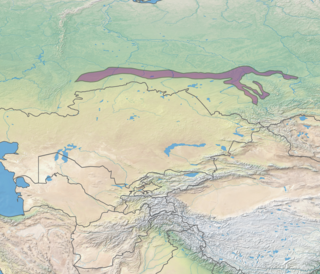
The West Siberian broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion is a thin band of mixed forest along the southernmost edge of the taiga in Western Siberia, just north of the forest-steppe region and south of the West Siberian taiga. The biodiversity of the zone is the highest in Siberia, due to its transitional position between many different ecoregions. The area acts as a long corridor for migration of animals along the east-west axis. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic ecozone, with a Humid Continental climate. It covers 223,516 km2 (86,300 sq mi).






























