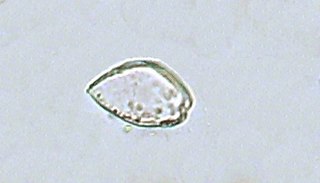
The Prorocentrales are a small order of dinoflagellates. They are distinguished by having their two flagella inserted apically, rather than ventrally as in other groups. One flagellum extends forward and the other circles its base, and there are no flagellar grooves. This arrangement is called desmokont, in contrast to the dinokont arrangement found in other groups. Accordingly, the Prorocentrales may be called desmoflagellates, and in some classifications were treated as a separate class Desmophyceae.

Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater blue-green algae. Over 50 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases.

The Elachistidae are a family of small moths in the superfamily Gelechioidea. Some authors lump about 3,300 species in eight subfamilies here, but this arrangement almost certainly results in a massively paraphyletic and completely unnatural assemblage, united merely by symplesiomorphies retained from the first gelechioid moths.

The Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, or California Delta, is an expansive inland river delta and estuary in Northern California. The Delta is formed at the western edge of the Central Valley by the confluence of the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers and lies just east of where the rivers enter Suisun Bay. The Delta is recognized for protection by the California Bays and Estuaries Policy. Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta was designated a National Heritage Area on March 12, 2019. The city of Stockton is located on the San Joaquin River on the eastern edge of the delta. The total area of the Delta, including both land and water, is about 1,100 square miles (2,800 km2). Its population is around 500,000 residents.

Palmaria palmata, also called dulse, dillisk or dilsk, red dulse, sea lettuce flakes, or creathnach, is a red alga (Rhodophyta) previously referred to as Rhodymenia palmata. It grows on the northern coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is a well-known snack food. In Iceland, where it is known as söl, it has been an important source of dietary fiber throughout the centuries.

The Fucales (fucoids) are an order in the brown algae. The list of families in the Fucales, as well as additional taxonomic information on algae, is publicly accessible at Algaebase.

Chlorococcales is an order of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. Individual specimens are sometimes found in soil, but mostly in fresh and marine waters. The order contains approximately 780 species.

Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins.

Elachista is a genus of gelechioid moths described by Georg Friedrich Treitschke in 1833. It is the type genus of the grass-miner moth family (Elachistidae). This family is sometimes circumscribed very loosely, including for example the Agonoxenidae and Ethmiidae which seem to be quite distinct among the Gelechioidea, as well as other lineages which are widely held to be closer to Oecophora than to Elachista and are thus placed in the concealer moth family Oecophoridae here.
Cyclamides are a class of oligopeptides, produced by cyanobacteria algae strains, such as microcystis aeruginosa and can be toxic. Cyclamides are synthesized through ribosomic pathways.
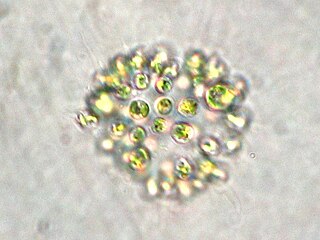
Microcystis is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Many members of a Microcystis community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Communities are often a mix of toxin-producing and nonproducing isolates.

Microcystis aeruginosa is a species of freshwater cyanobacteria that can form harmful algal blooms of economic and ecological importance. They are the most common toxic cyanobacterial bloom in eutrophic fresh water. Cyanobacteria produce neurotoxins and peptide hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Microcystis aeruginosa produces numerous congeners of microcystin, with microcystin-LR being the most common. Microcystis blooms have been reported in at least 108 countries, with the production of microcystin noted in at least 79.
Aerucyclamides are bio-active peptides isolated from Microcystis aeruginosa cyanobacteria.
Cyanopeptolins are a class of oligopeptides produced by Microcystis and Planktothrix algae strains, and can be neurotoxic. The production of cyanopeptolins occurs through nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS).
Thalassiothrix is a genus of Chromista belonging to the family Thalassionemataceae.
Amphiprora is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Amphipleuraceae.
Zygnemopsis desmidioides is a species of alga belonging to the family Zygnemataceae.









